Premature Ventricular Contraction - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Summary
TLDRThis script explains premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), abnormal heartbeats originating in the ventricles. It details the normal cardiac cycle, the role of pacemaker cells, and how PVCs disrupt it. The script describes how PVCs appear on an ECG, their potential causes, and the effects on the heart's rhythm. It also discusses the significance of compensatory pauses, different types of PVCs, and treatment options, emphasizing that while most PVCs are harmless, some may indicate a serious underlying condition.
Takeaways
- 💓 A premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is an early heartbeat that originates in the ventricles, disrupting the normal cardiac cycle.
- 🔌 The sinoatrial (SA) node normally sends electrical signals that coordinate the heartbeat, but in PVC, signals from the ventricles interrupt this sequence.
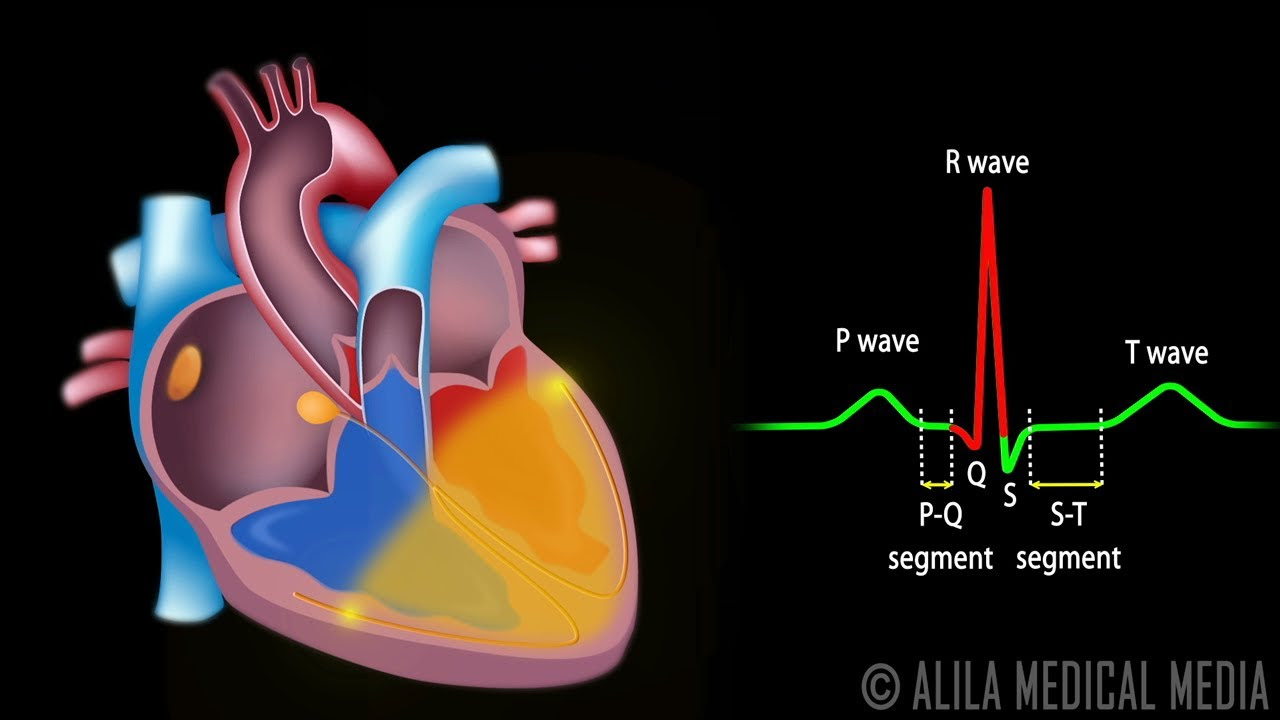
- 📊 On an electrocardiogram (ECG), atrial contractions appear as P-waves, ventricular contractions as QRS complexes, and ventricular repolarizations as T-waves.
- 🌊 The QRS complex, which indicates ventricular contraction, is typically less than 100 milliseconds and consists of three deflections: Q, R, and S waves.
- 🛑 Latent pacemakers such as the atrioventricular (AV) node, Bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers can generate electrical signals, but at a slower rate than the SA node.
- 🚫 Causes of PVCs include stressors like electrolyte imbalances, drugs, ischemic damage, or increased sympathetic activity.
- 🔄 Reentrant loops, where a depolarization wave circles around non-depolarizing tissue, can lead to continuous ectopic beats.
- 🔄 The direction of the ectopic focus determines the appearance of the QRS complex on ECG, with left or right bundle branch block patterns.
- ⏲️ Compensatory pauses occur when PVCs reset the SA node's timing, causing a longer interval between ventricular contractions.
- 🏥 PVCs are usually asymptomatic, but if frequent or symptomatic, they may be treated with medications or procedures like radiofrequency ablation.
Q & A
What is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC)?
-A premature ventricular contraction is an abnormal heartbeat that occurs when the ventricles contract earlier than normal in the cardiac cycle due to an abnormal contraction signal originating from within the ventricles rather than the sinoatrial (SA) node.
How does a normal cardiac cycle initiate contractions?
-In a normal cardiac cycle, the sinoatrial (SA) node sends an electrical signal that propagates through the atria, causing them to contract. This signal then moves to the atrioventricular (AV) node, where it is briefly delayed before traveling down to the ventricles, causing them to contract.
What is the significance of the PR segment on an ECG?
-The PR segment on an ECG corresponds to the pause in the atrioventricular (AV) node, which is the brief delay between the atrial depolarization and the ventricular depolarization.
What does the QRS complex represent on an ECG?
-The QRS complex on an ECG represents the ventricular depolarization, which is the electrical activity causing the ventricles to contract.
What are the three smaller waves that make up the QRS complex?
-The QRS complex is typically made up of three smaller waves: a Q wave (if the first wave after the P-wave is downwards), an R wave (the next upward deflection), and an S wave (any downward deflection after the R wave).
What are latent pacemakers and why are they significant?
-Latent pacemakers are cells in the AV node, Bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers that can generate an electrical potential and take over the pacemaker function if the SA node fails. They have slower depolarization rates and are significant as backup pacemakers for the heart.
What causes a premature ventricular contraction (PVC)?
-PVCs can be caused by enhanced automaticity in latent pacemaker cells or cardiac muscle cells due to factors such as electrolyte imbalances, drug use, ischemic damage, or increased sympathetic activity.
What is an early-afterdepolarization and a delayed-afterdepolarization?
-An early-afterdepolarization is a depolarization event that occurs during ventricular repolarization, while a delayed-afterdepolarization happens after repolarization is complete. Both can lead to ectopic beats.
What is a reentrant loop in the context of cardiac arrhythmias?
-A reentrant loop is a type of ventricular ectopic focus where a depolarization wave encounters non-depolarizing tissue, such as scar tissue, and circles around it, repeatedly sending depolarization waves to the heart tissue.
How can the origin of a PVC be determined from an ECG?
-The origin of a PVC can be determined by observing the QRS complex on an ECG. If the ectopic focus originates in the right ventricle, the QRS complex resembles a left bundle branch block, while if it originates in the left ventricle, it resembles a right bundle branch block.
What is a compensatory pause and how does it differ from a noncompensatory pause?
-A compensatory pause is a pause in the cardiac rhythm where a normal sinus complex lands exactly two times the normal sinus interval, following a PVC. A noncompensatory pause occurs when the sinus complex lands in less than twice the normal sinus interval after a PVC, indicating the PVC did not fully reset the sinus node's timing.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)