Heart Conduction System & ECG (EKG)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the intricacies of the human heart's cardiac conduction system, explaining how it coordinates heartbeats. It introduces the sinoatrial (SA) node as the heart's pacemaker, the role of the atrioventricular (AV) node in delaying signals for organized contractions, and the function of the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers in rapid signal transmission. The script also correlates these processes with an ECG (EKG), describing the significance of the P-wave, QRS complex, and T-wave, and how they reflect atrial and ventricular activity. Realistic anatomical visuals from Anatomage enhance the learning experience.
Takeaways
- 💓 The human heart has been beating continuously since the first heartbeat as a fetus, thanks to the cardiac conduction system.
- 🔍 The cardiac conduction system is a network of specialized tissue that coordinates heartbeats, including the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and the bundle of His.
- 📍 The SA node, located in the right atrium, acts as the heart's pacemaker, initiating the heartbeat by sending electrical signals.
- 🚦 The AV node introduces a delay to ensure the atria contract before the ventricles, allowing for efficient blood transfer.
- 🛤️ The bundle of His and bundle branches rapidly transmit the electrical signal from the AV node to the ventricles, preparing them for contraction.
- 🏭 The Purkinje fibers spread the signal throughout the ventricles, ensuring synchronized contraction for effective blood pumping.
- 📊 An ECG (electrocardiogram) measures the heart's electrical activity, with the P-wave, QRS complex, and T-wave corresponding to atrial depolarization, ventricular depolarization, and repolarization, respectively.
- 🩺 The P-wave on an ECG represents atrial depolarization, which leads to atrial contraction and the subsequent pushing of blood into the ventricles.
- 🏋️♂️ The QRS complex indicates ventricular depolarization, which is the signal for the ventricles to contract and pump blood out of the heart.
- 🔙 The T-wave signifies the repolarization of the ventricles, marking the end of their contraction phase and the beginning of relaxation.
- 🎥 Anatomage provides 3D models and virtual dissection tables that help visualize the complex structures of the heart in a three-dimensional space.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
-The SA node, also known as the pacemaker of the heart, is responsible for initiating the heartbeat by sending out electrical signals that trigger the contraction of the heart muscle.
How does the cardiac conduction system differ from cardiac muscle tissue?
-The cardiac conduction system is non-contractile and functions like nervous tissue, conducting electrical signals rapidly throughout the heart. In contrast, cardiac muscle tissue is contractile and pumps blood but conducts signals more slowly.
What is the purpose of the delay in the atrioventricular (AV) node?
-The delay in the AV node ensures that the atria contract and push blood into the ventricles before the ventricles contract. This sequence prevents the atria and ventricles from contracting simultaneously, allowing for efficient blood flow.
Why is the blood color in diagrams often depicted as blue for the right side of the heart and red for the left?
-In diagrams, blue is used to represent the right side of the heart, which contains deoxygenated blood, and red is used for the left side, which contains oxygenated blood. However, it's important to note that blood is always red; these are just conventional colors used for illustration.
What is the role of the interatrial pathway in the heart's electrical conduction?
-The interatrial pathway facilitates the rapid transmission of electrical signals from the SA node to the left atrium, ensuring that both atria contract in unison to efficiently move blood into the ventricles.
How does the bundle of His contribute to the heart's electrical activity?
-The bundle of His, also known as the atrioventricular bundle, receives the signal from the AV node and rapidly transmits it through the left and right bundle branches, which then stimulate the ventricles to contract.
What is the significance of the QRS complex in an ECG?
-The QRS complex in an ECG represents the ventricular depolarization, which is the electrical signal passing through the ventricles causing them to contract and pump blood to the body and lungs.
What does the T-wave indicate on an ECG?
-The T-wave on an ECG signifies the repolarization of the ventricles, which is the return to the resting state after contraction, marking the end of the cardiac cycle's electrical activity.
How does the heart sound relate to the ECG?
-The first heart sound corresponds to the end of the QRS complex when the tricuspid and mitral valves close, while the second heart sound occurs at the end of the T-wave when the aortic and pulmonary valves close.
What is the role of the interatrial and internodal pathways in the heart's electrical conduction system?
-The interatrial pathway rapidly transmits the signal from the SA node to the left atrium, while the internodal pathways conduct the signal through the right atrium. Together, they ensure synchronized atrial contraction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The Heart, Part 2 - Heart Throbs: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #26

Pharmacology - ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS (MADE EASY)

Sistema Cardiovascular 3/6: Ciclo Cardíaco, Sístole e Diástole | Anatomia e etc

Potencial de ação cardíaco e contração do coração – Fisiologia Humana

The Heart and Circulatory System - How They Work
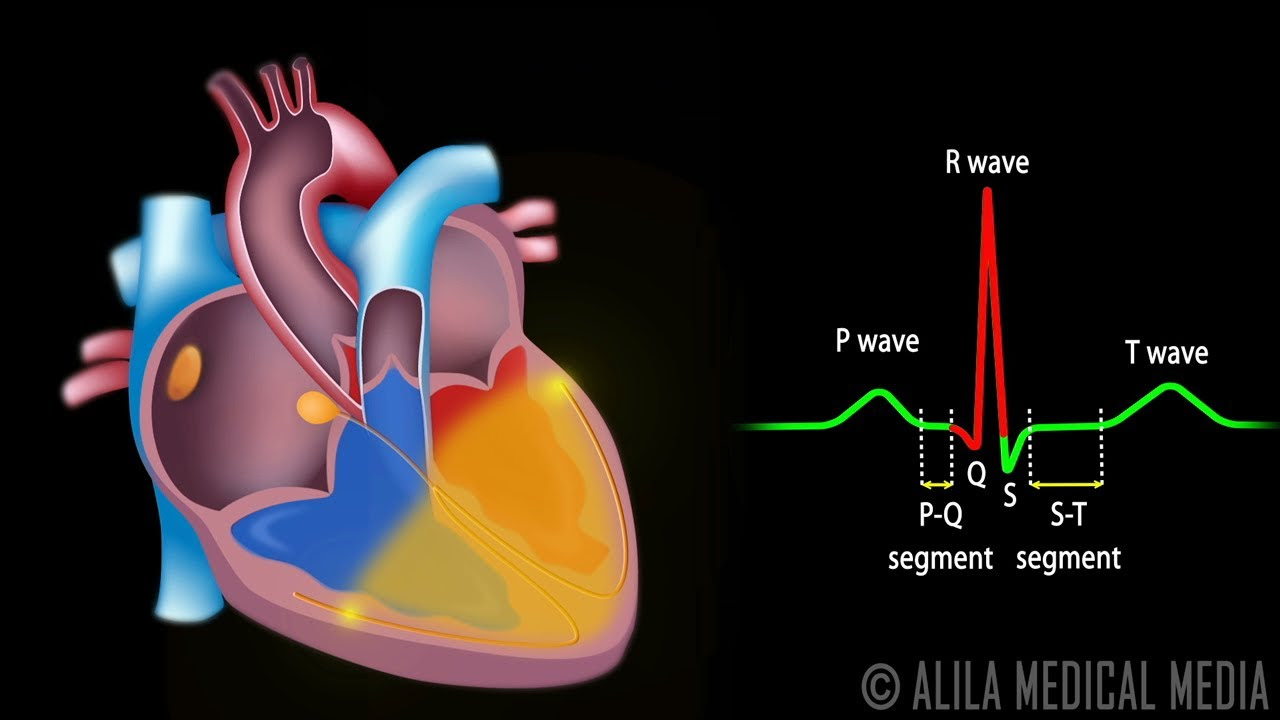
Cardiac Conduction System and Understanding ECG, Animation.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)