Understanding Intellectual Property (IP)
Summary
TLDRIntellectual property (IP) encompasses creations and ideas such as designs, processes, and logos. To safeguard IP from misuse, legal protection is available through patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. Technology transfer (T2) facilitates the licensing of patents and sharing of confidential information, enabling collaboration between entities to solve problems and innovate.
Takeaways
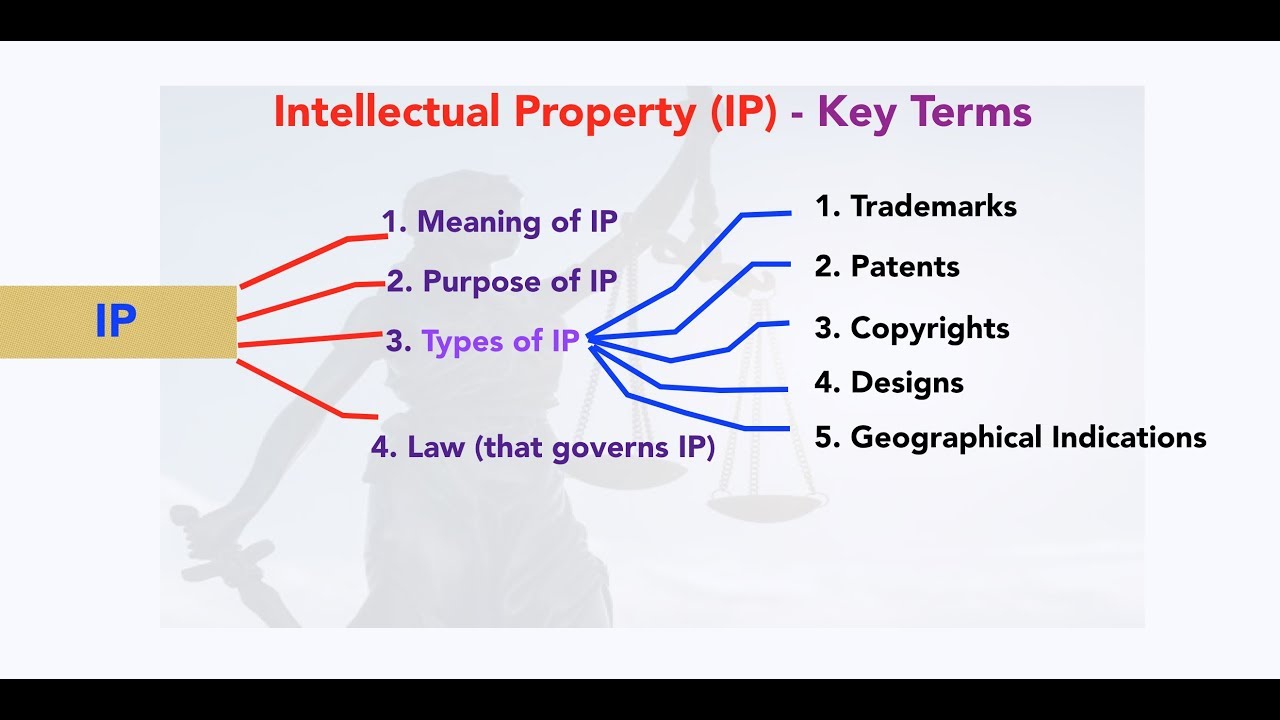
- 🧠 Intellectual Property (IP) encompasses creations of the mind, such as designs, processes, songs, logos, and even new plant varieties.
- 🏆 IP ownership gives the creator control over how their creation is used, manufactured, and who can profit from it.
- 🤔 Protecting IP in a digital world is crucial due to the ease of copying ideas and designs.
- 📜 There are legal mechanisms in place to safeguard IP, including patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets.
- 🛡️ Patents protect inventions, new processes, machines, and manufacturing methods.
- 🎨 Copyrights safeguard original works of art, music, writing, movies, and software.
- 🔖 Trademarks cover unique branding elements like business names, logos, slogans, and mascots.
- 🔒 Trade secrets ensure confidential information, such as manufacturing processes and formulas, remain undisclosed.
- 🛠️ Technology transfer (T2) facilitates the negotiation and licensing of IP, enabling the use and sharing of protected creations.
- 🤝 T2 supports collaboration between companies and individuals, as well as between the government and private sector for joint projects.
Q & A
What is intellectual property (IP)?
-Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions, designs, symbols, and even new plant varieties. It includes things a person has thought of or created, and the creator has the right to decide how it's used and who can profit from it.
What are some examples of intellectual property?
-Examples of intellectual property include designs, processes, songs, logos, discoveries, and symbols.
How can creators protect their intellectual property from misuse?
-Creators can protect their intellectual property through legal means such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets.
What is a patent and what does it cover?
-A patent is a form of legal protection that covers inventions, new processes, machines, and new ways of manufacturing things.
What does a copyright protect?
-Copyrights protect original works of authorship, including art, music, writings, movies, and software.
What is a trademark and what does it cover?
-A trademark is used to protect unique branding and identifiers such as business names, logos, slogans, and mascots.
What are trade secrets and how do they protect intellectual property?
-Trade secrets ensure that confidential information like manufacturing processes, formulas, and compilations of data are kept from falling into the wrong hands.
Why is it important for creators to protect their intellectual property?
-Protecting intellectual property is crucial as it ensures that the creator maintains control over their creations, prevents unauthorized use, and allows them to profit from their work.
What is technology transfer (T2) and how does it relate to intellectual property?
-Technology transfer, or T2, is the process that helps negotiate the use, sharing, and assigning of intellectual property. It facilitates licensing patents and sharing confidential information between parties to solve problems or create new products.
How can technology transfer help in the protection and utilization of government technology?
-Technology transfer can make it easy for companies and individuals to license government patents or share confidential information, enabling joint projects between the government and private sector.
What are the challenges in protecting intellectual property in a digital world?
-In a digital world, the ease of copying ideas or designs presents a challenge. However, the existence of laws and legal protections like patents, copyrights, and trademarks helps mitigate these challenges.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)