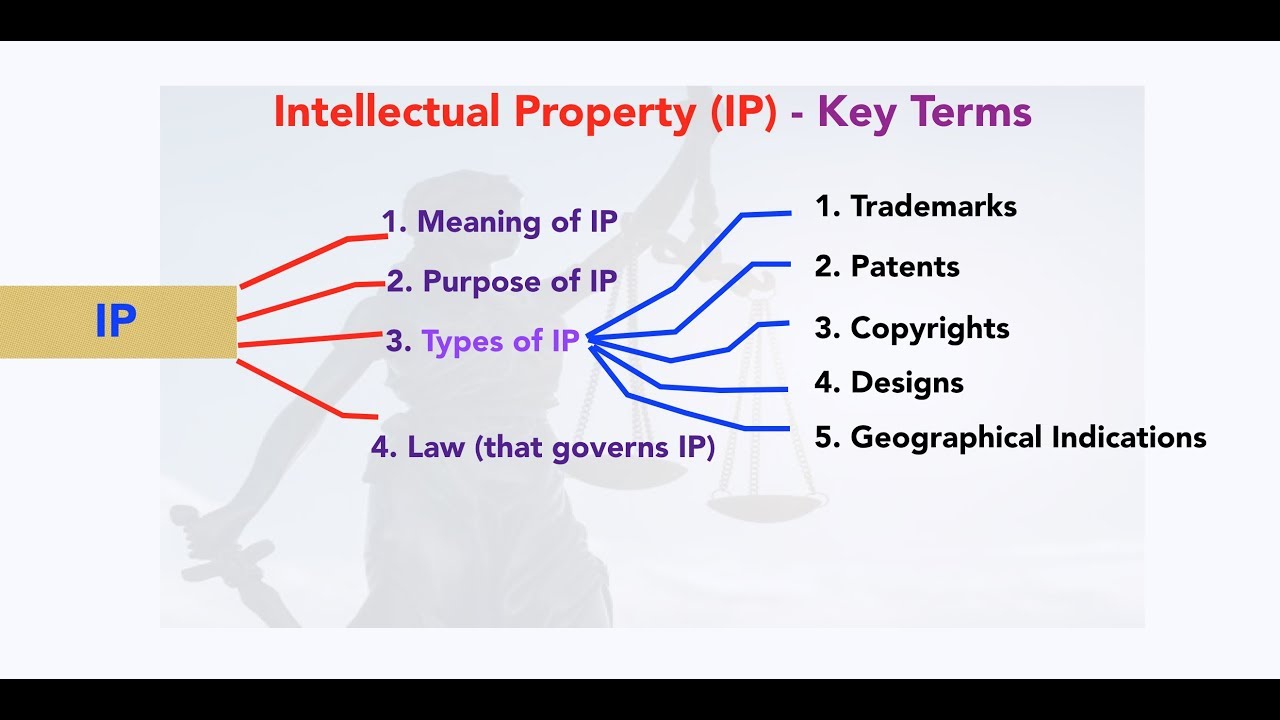
Copyrights, Designs, and Patents Act (1988)
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a comprehensive yet simplified overview of the Copyrights, Designs, and Patents Act of 1988 in the UK, focusing on intellectual property (IP) law. It explains how the law protects creations of the mind like books, music, and inventions. The video covers the basics of copyright, trademarks, and patents, including automatic rights, fair use, and legal processes for enforcing these protections. While the law is complex, it highlights essential knowledge for anyone working with intellectual property, whether it's about obtaining permissions or understanding patent applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Copyright protects creations of the mind, such as books, software, music, and photos.
- 😀 Copyright is an automatic right in the UK and lasts for a set number of years (usually 50-70).
- 😀 You should always get permission before using copyrighted material, whether it's granted or paid for.
- 😀 Fair use exceptions exist, such as using small excerpts of copyrighted work for education or commentary.
- 😀 A trademark protects logos, brand names, and other identifying marks, helping consumers recognize products.
- 😀 The TM symbol indicates an unregistered trademark, while the ® symbol shows a registered trademark.
- 😀 Patents protect inventions, and obtaining one can be a costly and strict process, often requiring specialist legal help.
- 😀 Patents generally cover physical products or technological innovations, not things like software.
- 😀 If your intellectual property is stolen, you can request removal of the infringing content or pursue legal action.
- 😀 While law enforcement may get involved in large-scale intellectual property crimes, individual cases usually require court action.
- 😀 This law is designed to protect ideas from being copied, not physical items like cars or laptops.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of the Copyrights, Designs, and Patents Act?
-The primary purpose of the Copyrights, Designs, and Patents Act is to protect intellectual property (IP), which includes creations of the mind such as books, digital arts, software, and photos.
What does intellectual property (IP) refer to under this law?
-Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind, such as ideas, inventions, artistic works, and other creations that are the result of human thought.
How does the law define copyright, and what does it protect?
-Copyright is an automatic right granted to creators to protect their works, such as books, music, and software, from being copied or used without permission. It protects the idea behind the work, not the physical item itself.
What are some ways creators can enforce their copyright under this law?
-Creators can enforce their copyright by requesting that stolen works be taken down or that payment be made for use of their work. If the person does not comply, creators can prosecute them through the courts.
What challenges do creators face when trying to enforce their copyright?
-Enforcing copyright can be difficult, as it may take a long legal process to remove infringing content. Not all websites have simple tools, like YouTube's copyright strike, to address the issue.
What is the general duration of copyright protection in the UK?
-In the UK, copyright protection typically lasts 50 or 70 years, depending on the type of work. This is why older works, like classic books, may no longer have copyright protection and can be republished freely.
What is the significance of the copyright symbol (©)?
-The copyright symbol (©) indicates that a work is protected by copyright law and that others should seek permission before using it. It serves as a reminder that unauthorized use is prohibited.
What is the difference between trademarks and copyrights?
-Trademarks are used to protect brand names, logos, and distinctive elements related to a product or service, while copyrights protect original works of authorship, such as literary, artistic, and musical creations.
How do patents differ from copyrights and trademarks?
-Patents protect inventions, such as new technologies or products, by granting exclusive rights to the inventor. Patents require a formal application process and are more expensive to obtain compared to copyrights and trademarks, which are more straightforward.
What is the purpose of fair dealing or fair use in copyright law?
-Fair dealing or fair use allows limited use of copyrighted works without permission, such as for education or commentary. However, there are restrictions, and using copyrighted material for commercial purposes typically requires permission.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)