Strategies to Solve Multi Step Linear Equations with Fractions
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Anil Kumar introduces two strategies to solve equations involving fractions: cross multiplication and finding the lowest common multiple (LCM). He demonstrates these methods with eight examples, showing how to eliminate fractions and simplify equations to linear forms. The video is designed to clarify concepts and improve problem-solving skills, encouraging viewers to practice the techniques and check their solutions for accuracy.
Takeaways
- 📘 The video series by Anil Kumar focuses on solving equations with fractions, aiming to clarify concepts through eight examples.
- 🔢 Two main strategies are introduced: 'cross multiplication' and 'getting rid of fractions', which are essential for simplifying equations.
- ✖️ 'Cross multiplication' is a method where the denominator is multiplied by the term on the other side of the equation to eliminate fractions.
- 🔑 The 'getting rid of fractions' strategy involves finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) of the denominators to simplify the equation.
- 📝 It's recommended to pause the video, copy the questions, and then solve them one by one following the strategies discussed.
- 🔄 In cases with multiple terms, finding the LCM is crucial as it allows for the cancellation of fractions and simplifies the equation to a linear form.
- 🧮 An example given is solving \( \frac{x + 2}{3} = \frac{4}{1} \) by cross multiplication, resulting in \( x + 2 = 12 \) and thus \( x = 10 \).
- 🔄 The video demonstrates how to handle equations with different terms and denominators by multiplying through by the LCM to clear the fractions.
- 📉 For equations with variables in the denominator, the LCM is used to eliminate the variable and solve for the variable.
- 🔍 The video emphasizes the importance of checking solutions by substituting back into the original equation to ensure accuracy.
- 📈 The series is designed to build confidence in solving equations with fractions, with a call to action for viewers to apply the strategies and share their feedback.
Q & A
What are the two strategies mentioned in the video for solving equations with fractions?
-The two strategies mentioned are cross multiplication and finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) to eliminate fractions.
How does cross multiplication help in solving equations with fractions?
-Cross multiplication involves multiplying the denominator of one fraction by the numerator of the other fraction and vice versa, which helps to eliminate the fractions and simplify the equation.
What is the purpose of finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) in solving equations with fractions?
-Finding the LCM allows you to multiply each term in the equation by the LCM, which results in a linear equation without fractions, making it easier to solve.
How do you check if the solution to a fraction equation is correct?
-You can check the solution by substituting the value of the variable back into the original equation and verifying if both sides of the equation are equal.
In the video, what is the first example of an equation solved using cross multiplication?
-The first example is \( \frac{x + 2}{3} = \frac{4}{1} \), which simplifies to \( x + 2 = 12 \) after cross multiplication, leading to the solution \( x = 10 \).
What is the significance of the distributive property when multiplying terms by the LCM?
-The distributive property is significant because it allows you to multiply each term inside the parentheses by the LCM separately, which is necessary for eliminating the fractions in the equation.
How does the video demonstrate solving an equation with multiple terms and different denominators?
-The video demonstrates solving such equations by first finding the LCM of the denominators and then multiplying each term by this LCM, which leads to a linear equation without fractions.
What is the importance of applying the same operation to both sides of an equation?
-Applying the same operation to both sides of an equation is important to maintain equality, which is a fundamental principle in solving equations.
How does the video handle equations where the variable is in the denominator?
-The video suggests finding the LCM that includes the variable in the denominator, multiplying each term by this LCM, and then solving the resulting equation.
What is the final advice given in the video for solving equations with fractions?
-The final advice is to go through the examples again to reinforce understanding, and to apply the learned strategies to solve any equation involving fractions.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
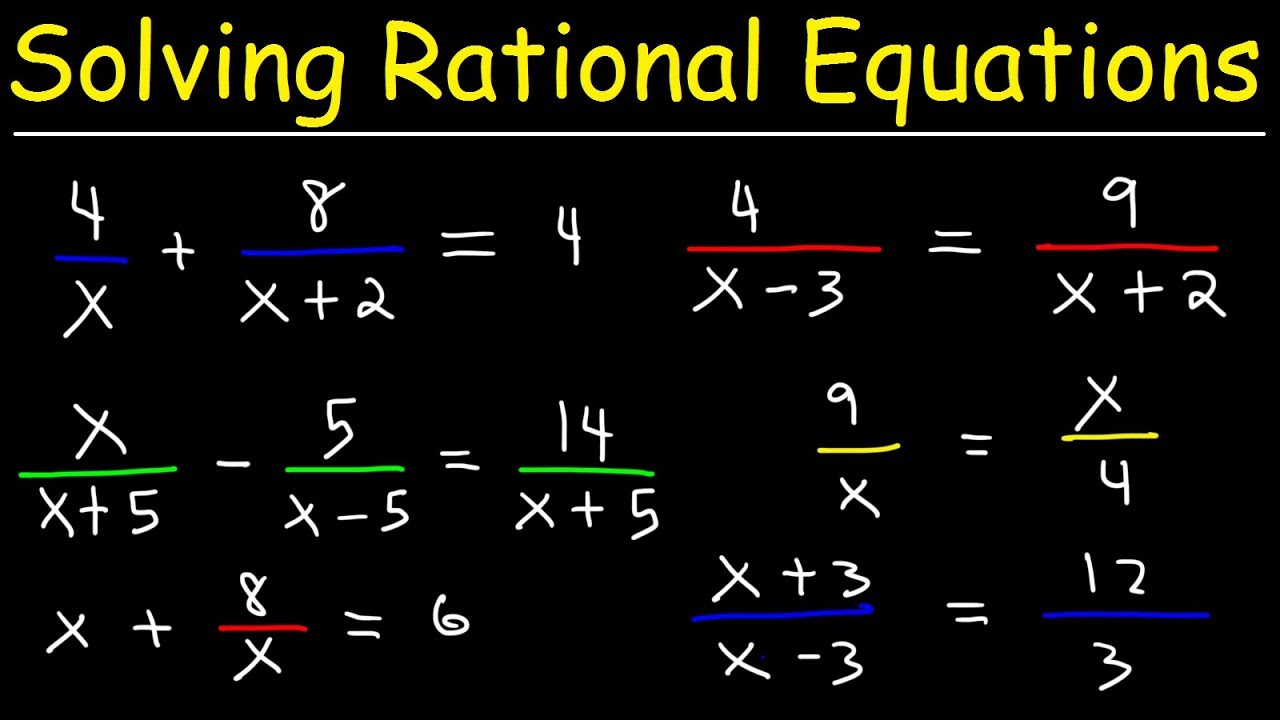
Solving Rational Equations

CARA MEMBANDINGKAN PECAHAN #KELAS 4#cara_membandingkan_pecahan

FRAÇÃO | ADIÇÃO e SUBTRAÇÃO de FRAÇÕES. Método convencional e o método BORBOLETA

Le quattro operazioni fondamentali con le frazioni

Adição | Subtração | Multiplicação | Divisão
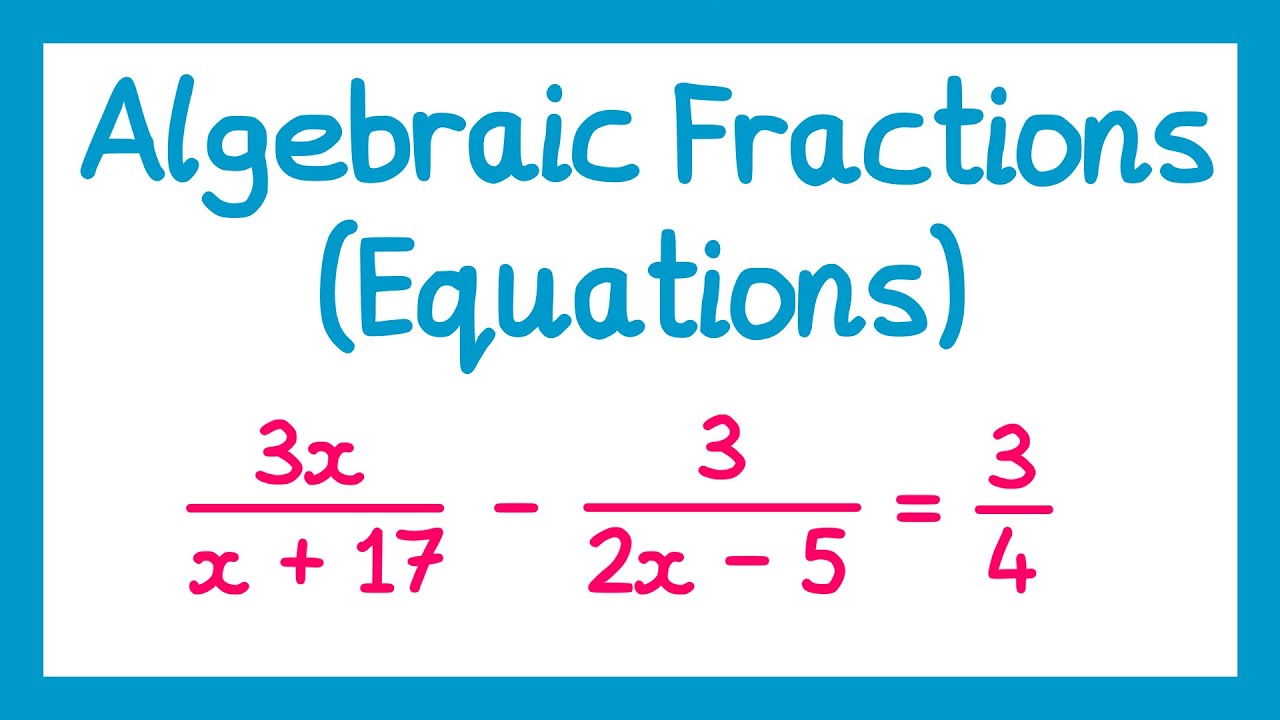
Algebraic Fractions (Equations) - GCSE Higher Maths
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
