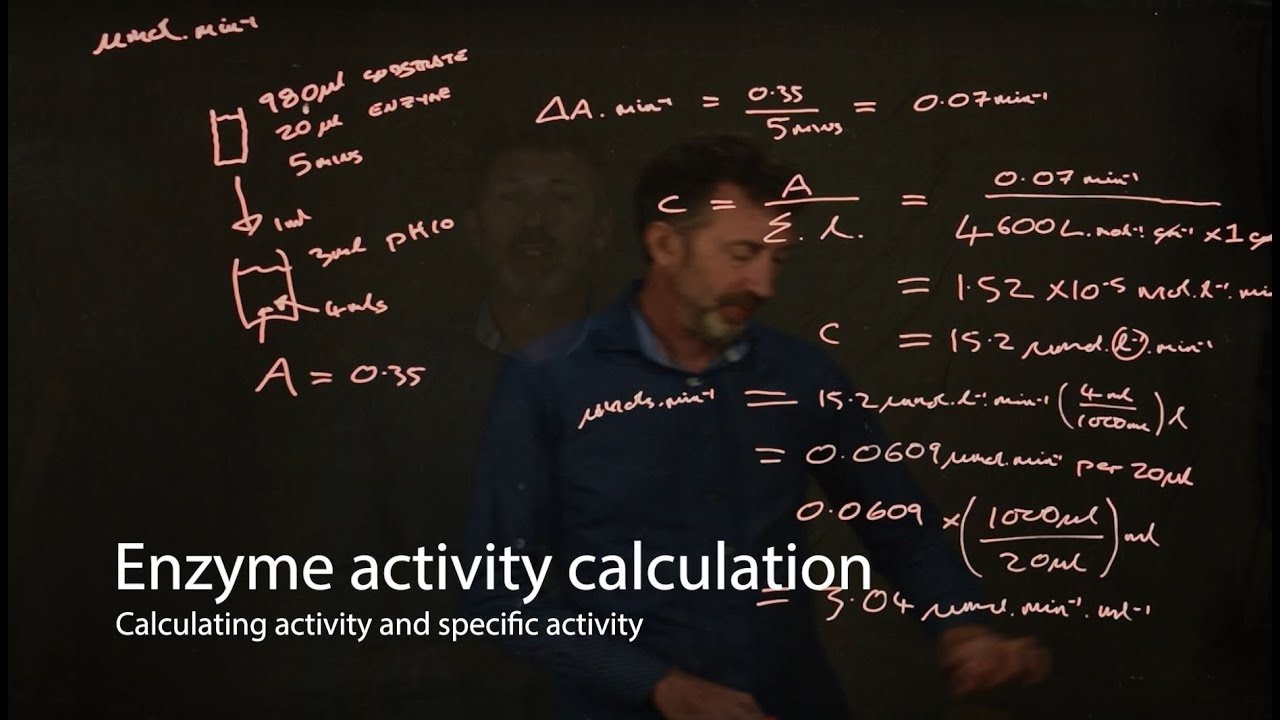The Determination of Enzyme Specific Activity
Summary
TLDRThis video script details an experiment on determining enzyme specific activity, focusing on glutathione S-transferase (GST). It covers the preparation of cytosolic fractions from mice, measuring GST activity using the CDNB method, creating a BSA standard curve with the Biuret method, and calculating protein content and enzyme specific activity. The script also discusses the importance of GST in detoxification and its relevance in cancer treatment, where inhibiting GST can enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The experiment aims to determine the specific activity of glutathione S-transferase (GST) enzyme and protein concentration using the Bradford method.
- 🧬 The activity of GST enzyme in protein mixtures is dependent on the amount of protein used, necessitating the knowledge of protein content in the mixture.
- 📚 Monomer and polymer concepts are introduced, with monomers being the building blocks like amino acids, and polymers being long chains like proteins.
- 🌟 Amino acids, the monomers of proteins, are differentiated by their R groups and can polymerize to form linear chains, such as peptides.
- 🔍 Three types of protein quantitative analysis are discussed: volumetric, gasometric, and spectrophotometry, with the experiment using visible light spectrophotometry.
- 📈 The Bradford method is chosen for protein quantification, which involves a color reaction with Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 dye, measured at 550 nm.
- 🛠️ The preparation of cytosolic fraction containing GST from mice involves several steps of centrifugation to isolate the enzyme.
- 🧪 The enzyme activity of GST is determined using the CDNB method, which measures the formation of a conjugate product at 340 nm over time.
- 📊 A standard curve using bovine serum albumin (BSA) is created to measure the concentration of the GST enzyme in the sample.
- ⚖️ The specific activity of the enzyme is calculated by dividing the enzyme units by the protein concentration, indicating the enzyme's purity and efficiency.
- 💊 The importance of measuring enzyme activities is highlighted, particularly in pharmaceutical fields, where GST enzymes play a role in detoxification and cancer treatment.
Q & A
What is the main objective of the experiment described in the script?
-The main objective of the experiment is to determine the specific activity of the GST enzyme, measure the protein concentration using the Biuret method, and understand the fundamentals of enzyme activity in relation to protein content.
What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer as described in the script?
-A monomer is a single small molecule that can be joined with other identical molecules to form a polymer. In the context of proteins, amino acids are the monomers, and proteins are the polymers formed by the linkage of these amino acids.
What are the elements that typically make up amino acids, the monomers of proteins?
-Amino acids, which are the monomers of proteins, typically contain elements such as hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and carbon (C).
What are the different types of protein quantitative analysis mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions three types of protein quantitative analysis: volumetric analysis, gasometric analysis, and spectrophotometry, with the latter including UV and visible light spectrophotometry.
Why is it necessary to measure the protein content in a sample before determining enzyme activity?
-Measuring the protein content is necessary because the activity of enzymes like GST in a protein mixture depends on the amount of protein present. This information is crucial for accurately determining the specific activity of the enzyme.
What is the Biuret method used for in the experiment?
-The Biuret method is used in the experiment to determine the protein concentration in the cytosolic fraction containing the GST enzyme by measuring the color complex formed between the protein and the Biuret reagent at a wavelength of 550 nanometers.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the Biuret method for protein quantification?
-The advantages of the Biuret method include its simplicity and speed, and the fact that the protein concentration measured is comparable to the polypeptide bond. Disadvantages include lower sensitivity and sometimes unstable color development.
What is the significance of measuring enzyme activities and protein concentrations in pharmaceutical fields?
-Measuring enzyme activities and protein concentrations is significant in pharmaceutical fields because it helps in understanding the detoxification processes, such as the role of GST enzymes in the excretion of xenobiotics and chemotherapeutic agents, which can be crucial in the treatment of diseases like cancer.
What is the purpose of creating a standard curve using the BSA method in the experiment?
-The purpose of creating a standard curve using the BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) method is to measure the concentration of the GST enzyme in the cytosolic fraction by comparing the absorbance values obtained from the sample to the known concentrations of BSA.
How is the specific activity of an enzyme calculated in the experiment?
-The specific activity of an enzyme is calculated by dividing the total enzyme units, which is the amount of enzyme that catalyzes one micromole of substrate reaction per minute, by the protein concentration in milligrams per milliliter.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)