Explaining File Systems: NTFS, exFAT, FAT32, ext4 & More
Summary
TLDRThis video explores various computer file systems, explaining their roles in organizing data on storage devices. It covers FAT, NTFS, exFAT, ext4, HFS+, and APFS, detailing their compatibility, limitations, and optimal use cases. The script emphasizes the importance of choosing the right file system for system drives, USBs, and external storage, highlighting the need for compatibility and understanding file size restrictions to avoid data loss.
Takeaways
- 😀 File systems are standards for organizing data on storage devices and are chosen during formatting.
- 🔍 Different file systems are available depending on the operating system and drive type.
- 📚 The first Windows file system was FAT, with variants FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32, each supporting larger file and volume sizes.
- 📁 FAT32 is popular for its compatibility and is often used for USB drives and memory cards, but has a 4GB file size limit on Windows.
- 💾 NTFS was introduced to overcome FAT32 limitations, offering a virtually unlimited file size and features like journaling and file permissions.
- 🛡️ NTFS is required for modern Windows installations due to its robustness and advanced features.
- 🔄 exFAT was designed for high-capacity USB drives and memory cards, with a large file size limit and improved compatibility.
- 🌐 exFAT has wider non-Windows support, including read and write capabilities on Macs and Android, but may require drivers on Linux.
- 🔧 The ext file system family, starting with ext in 1992 and evolving to ext4, is specific to Linux and does not have native support on Windows or macOS.
- 🍎 HFS and its upgrade HFS+ are Apple's file systems, with HFS+ supporting journaling and large file sizes, while APFS is optimized for SSDs.
- 🚫 Apple's file systems are not natively supported by Windows or other non-Apple operating systems.
- 🔄 ZFS is a unique file system that integrates volume management, offering enhanced data protection and currently available on Linux, FreeBSD, and other OSes.
- 🔑 Choosing a file system depends on the OS, device type, and need for compatibility with other systems.
- 🔄 To check a drive's file system, use the properties feature in the OS, but be aware that changing it requires reformatting and data loss.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a file system?
-A file system's primary function is to organize data on storage devices, such as hard drives, SSDs, or USB flash drives, by dividing the storage space into virtual compartments called clusters and maintaining an index of where files are located and where free space is available.
What are the differences between FAT32 and NTFS file systems?
-FAT32 supports a maximum file size of 4 GB and volume sizes of up to 32 GB when formatted in Windows, making it widely compatible across various operating systems. NTFS, on the other hand, supports much larger file sizes (up to 16 exabytes) and offers features like journaling, file permissions, and encryption, making it more suitable for system drives on Windows. However, NTFS has limited compatibility with non-Windows systems.
Why is FAT32 still widely used despite its limitations?
-FAT32 remains popular because of its high level of compatibility across different operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. It's commonly used for USB flash drives, memory cards, and other external storage devices, particularly when cross-platform compatibility is essential.
What advantages does the exFAT file system offer over FAT32?
-exFAT offers a significantly larger maximum file size (up to 16 exabytes) compared to FAT32's 4 GB limit, making it ideal for high-capacity storage devices like SDXC memory cards and USB flash drives. It also enjoys wider compatibility across newer versions of macOS and Android, although it may require extra drivers on some Linux systems.
What are the main features of the EXT4 file system used in Linux?
-EXT4, the most modern dedicated Linux file system, supports a maximum file size of 16 terabytes and a maximum volume size of 1 exabyte. It also includes journaling, which helps protect against data corruption in case of crashes or power failures.
Why is NTFS the preferred file system for modern Windows installations?
-NTFS is preferred for Windows installations due to its support for large file sizes (up to 16 exabytes), journaling to recover from crashes, and advanced features like file permissions and encryption. These features make NTFS more robust and secure compared to older file systems like FAT32.
What are the compatibility limitations of NTFS with other operating systems?
-NTFS has limited compatibility with non-Windows systems. For example, NTFS volumes are read-only by default on macOS and older Linux distributions. Some devices, such as standalone media players, may not support NTFS at all.
When would it be appropriate to use exFAT instead of NTFS?
-exFAT is appropriate when you need to share files between a Windows PC and a Mac, or when you're working with large files that exceed the 4 GB limit of FAT32. It's also suitable for flash drives and memory cards with capacities of 32 GB or more, particularly when cross-platform compatibility is required.
What is the significance of journaling in a file system?
-Journaling is a feature in file systems like NTFS and EXT4 that maintains a record of changes made to files. This helps the system recover and prevent data corruption in the event of a crash or power failure.
What problem did the video creator encounter with FAT32, and how was it resolved?
-The video creator encountered an issue when trying to decompress a file larger than 4 GB on a FAT32-formatted flash drive. The process failed because FAT32 cannot handle files larger than 4 GB. The problem was resolved by moving the file to a drive with a file system that supports larger files, such as NTFS.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

L-7.1: File System in Operating System | Windows, Linux, Unix, Android etc.
NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT - Everything You Need To Know

Perangkat Keras (Hardware) - Informatika kelas 7 SMP/ MTs (Sistem Komputer)

9. OCR A Level (H046-H446) SRL3 - 1.1 Input, output and storage devices

COMPUTER INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES FOR CHILDREN || BASIC COMPUTER || COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS
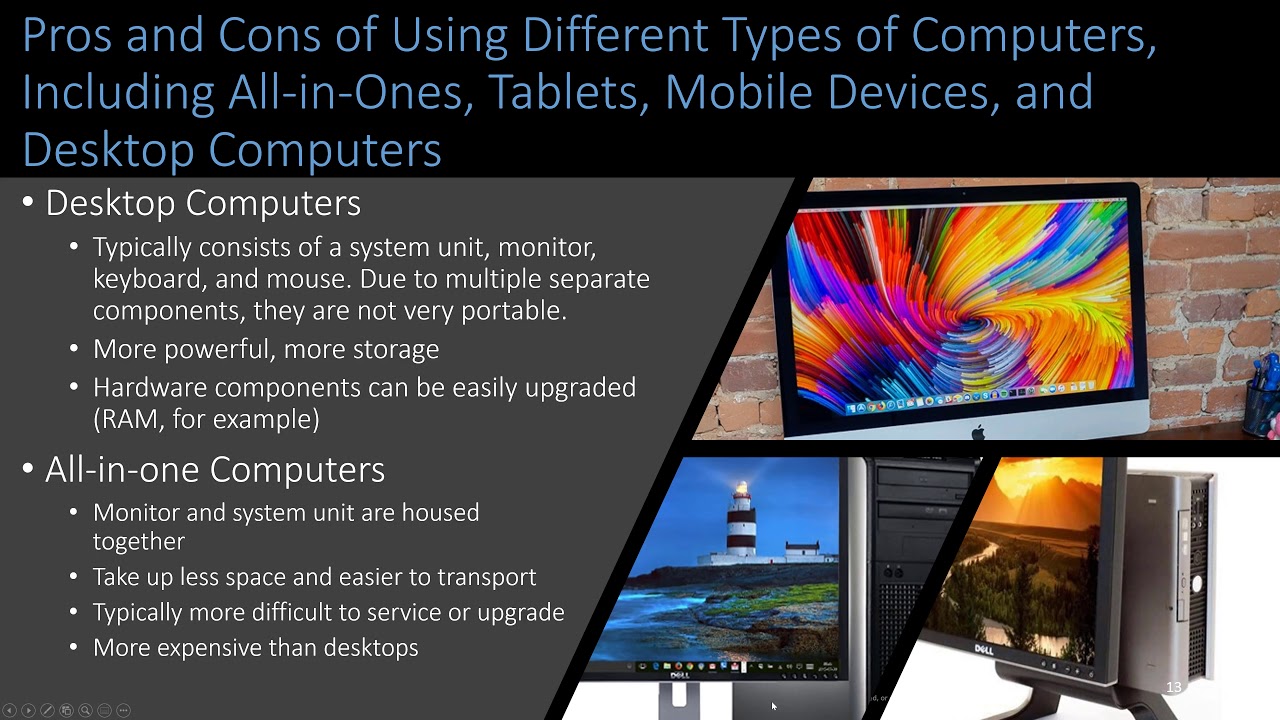
Computer Concepts - Module 3: Computer Hardware Part 1B (4K)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
