Orthographic Projection Explained
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Cal's Beak introduces the concept of multi-view drawings and orthographic projection, a technique for representing three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane. He explains the process of determining front, side, and top views, using an imaginary box to project the object's edges onto different planes. Cal demonstrates how to translate this method into a paper drawing, starting with the front view and then creating top and side views, to produce a comprehensive multi-view sketch. This tutorial aims to deepen viewers' understanding of orthographic projection.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is an educational tutorial on multiview drawings and orthographic projection.
- 👨🏫 It is based on a method taught by a professor from the University of Mind U.
- 🎨 The tutorial uses a 3D object with contours, edges, and a hole to demonstrate the concept.
- 👀 The front view is chosen based on visibility of the object's contours.
- 📐 An 'invisible box' is used to conceptualize the projection of the object's edges onto different planes.
- 📝 The front, side, and top views are the primary views used in the demonstration.
- 🔄 The process involves projecting the object's edges onto the planes of the imaginary box.
- 🖌️ Drawing on paper starts with the front view, then moves to the top, and finally the side view.
- 📏 The tutorial emphasizes the importance of proper layout for the multiview sketches.
- 💡 The 'invisible box' trick is a helpful tool for understanding and creating multiview drawings.
- 🔑 The video aims to provide a deeper understanding of orthographic projection for the viewer.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is multi-view drawings or orthographic projection, which is a method to represent a three-dimensional object in two dimensions from different angles.
Who is the speaker in the video script?
-The speaker in the video script is Cal, who is presumably a knowledgeable individual in the subject matter, possibly a professor or an expert in the field.
What is the purpose of using an 'invisible box' in the explanation?
-The 'invisible box' is used as a conceptual tool to help understand the process of orthographic projection by visualizing how the edges of the object project onto the different planes of the box.
What are the three primary views that the script mentions for a multi-view drawing?
-The three primary views mentioned in the script are the front view, the top view, and the side view.
How does the script suggest starting the drawing process for a multi-view sketch?
-The script suggests starting with the front view as it often provides the most contours and is a good place to begin when drawing a multi-view sketch.
What is the significance of the top view in orthographic projection?
-The top view in orthographic projection is significant as it provides a planar representation of the object from above, showing the object's features as they would appear when viewed from the top.
What does the script imply about the relationship between the object's edges and the planes of the 'invisible box'?
-The script implies that the edges of the object project straight onto the corresponding planes of the 'invisible box', which helps in creating an accurate representation in the multi-view drawing.
How does the script describe the process of transitioning from the front view to the side view in a multi-view drawing?
-The script describes the process as turning the object to the side, which allows the edges to be projected onto the side plane, thus creating the side view.
What is the final step mentioned in the script for creating a multi-view sketch?
-The final step mentioned in the script is laying out the top, front, and right side views in a proper arrangement to complete the multi-view sketch.
What advice does the script give for gaining a deeper understanding of orthographic projection?
-The script advises using the trick of envisioning a box around the object to help understand how to create a multi-view drawing and to gain a deeper understanding of orthographic projection.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Disegno Tecnico. Capire le Proiezioni Ortogonali, in 6 minuti
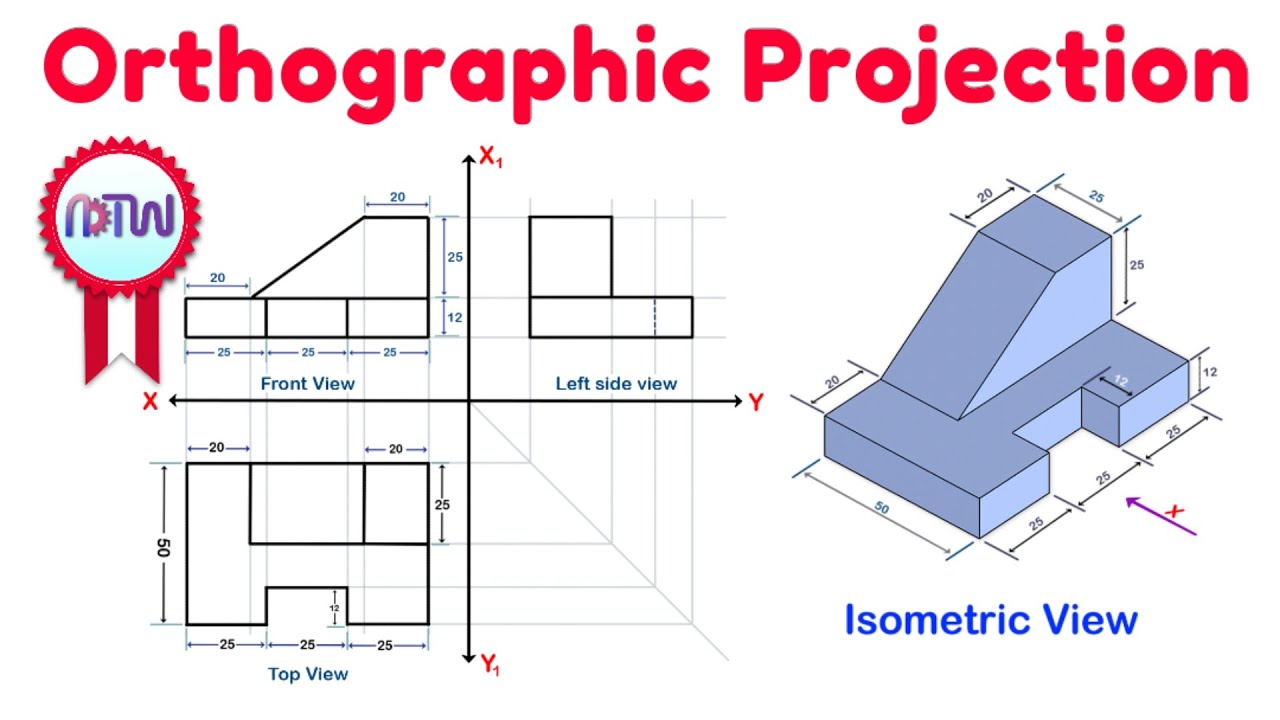
Orthographic Projection from isometric view in Engineering drawing
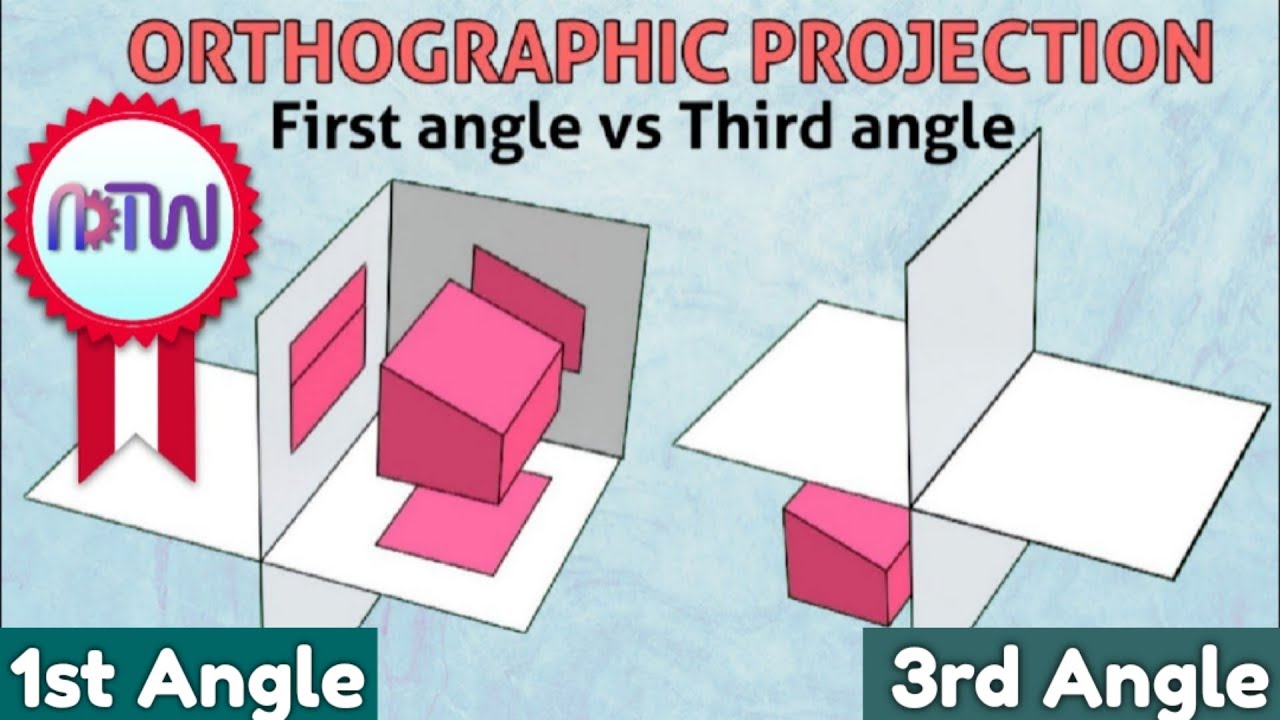
First angles vs Third angle method | Orthographic projections animation

Menggambar Perspektif | Video Pembelajaran Seni Budaya kelas 8 Smt 1 Kurikulum Merdeka

Types of Pictorial Drawings

How to Draw Architectural Floor Plans: What is a Floor Plan? Floorplans for Architecture Students
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)