Top 10 Analog Inputs in Robotics
Summary
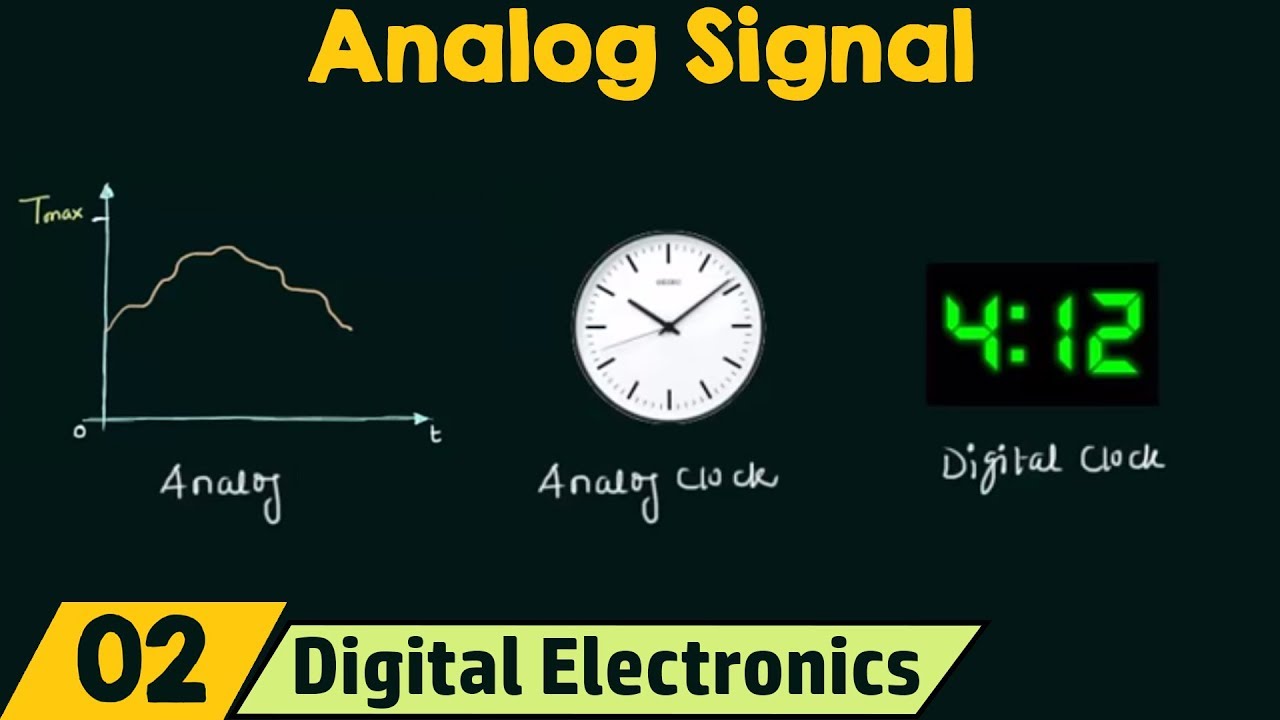
TLDRAnalog inputs in robotics are crucial for providing detailed environmental data through continuous signals, as opposed to discrete binary states. They enable robots to sense and measure variables like position, force, temperature, and light, enhancing their interaction with the world. Types of analog inputs include position sensors, encoders, force/torque sensors, pressure sensors, temperature sensors, light sensors, strain gauges, voltage sensors, distance sensors, and gas sensors. These inputs are converted to digital signals for processing by the robot's control system, contributing to the versatility and adaptability of robotics in various applications.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Analog inputs in robotics are crucial for sensing and interacting with the environment through continuous and fluctuating quantities.
- 🎨 Without analog inputs, robotics would lack the depth and detail, much like painting with only two colors.
- 📏 Position sensors like potentiometers provide an analog voltage proportional to the position of a robot's movable part.
- 🔄 Analog encoders offer precise measurements of angles and positions through varying voltage signals.
- 🤏 Force and torque sensors enable robots to safely manipulate objects by providing analog readings of applied forces.
- 📡 Analog pressure sensors measure fluid or gas pressure, offering proportional voltage or current outputs.
- 🌡️ Temperature sensors like thermistors or thermocouples convert temperature changes into varying voltage levels.
- 🔆 Light dependent resistors and photodiodes react to light intensity by changing their resistance or voltage.
- 📷 Analog cameras capture light intensity across an image, providing continuous voltage signals for image representation.
- 📏 Strain gauges measure structural integrity by detecting deformation through changes in resistance.
- 🔌 Voltage sensors monitor power supply conditions by providing analog outputs of electrical voltage levels.
- 📐 Analog distance sensors offer voltage outputs that vary with the distance to an object.
- 💨 Analog gas sensors measure environmental gas concentrations, providing essential data for safety and control.
- ⚙️ Analog signals are converted to digital signals by analog-to-digital converters for processing by the robot's control system.
- 🤖 Analog inputs contribute to the versatility and adaptability of robots in various applications.
Q & A
What are analog inputs in the context of robotics?
-Analog inputs in robotics are signals or data that represent continuous and fluctuating quantities. Unlike discrete binary states, analog inputs can take on a range of values, providing nuanced and detailed information about the environment.
Why are analog inputs important in robotics?
-Analog inputs are crucial because they allow robots to sense, measure, and interact with a variety of physical variables such as position, force, temperature, and more. This enables robots to perform tasks with greater precision and adaptability.
What would be the impact of a world without analog inputs in robotics?
-Without analog inputs, robotics would lose much of its depth and nuance. It would be akin to trying to paint a masterpiece with only two colors, severely limiting the ability of robots to interact effectively with their environment.
Can you name some types of analog inputs used in robotics?
-Some common types of analog inputs in robotics include position sensors (e.g., potentiometers), analog encoders, force or torque sensors, pressure sensors, temperature sensors, light-dependent resistors, analog cameras, strain gauges, voltage sensors, distance sensors, and gas sensors.
How do position sensors like potentiometers work in robotics?
-Position sensors like potentiometers provide an analog voltage proportional to the position of a movable part, such as a robot joint. This allows for precise control and measurement of the robot's movements.
What role do force or torque sensors play in robotics?
-Force or torque sensors provide analog readings that indicate the force or torque applied to a robot's end effector or manipulator. This is essential for tasks like safe object manipulation, where precise control of force is required.
How do analog temperature sensors function in robotics?
-Analog temperature sensors, such as thermistors or thermocouples, produce varying voltage levels based on the temperature they sense. This allows robots to monitor and respond to temperature changes in their environment.
What is the process of converting analog signals to digital in robotics?
-Analog signals are converted to digital signals using analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). This process involves discretizing the continuous analog signal into discrete digital values that can be processed by the robot's microcontroller or control system.
Why are analog distance sensors important in robotics?
-Analog distance sensors provide voltage outputs that vary according to the distance between the sensor and an object. This information is crucial for tasks like navigation, obstacle avoidance, and precise positioning.
What is the significance of analog gas sensors in robotics?
-Analog gas sensors measure the concentration of specific gases in the environment and provide varying analog outputs. These sensors are important for applications like environmental monitoring, safety checks, and detecting hazardous conditions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)