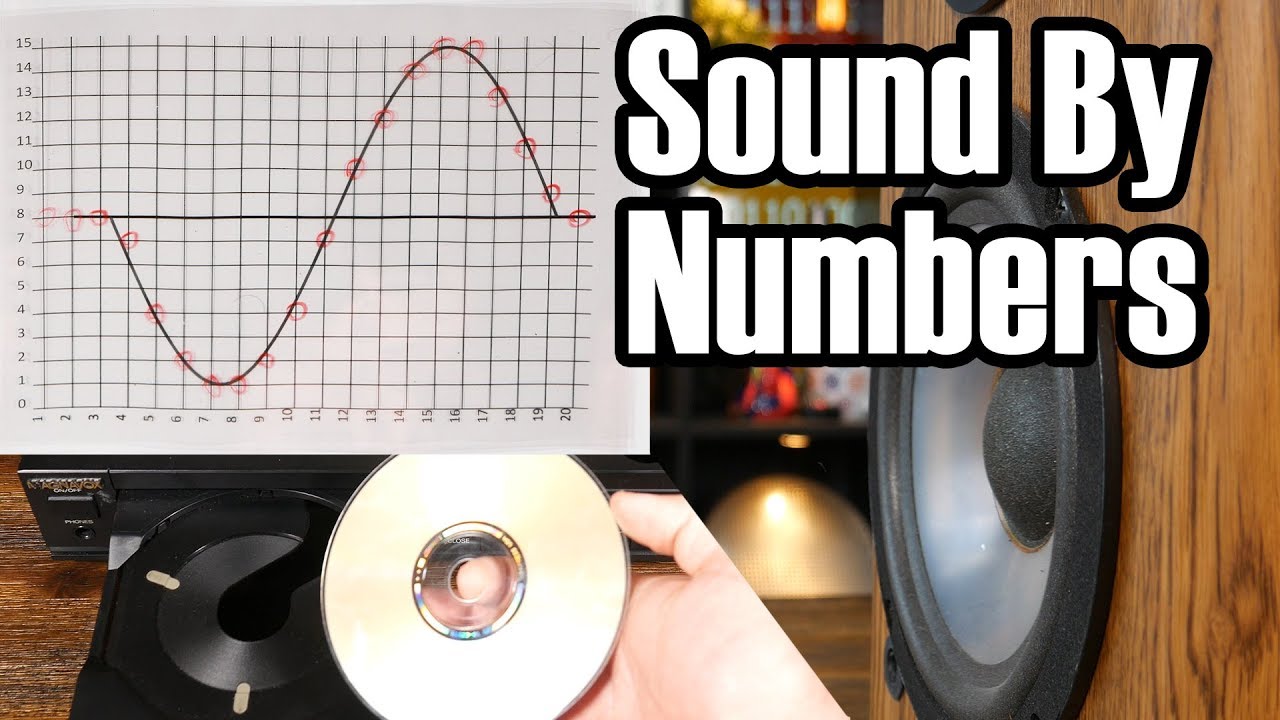
PCM - Analog to digital conversion
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Sunny explains Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), a method for converting analog signals into digital ones. PCM involves three main steps: sampling, quantizing, and encoding. Sampling selects discrete points from the continuous analog signal, while quantizing rounds each sample to a finite set of values based on bit depth. Finally, encoding converts the quantized values into binary numbers. Through simple examples and clear explanations, Sunny demonstrates how PCM allows for the accurate digital representation of analog signals like phone calls or audio, making it easy to understand this crucial process in digital communication.
Takeaways
- 😀 PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) is a method used to convert analog signals into digital signals through three steps: sampling, quantizing, and encoding.
- 😀 Sampling is the process of taking discrete values from an analog signal at regular intervals to represent it digitally.
- 😀 The sampling rate refers to the number of samples taken per second, commonly measured in Hertz (Hz).
- 😀 Different systems use different standard sample rates, for example, 8 kHz for telephone calls, 44 kHz for audio CDs, and up to 1 MHz for Blu-ray discs.
- 😀 Quantizing is the process of converting the sampled values into specific levels, and it involves rounding the sample amplitudes to a finite set of values.
- 😀 The bit depth determines the number of levels available for each sample, such as 8-bit, 16-bit, or 24-bit, which translates to different possible amplitude levels.
- 😀 For example, 8-bit depth offers 256 levels, 16-bit depth gives 65,536 levels, and 24-bit depth allows 16.8 million levels.
- 😀 Quantizing rounds each sampled value to the nearest level, and each level is associated with a specific binary value.
- 😀 Encoding involves converting the quantized samples into binary numbers, creating a stream of zeros and ones representing the original analog signal.
- 😀 PCM effectively transforms an analog signal into a stream of binary values that can be transmitted or stored digitally, maintaining the original signal's characteristics.
Q & A
What is Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)?
-Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a method used to convert analog signals into digital signals. It involves three main steps: sampling, quantizing, and encoding.
What is the first step in PCM and how does it work?
-The first step in PCM is sampling. Sampling involves measuring the amplitude of the analog signal at regular intervals. This converts the continuous analog signal into a discrete signal.
What is a sample rate in PCM?
-The sample rate is the number of samples taken per second to represent the analog signal. It is measured in Hertz (Hz). For example, a telephone uses an 8 kHz sample rate, while audio CDs use a 44 kHz sample rate.
What is the relationship between sample rate and quality?
-A higher sample rate results in better signal representation and sound quality. For example, audio CDs have a sample rate of 44,000 samples per second, which provides good sound quality, while higher sample rates like 1 MHz can offer even better quality for high-fidelity sound.
What is the second step in PCM and how does it function?
-The second step is quantizing. Quantizing involves rounding off each sample's amplitude to the nearest value from a predefined set of levels. This is done to represent the sample with a specific value, often in binary form.
What is bit depth and how does it affect quantizing?
-Bit depth refers to the number of possible values a sample can be quantized into. A higher bit depth allows for more precise representation of each sample. Common bit depths include 8-bit, 16-bit, and 24-bit. For example, a 16-bit depth provides 65,536 possible levels.
What are the most common bit depths used in PCM?
-The most common bit depths used in PCM are 8-bit, 16-bit, and 24-bit. For audio, 16-bit depth is typical for CDs, while higher depths like 24-bit are used for higher-quality audio, such as Blu-ray.
What is the purpose of the encoding step in PCM?
-The encoding step converts the quantized samples into binary numbers. These binary numbers can be stored, transmitted, or processed by digital systems.
How does the quantizing process work in PCM?
-During quantizing, each sample’s amplitude is rounded to the nearest value from a finite set of levels, corresponding to specific binary values. This process ensures that the continuous analog signal is represented with discrete values.
Why is PCM considered an effective method for converting analog signals to digital?
-PCM is effective because it preserves the characteristics of the original analog signal while converting it into a form that can be easily processed, stored, and transmitted by digital systems. The process involves precise steps like sampling, quantizing, and encoding to ensure accurate representation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)