Transactional Model
Summary
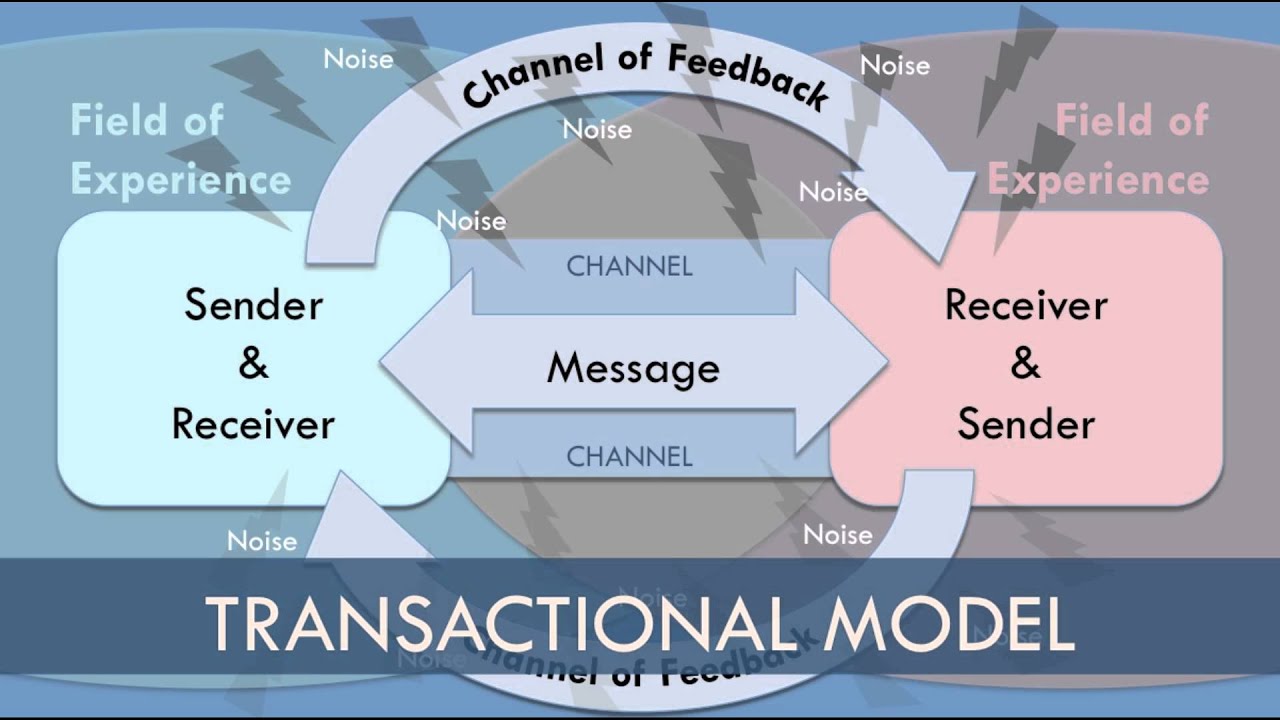
TLDRThe script explores the Transactional Model of communication, emphasizing the dynamic process where a sender encodes and sends a message to a receiver who then decodes it. The model highlights the reciprocal nature of communication, as the receiver can become a sender, and vice versa. It also addresses the impact of noise, which can disrupt the communication process, and the importance of channels, like audio for public speaking, in message transmission. The script illustrates how non-verbal cues and even environmental factors can influence the clarity and effectiveness of communication.
Takeaways
- 🔁 The Transactional Model emphasizes the interactive nature of communication where roles can switch between sender and receiver.
- 📨 The sender encodes a message to be sent, highlighting the importance of clear and effective encoding for successful communication.
- 🔍 The receiver decodes the message, underlining the necessity for accurate interpretation to avoid misunderstandings.
- 🔄 The receiver can become a sender by encoding a new message, illustrating the dynamic and reciprocal nature of communication.
- 😯 Non-verbal cues can also communicate confusion or understanding, showing that communication is not limited to verbal exchanges.
- 👥 Noise can interrupt communication, such as external sounds or environmental factors, which can hinder the clarity of the message.
- 👂 Channels refer to the medium through which messages are transmitted, like voice for a public speaker and hearing for the audience.
- 📣 The speaker's channel is audio, specifically the spoken word, while the receiver's channel is also audio but focused on hearing the message.
- 👤 Communication can be adapted for different audiences, such as providing an assistant for non-hearing individuals to decode the message.
- 🔗 The model demonstrates that communication is a continuous process involving encoding, decoding, and feedback.
- 🌐 The Transactional Model is a foundational theory in communication studies, applicable to various contexts including public speaking.
Q & A
What is the Transactional Model in communication?
-The Transactional Model in communication is a core theory that describes the process where a message is sent from a sender to a receiver, decoded, and then a response is encoded and sent back, making the receiver a sender and vice versa.
Who are the two main participants in the Transactional Model?
-The two main participants in the Transactional Model are the sender, who initiates the communication by encoding a message, and the receiver, who decodes the message and potentially responds.
What is the process of encoding in the context of the Transactional Model?
-Encoding in the Transactional Model refers to the process where the sender translates their thoughts or information into a message that can be sent to the receiver.
What is decoding in the Transactional Model?
-Decoding in the Transactional Model is the process where the receiver interprets the message sent by the sender, turning the encoded message back into a comprehensible form.
How can the roles of sender and receiver change in the Transactional Model?
-In the Transactional Model, the roles can change dynamically. Once the receiver decodes the message and responds, they effectively become the sender, and the original sender becomes the receiver of the new message.
What is the role of non-verbal communication in the Transactional Model?
-Non-verbal communication plays a significant role as it can convey messages through facial expressions, body language, and other non-spoken cues, which can be decoded by the receiver as part of the communication process.
What is meant by 'noise' in the context of the Transactional Model?
-In the Transactional Model, 'noise' refers to any distraction or interference that can disrupt the communication process, such as external sounds, environmental conditions, or visual distractions.
Can you provide an example of noise that could interrupt a public speaker?
-Examples of noise that could interrupt a public speaker include someone coughing, a sudden sneeze, or the room temperature being too hot or cold, all of which can distract the audience and interfere with the message being communicated.
How are channels used in the Transactional Model?
-Channels in the Transactional Model are the means through which messages are transmitted. For instance, in public speaking, the channel for the speaker is their voice (audio), and for the receiver, it is their hearing (also audio).
What happens if the receiver is non-hearing in the context of the Transactional Model?
-If the receiver is non-hearing, an assistant or interpreter may decode the spoken message for them, effectively becoming the channel through which the non-hearing receiver understands the communication.
How does the Transactional Model account for message misunderstandings?
-The Transactional Model accounts for misunderstandings through the feedback loop where the receiver's confusion or lack of understanding can be non-verbally communicated back to the sender, prompting a need for clarification or rephrasing of the message.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)