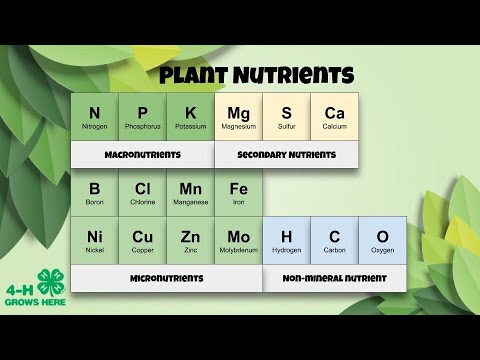
Plant Nutrient Deficiency Symptoms (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host explores nutrient deficiencies in maize plants, focusing on nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The visual effects of these deficiencies are examined, such as the pale leaves in nitrogen-deficient plants and the purple coloration in phosphorus-deficient ones. The video also discusses the environmental factors contributing to these deficiencies and the importance of these nutrients in plant growth and health.
Takeaways
- 🌱 The video is set in a greenhouse where a study on maize plants is being conducted to understand the effects of nutrient stress, specifically the lack of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- 🔍 The presenter shows four maize plants with different nutrient deficiencies: a control plant with optimal nutrients, and three others deficient in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium respectively.
- 🟢 Nitrogen deficiency is characterized by pale or yellowish leaves, starting with the older leaf tissue due to the plant's ability to reallocate nitrogen from older to newer growth.
- 🌾 Phosphorus deficiency results in stunted growth, delayed development, and purpling of older tissues as the plant moves phosphorus to new growth, leaving the older leaves discolored.
- 💧 Potassium deficiency can occur in weathered soils and affects protein synthesis, stomatal regulation, and cell wall thickening, leading to sensitivity to water deficit and disease susceptibility.
- 🍃 Chlorosis, or yellowing of leaves, is a common symptom of both nitrogen and potassium deficiencies, but the pattern of manifestation differs, with potassium deficiency starting at the leaf margins.
- 🌿 Nitrogen is a critical component of amino acids, nucleic acids like DNA, and chlorophyll, which is why its deficiency affects the green color of leaves.
- 🌱 Phosphorus is important for energy transfer compounds like ATP and is involved in root growth, especially under phosphorus stress, which can lead to increased root proliferation.
- 🌳 Potassium, being mobile in plants, is moved from older to newer tissues during deficiency, causing symptoms to first appear in older leaves.
- 🌡 The availability of phosphorus in the soil can be affected by soil pH, as it may be tied up with calcium or aluminum, making it unavailable to plants.
- 🌳 The video aims to help viewers diagnose nutrient deficiencies in their own plants by understanding the visual symptoms of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium deficiencies.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the study being conducted in the greenhouse?
-The main focus of the study is to observe the effects of nutrient stress on maize plants, specifically the deficiencies of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and to understand the visual differences in the above-ground biomass.
What is the role of nitrogen in plant growth?
-Nitrogen is a critical component of amino acids, nucleic acids like DNA, and chlorophyll. It is the most required macronutrient for plant growth and is essential for the normal green color of leaves.
How does nitrogen deficiency manifest in plant leaves?
-Nitrogen deficiency is visible as chlorosis, where leaves turn pale green to yellowish. It typically starts in the older leaf tissue, along the mid-rib, and progresses in a V-shaped pattern towards the tip of the leaf.
In what type of soil is nitrogen deficiency most prevalent?
-Nitrogen deficiency is most prevalent in soils with very low organic matter and in sandy soils where nitrogen can easily leach out.
What is the role of phosphorus in plants?
-Phosphorus is an important component of nucleic acids like DNA and energy transfer compounds like ATP. It is crucial for growth, development, and the regulation of flowering time.
What are the visible symptoms of phosphorus deficiency in plants?
-Phosphorus deficiency can cause stunted growth, delayed development, and the accumulation of anthocyanins, which results in purpling of the lower stem and older leaves.
Why might phosphorus be unavailable to plants even if it is present in the soil?
-Phosphorus may be unavailable to plants if it is tied up with calcium or aluminum, depending on the soil's pH, making it not plant-available despite being present in the soil.
How does potassium deficiency affect plant sensitivity to water deficit?
-Potassium deficiency makes plants more sensitive to water deficit because potassium is involved in stomatal regulation, and a deficiency can impair the plant's ability to regulate water loss through transpiration.
What are the roles of potassium in plant cells?
-Potassium is important for protein synthesis, stomatal regulation, and cell wall thickening, which contributes to disease resistance.
How does potassium deficiency present in plant leaves?
-Potassium deficiency first appears as chlorosis or necrosis in the lower leaf tissue, starting at the leaf margins rather than the mid-rib, as the plant moves potassium from older to newer growth.
What is the common response of plants to phosphorus stress?
-In response to phosphorus stress, some plant species may allocate more growth to root development rather than shoot growth, leading to increased root proliferation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)