Nutrisi Mineral Tanaman dan Asimilasi
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the lecturer explores the essential topic of plant nutrition, focusing on mineral nutrients and their role in plant growth. The script covers the importance of macronutrients (like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and micronutrients (such as iron, zinc, and copper), explaining their functions and how deficiencies affect plants. It also highlights nitrogen assimilation and the processes involved in transforming nitrogen into forms usable by plants. The lecturer emphasizes the role of fertilizers, both organic and chemical, in supplementing soil nutrients and ensuring healthy plant growth, with practical insights for agricultural practices.
Takeaways
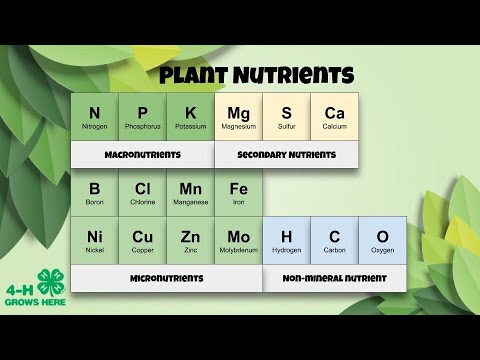
- 😀 Nutrient mineral plants are essential elements required for plant growth and metabolism. These are categorized as macro, micro, and beneficial nutrients.
- 😀 Macro-nutrients include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, calcium, and magnesium, which plants need in larger amounts.
- 😀 Micro-nutrients, such as iron, manganese, zinc, boron, copper, molybdenum, and chlorine, are needed by plants in smaller amounts but are still essential for growth.
- 😀 Beneficial nutrients like selenium and sodium are needed by specific plants for optimal growth but are not essential for all plants.
- 😀 Plants absorb nutrients through roots, but some, like carbon dioxide, can also be absorbed through leaves in a process known as foliar application.
- 😀 Foliar fertilization is useful when plants face root issues or need immediate nutrient absorption, but over-application can lead to leaf burn.
- 😀 Nitrogen is a key element for the formation of proteins, amino acids, vitamins, and nucleic acids like DNA and RNA, critical for plant and human life.
- 😀 Phosphorus plays a vital role in energy transfer through ATP and ADP, and is important for DNA, cell division, and root development.
- 😀 Potassium is crucial for regulating water balance, turgor pressure, and enzyme activation, contributing to plant quality, particularly for seeds and fruit.
- 😀 Calcium strengthens cell walls and regulates various plant growth processes, while magnesium is a vital component of chlorophyll, enabling photosynthesis.
- 😀 Deficiency of different nutrients causes various symptoms in plants, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or deformed flowers, and can be identified to adjust nutrient supply.
Q & A
What are macro and micro nutrients for plants, and how do they differ?
-Macro nutrients are essential elements required by plants in larger quantities, including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, calcium, and magnesium. Micro nutrients, on the other hand, are required in much smaller amounts but are still essential for plant growth, such as iron, manganese, zinc, boron, copper, molybdenum, and chlorine.
Why do plants need nitrogen, and what role does it play in plant growth?
-Nitrogen is a critical component of amino acids, proteins, DNA, and RNA, which are vital for plant growth. It is particularly essential for vegetative growth as it contributes to the formation of proteins and chlorophyll.
What is the difference between macro and micro nutrients in terms of plant requirements?
-Macro nutrients are needed by plants in larger amounts and include elements like nitrogen and potassium, while micro nutrients are required in trace amounts but are still crucial for processes such as enzyme activation and DNA synthesis.
What are some examples of beneficial nutrients, and why are they important?
-Beneficial nutrients, like selenium and sodium, are not essential for all plants but can enhance growth in certain species, such as rice. These nutrients are supplementary and not universally required but can improve plant health under specific conditions.
How do plants absorb water and nutrients, and why is this important?
-Plants absorb water through their roots, and water is essential for nutrient transport. Additionally, nutrients like oxygen can be absorbed through the leaves. The uptake of minerals and water is crucial for metabolic processes and overall plant health.
What is foliar application, and when is it used in agriculture?
-Foliar application involves spraying nutrients directly onto plant leaves. It is often used when plants have root problems or need rapid nutrient absorption. However, excessive concentration of fertilizers can harm the plant, causing leaf burn.
What are the primary functions of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in plant growth?
-Nitrogen supports vegetative growth, phosphorus is vital for DNA and RNA formation, and potassium helps regulate water retention and promotes root growth and fruit quality. Together, they are key components in fertilization for healthy plant development.
What happens when a plant lacks a specific nutrient?
-Deficiency in specific nutrients leads to visible symptoms such as yellowing leaves (nitrogen deficiency), purple leaves (phosphorus deficiency), or stunted growth and poor fruit quality (potassium deficiency). Each nutrient plays a unique role in plant health and development.
How do plants assimilate nitrogen, and what is its importance in the soil?
-Plants assimilate nitrogen through the conversion of nitrogen gas (N2) into forms they can use, like ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-). This process is essential because nitrogen in its gaseous form is not reactive and cannot be directly absorbed by plants.
What is the role of beneficial bacteria in nitrogen fixation, and how does this process benefit plants?
-Bacteria like Rhizobia in legume roots play a crucial role in nitrogen fixation by converting nitrogen gas in the air into usable forms such as ammonium. This natural process enriches the soil with nitrogen, benefiting plants and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)