Difference between Molarity and Molality
Summary
TLDRThis educational script introduces the concepts of molarity and molality, two methods for measuring solution concentration. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, disregarding the solvent's volume. Molality, however, is the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. The script provides examples of how to calculate each, emphasizing the importance of understanding these terms for accurate chemical analysis.
Takeaways
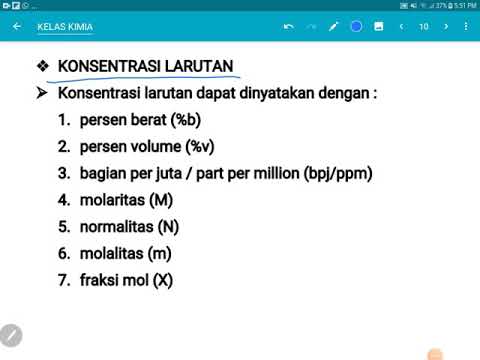
- 🔍 Concentration is defined as the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent.
- 📝 The difference between molarity and molality is crucial for understanding how to measure the concentration of a solution.
- 🔬 Molarity (denoted by M) measures the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, not considering the solvent.
- 📦 Molality (denoted by m) measures the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
- 🧪 To prepare a molar solution, dissolve a specific number of moles of solute in water until the total volume reaches one liter.
- 🧊 To prepare a molal solution, dissolve a specific number of moles of solute in one kilogram of solvent.
- 📈 Molarity is expressed in moles per liter (e.g., 5 M means 5 moles per liter).
- 📉 Molality is expressed in moles per kilogram (e.g., 5 m means 5 moles per kilogram of solvent).
- 📚 The formula for molarity is the number of moles of solute divided by the volume of the solution.
- 📏 The formula for molality is the number of moles of solute divided by the mass of the solvent.
- 🔑 Understanding molarity and molality is essential for various chemical calculations and experiments.
Q & A
What is concentration in the context of solutions?
-Concentration is defined as the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent, which indicates the amount of substance present in a solution.
How is the concentration of a solution measured?
-The concentration of a solution is typically measured using molarity or molality, which are terms that quantify the amount of solute in a solution.
What is molarity and how is it denoted?
-Molarity measures the number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution and is denoted by the capital letter 'M'.
What is the formula for calculating molarity?
-The formula for calculating molarity is the number of moles of solute divided by the volume of the solution in liters.
How would you prepare a solution with a molarity of 5 M of HCl?
-To prepare a 5 M HCl solution, you would dissolve 5 moles of HCl in enough water to make the total volume of the solution one liter.
What does the 'M' in molarity signify?
-The 'M' in molarity signifies 'moles per liter', indicating the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
What is molality and how is it denoted?
-Molality measures the number of moles of solute dissolved in 1 kg of solvent and is denoted by the lowercase letter 'm'.
What is the formula for calculating molality?
-The formula for calculating molality is the number of moles of solute divided by the mass of the solvent in kilograms.
How would you prepare a solution with a molality of 5 m of HCl?
-To prepare a 5 m HCl solution, you would dissolve 5 moles of HCl in 1 kg of water.
What does the 'm' in molality signify?
-The 'm' in molality signifies 'moles per kilogram', indicating the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
What is the main difference between molarity and molality?
-The main difference between molarity and molality is that molarity is based on the volume of the solution (in liters), while molality is based on the mass of the solvent (in kilograms).
Why might someone choose to use molality instead of molarity?
-Molality might be chosen over molarity when the solution's density changes with concentration, as molality is independent of the solution's volume and is a more stable measure of concentration in such cases.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)