Unit 1 Macro Review - Basic Economic Concepts
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host eases viewers' anxiety about an upcoming test by discussing key economic concepts like scarcity, opportunity cost, factors of production, and the production possibilities curve (PPC). The host explains how scarcity forces trade-offs, the importance of opportunity cost, and the PPC's role in illustrating efficiency and economic growth. The video also covers comparative advantage, specialization, supply and demand, and market equilibrium, highlighting how these concepts influence trade and prices. The host encourages viewers to subscribe and provides resources for further study.
Takeaways
- 📚 Economics is fundamentally about making choices due to scarcity of resources, where the desire for more than is available necessitates trade-offs.
- 💰 Opportunity cost is a central concept, representing the value of the next best alternative that is given up when making a choice.
- 🛠 Resources, or factors of production, include land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship, and established knowledge, which are essential for production.
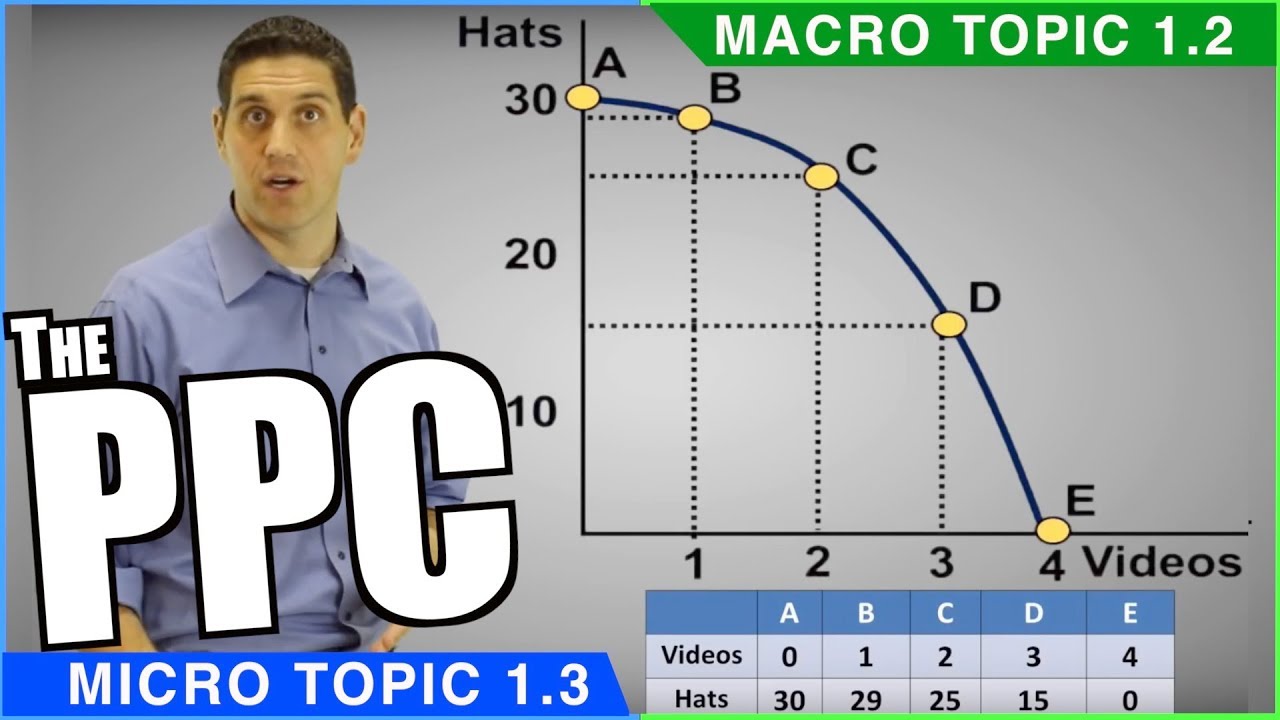
- 📈 The production possibilities curve (PPC) illustrates the maximum potential output of two goods, highlighting the trade-offs and opportunity costs inherent in resource allocation.
- 🔄 Economic growth can shift the PPC outward, reflecting an increase in production capabilities due to more factors of production, while a contraction can shift it inward.
- 🔺 The PPC can have different shapes, indicating constant, increasing, or decreasing opportunity costs, with the concave shape being more realistic in many cases.
- 🌐 Comparative advantage is the key to understanding how trade benefits all parties involved, as it dictates that each party should specialize in producing what they can produce most efficiently.
- 🔄 Specialization leads to increased productivity and is the basis for trade, where each party focuses on producing what they have a comparative advantage in and then trades for other goods.
- 📉 The law of demand states that as the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa, reflecting consumers' preference for lower prices.
- 📈 The law of supply indicates a positive relationship between price and quantity supplied, where an increase in price leads to an increase in the willingness to sell.
- 💡 Market equilibrium is the point where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded, and any disequilibrium due to surplus or shortage provides signals for price adjustments.
Q & A
What is scarcity in economics?
-Scarcity is the fundamental problem of economics, occurring whenever there is a greater quantity desired than available, leading to the necessity of making choices.
What does the production possibilities curve (PPC) show?
-The PPC shows what it is possible for an economy to produce, highlighting scarcity, trade-offs, and opportunity costs.
What is opportunity cost?
-Opportunity cost is the true cost of something, defined as what you give up to get it. It represents the value of the best alternative foregone.
What are the factors of production?
-The factors of production are land (natural resources), labor (effort and skill of workers), capital (physical and human), entrepreneurship (innovation and risk-taking), and established knowledge.
What is the law of demand?
-The law of demand states that price and quantity demanded are inversely related, meaning as the price rises, quantity demanded falls, and as the price falls, quantity demanded rises.
What causes a shift in the demand curve?
-A shift in the demand curve can be caused by changes in tastes and preferences, the price of related goods, income, the number of buyers, and expected future prices.
What is the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage?
-Absolute advantage is when a person or country can produce more of a good or service with the same resources, while comparative advantage is when a person or country can produce something at a lower opportunity cost.
What is the law of supply?
-The law of supply states that as the price increases, the quantity supplied increases, and as the price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases, indicating a positive relationship between price and quantity supplied.
What factors can shift the supply curve?
-Factors that can shift the supply curve include changes in technology, input costs, government policies (taxes and subsidies), expectations about future prices, the price of related goods, and the number of sellers.
What happens when both supply and demand increase simultaneously?
-When both supply and demand increase simultaneously, the quantity will definitely increase, but the effect on price is uncertain, depending on the relative magnitudes of the shifts in supply and demand.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Macro 1.2 - Production Possibilities Curve - NEW!

Production Possibilities Curve
Production Possibilities Curve Review

Production Possibilities Curve- Macro Topic 1.2 (Micro Topic 1.3)
Production Possibilities Curve as a model of a country's economy | AP Macroeconomics | Khan Academy

Microeconomics Unit 1 COMPLETE Summary - Economic Thinking
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)