Production Possibilities Curve as a model of a country's economy | AP Macroeconomics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the instructor explains the production possibilities curve (PPC) using the fictional country Utenslandia, which produces forks and spoons. The PPC illustrates the trade-offs in production efficiency, showing how resources can be optimally utilized. Points on the curve indicate efficient production, while those inside denote inefficiency, and those beyond are unattainable without additional resources. The discussion covers how economic growth can shift the PPC outward due to increased resources, while war can cause contraction, highlighting the impact of external factors on a nation's production capabilities.
Takeaways
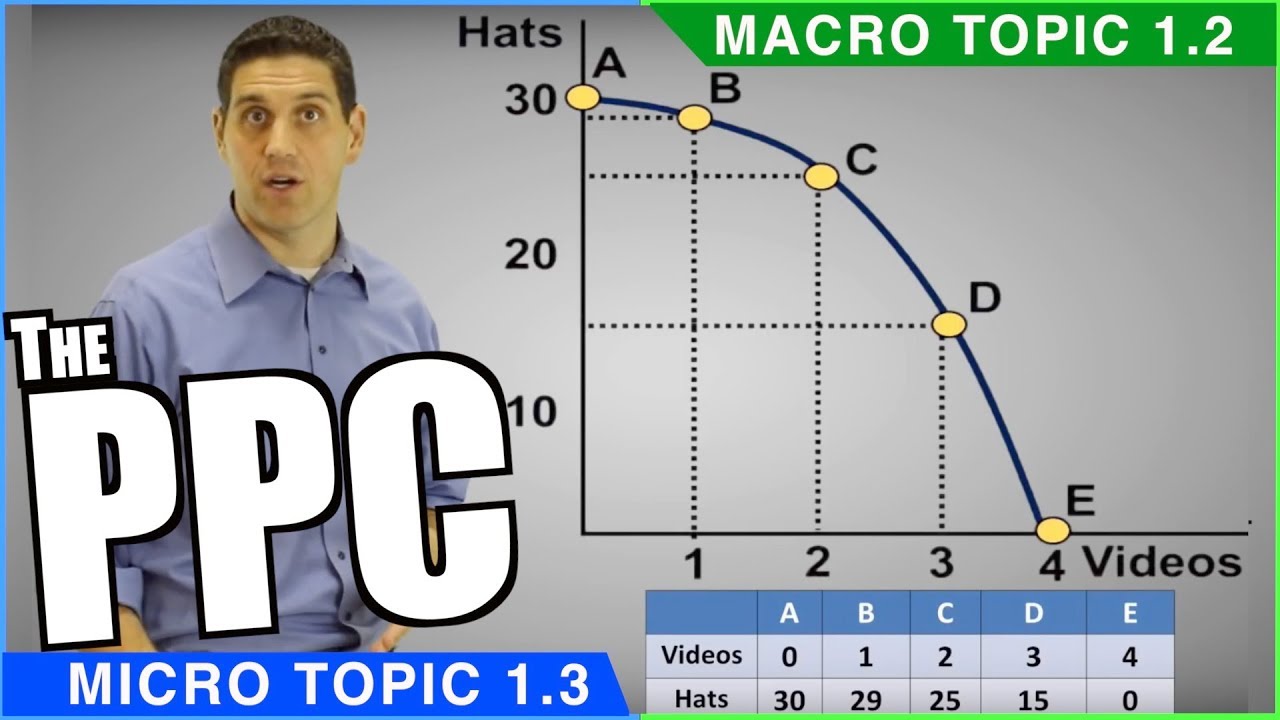
- 😀 The production possibilities curve (PPC) illustrates the maximum combinations of two goods a country can produce with its resources.
- 📈 Points on the PPC indicate efficient production, where resources are fully utilized.
- 📉 Points within the PPC represent inefficient production, where not all resources are being used effectively.
- 🚫 Points beyond the PPC are unattainable with the current resource level unless additional inputs are acquired.
- 🌱 Economic growth can shift the PPC outward, allowing for greater production capacity due to increased resources or improved technology.
- 🔄 Economic contraction shifts the PPC inward, indicating a reduction in production capacity, often due to loss of resources.
- ⚖️ The PPC demonstrates the trade-off between producing different goods, highlighting opportunity costs.
- 🏗️ Factors influencing shifts in the PPC include increases in land, labor, capital, or technological advancements.
- 💔 Events like wars can damage resources, leading to inefficiencies and a contracted PPC.
- 📊 The PPC serves as a valuable model for understanding resource allocation and economic efficiency.
Q & A
What is the main concept introduced in the transcript regarding Utenslandia?
-The main concept is the production possibilities curve (PPC), which illustrates the trade-off between producing two goods, in this case, forks and spoons, based on limited resources.
How does the production possibilities curve represent efficiency?
-Points on the curve indicate efficient production, where all resources are utilized optimally. Points inside the curve reflect inefficiency, while points outside are unattainable without additional resources.
What happens to the production possibilities curve during a recession?
-During a recession, if Utenslandia is unable to use its resources efficiently, its production point moves inside the curve, indicating a reduction in production efficiency.
What does it mean for a point to be outside the production possibilities curve?
-A point outside the curve represents a production level that cannot be achieved with the current resources. To reach that point, Utenslandia would need more land, labor, or capital.
What factors can cause the production possibilities curve to shift outward?
-The curve can shift outward due to increased land, more factories (capital), a larger labor force, or advancements in technology, allowing for greater production capacity.
What is the impact of war on Utenslandia's production capabilities?
-War can destroy resources, reduce labor, and damage infrastructure, causing the production possibilities curve to shift inward, indicating a decrease in production capacity.
How does the concept of opportunity cost relate to the production possibilities curve?
-Opportunity cost is illustrated by the trade-offs between producing forks and spoons, indicating how many forks must be sacrificed to produce additional spoons, highlighting scarcity.
What are some potential drivers of economic growth mentioned in the transcript?
-Potential drivers of economic growth include increased land, additional capital investment, an expanded labor force, better technology, and an entrepreneurial spirit.
Why is it important for a country to understand its production possibilities curve?
-Understanding the PPC helps a country recognize its production limits, make informed resource allocation decisions, and strategize for efficiency and growth.
What does the area inside the production possibilities curve signify?
-The area inside the curve signifies inefficiency, where the country is not fully utilizing its resources, resulting in lower production than possible.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Production Possibilities Curve Review

Macro 1.2 - Production Possibilities Curve - NEW!

Production Possibilities Curve

Business cycles and the production possibilities curve | APⓇ Macroeconomics | Khan Academy

INTRODUCTION TO MICROECONOMICS CLASS 11 ECONOMICS CHAPTER 1 ONE SHOT 2025-2026

Unit 1 Macro Review - Basic Economic Concepts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)