What Alcohol Does to Your Brain | Dr. Andrew Huberman
Summary
TLDRAlcohol's structure allows it to be both water- and fat-soluble, enabling it to pass into all cells and tissues in the body, leading to direct cellular damage. The primary type of alcohol consumed, ethanol, is toxic and converted into acetaldehyde, a poison that kills cells, and then into acetate, a usable fuel. This metabolic process is costly and provides no nutritive value, classifying alcohol as empty calories. Alcohol also disrupts neural circuits, affecting the prefrontal cortex's top-down inhibition, leading to increased impulsivity and loud behavior. Regular consumption can alter the brain's circuits, reinforcing habitual and impulsive behavior.
Takeaways
- 💧 Alcohol is both water-soluble and fat-soluble, allowing it to penetrate all body cells and tissues easily.
- 🚨 Only ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is safe for human consumption, but it's still toxic and causes cell stress and damage.
- 🔄 Ethanol is metabolized in the body through conversion to acetaldehyde and then to acetate, involving NAD in the process.
- ☠️ Acetaldehyde, a byproduct of ethanol metabolism, is highly toxic and can indiscriminately damage and kill cells.
- 🔬 The conversion of ethanol to acetaldehyde and then acetate is crucial for detoxification but is also a source of metabolic cost.
- 🍷 The inebriating effect of alcohol is due to acetaldehyde, disrupting neural circuits and leading to drunkenness.
- 🧠 Alcohol's water and fat solubility allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier and affect various brain areas.
- 🗣️ Consumption of alcohol can suppress the prefrontal cortex, reducing inhibition and leading to impulsive behavior and louder speech.
- 💃 Long-term alcohol consumption can alter brain circuits related to habitual and impulsive behavior.
- 🔒 Alcohol disrupts the neural networks involved in memory formation, contributing to blackouts and memory loss.
Q & A
Why is alcohol considered both water-soluble and fat-soluble?
-Alcohol's structure allows it to dissolve in both water and fats, enabling it to pass into all the cells and tissues of the body easily.
What are the three main types of alcohol, and which one is safe for human consumption?
-The three main types of alcohol are isopropyl, methyl, and ethyl alcohol. Ethyl alcohol, also known as ethanol, is the only type fit for human consumption.
What is the toxic effect of ethanol on the body?
-Ethanol is toxic to the body and causes substantial stress and damage to cells. It needs to be converted into other substances within the body due to its toxicity.
What role does NAD play in the metabolism of ethanol?
-NAD, a molecule present in all cells, is involved in the biochemical pathways that convert ethanol into acetaldehyde and then into acetate, which the body can use as fuel.
Why is acetaldehyde considered particularly harmful?
-Acetaldehyde is poison and is more harmful than ethanol. It damages and kills cells indiscriminately.
How does alcohol affect the prefrontal cortex and impulsive behavior?
-Alcohol suppresses the activity of neurons in the prefrontal cortex, leading to a decrease in top-down inhibition and an increase in impulsive behavior.
What is the impact of alcohol on memory formation and storage?
-Alcohol has a strong effect on suppressing the neural networks involved in memory formation and storage, which is why people often forget events from a night of drinking.
How does alcohol consumption affect social behavior at parties?
-Alcohol consumption can lead to louder voices, increased gesticulation, and spontaneous actions like dancing due to the release of impulsive behavior from prefrontal cortex suppression.
What is the term used to describe the increase in habitual and impulsive behavior due to frequent alcohol consumption?
-The increase in habitual and impulsive behavior due to frequent alcohol consumption is a result of changes in the neural circuits that underlie these behaviors.
How does the blood-brain barrier interact with alcohol?
-Although the blood-brain barrier prevents most substances from entering the brain, alcohol, being water- and fat-soluble, easily crosses this barrier and enters the brain's environment.
What are the major cell types in the brain that alcohol affects?
-Alcohol affects neurons, or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are found between nerve cells in the brain.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How do vitamins work? - Ginnie Trinh Nguyen

How The Oxygen You Breathe Gets Delivered to the Cells of Your Body

How cancer develops | Bupa Health
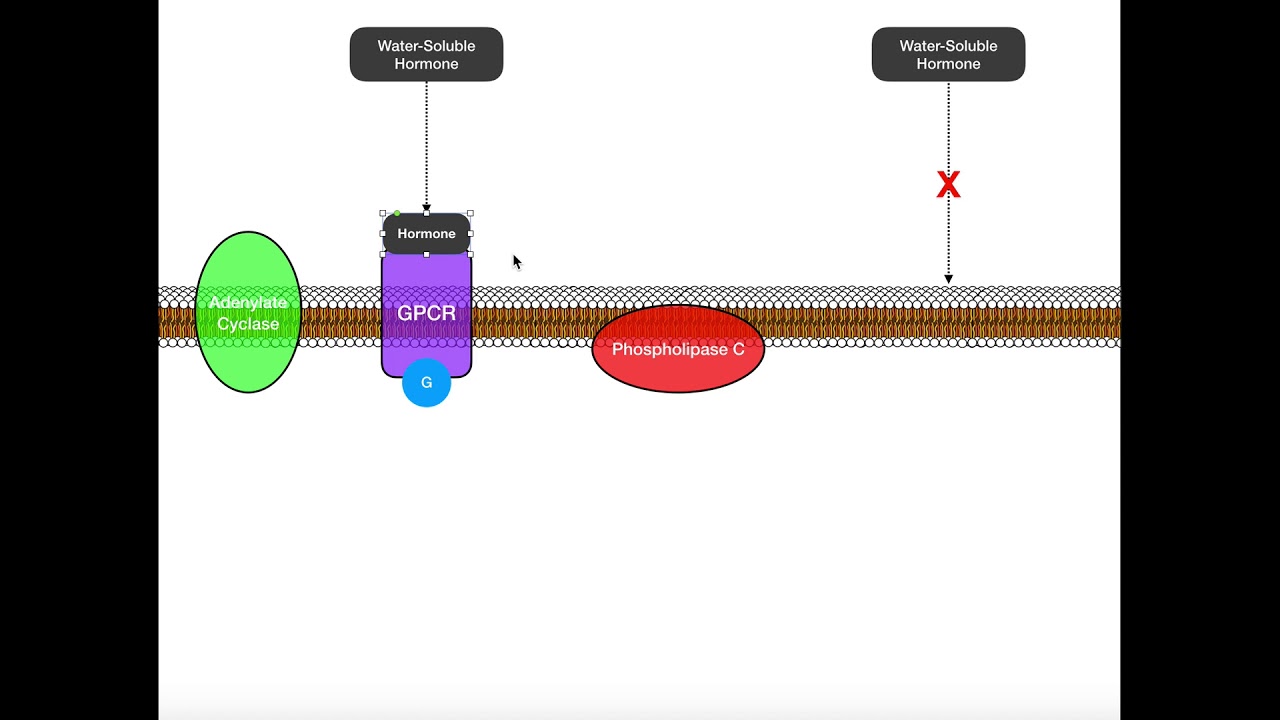
Overview & Comparison of Water- vs Lipid-Soluble Hormones

JARINGAN PADA HEWAN DAN TUMBUHAN | SISTEM ORGANISASI KEHIDUPAN

What Are Micronutrients And Macronutrients ? | VisitJoy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)