Fisika SMA - Gerak Lurus (2) - Kelajuan dan Kecepatan Sesaat, Kelajuan dan Kecepatan Rata-rata (I)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces the concepts of instantaneous velocity and speed, average velocity and speed, and their differences. It explains that speed is a scalar quantity, always positive, and represents the rate of motion, while velocity is a vector, providing both magnitude and direction. The script uses examples, such as a car moving east at a constant speed, to illustrate these concepts. It also covers how to calculate average velocity and speed for objects with varying speeds over time, emphasizing the importance of understanding both direction and magnitude in motion analysis.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is an educational tutorial focused on the concepts of instantaneous velocity and speed, as well as average velocity and speed in the context of straight-line motion.
- 🔍 Speed is defined as a scalar quantity that represents how fast an object is moving, without regard to direction, and is always positive.
- 🚀 Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that includes both the speed of an object and its direction, allowing for positive or negative values indicating direction.
- 🌐 The relationship between speed and distance is expressed by the formula speed = distance/time, while velocity is described by the formula velocity = displacement/time.
- 📐 For objects moving at a constant speed, the speed and velocity are numerically the same, but velocity also includes directional information.
- 📈 The script discusses how to calculate the average velocity and speed for objects with varying instantaneous velocities, emphasizing the difference between the two when direction changes.
- 📊 Instantaneous velocity is equal to the magnitude of instantaneous speed, but average velocity and speed can differ, especially when considering the direction of motion.
- 📝 The script provides examples and illustrations to explain the concepts, including a scenario with a car moving east at a constant speed and a particle with changing velocities and directions.
- 🧩 The tutorial includes practical examples, such as a race where participants run a route with varying directions and distances, to demonstrate the calculation of average velocity and speed.
- 🔢 The importance of understanding the difference between average velocity (which can be zero if the displacement is zero) and average speed (which is never zero as it depends on the total distance traveled) is highlighted.
- 🏃♂️ The video concludes with a problem-solving approach to calculate the average velocity and speed for a group of children running around a circular park, and for Doni running on a circular jogging track.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the concept of instantaneous velocity and speed, average velocity and speed, and the difference between them in the context of straight-line motion.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
-Speed is a scalar quantity that represents the magnitude of how fast an object is moving, and it is always positive. Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that includes both the magnitude and the direction of the object's motion, and it can be positive or negative depending on the direction of movement.
How is speed related to distance and time?
-Speed is calculated as the distance traveled by an object divided by the time taken to travel that distance, expressed as the formula: Speed = Distance / Time.
How is velocity related to displacement and time?
-Velocity is calculated as the displacement (change in position) of an object divided by the time taken, which can be represented by the formula: Velocity = Displacement / Time.
What is the significance of the direction in velocity?
-The direction in velocity is significant because it indicates the direction of the object's motion. A positive value indicates motion in one direction (e.g., east), while a negative value indicates motion in the opposite direction (e.g., west).
How can you calculate the average speed of an object that moves with a constant speed?
-For an object moving with a constant speed, the average speed is the same as the instantaneous speed, which is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken.
What is the formula to calculate the average velocity of an object with varying speeds?
-The average velocity of an object with varying speeds is calculated by summing all the instantaneous velocities and dividing by the number of data points, or by using the formula: Average Velocity = Total Displacement / Total Time.
How can you determine the total displacement of an object that changes its speed at different times?
-The total displacement can be determined by adding up all the individual displacements at different times, considering the direction of each movement.
What is the relationship between the total distance traveled and the total displacement?
-The total distance traveled is the sum of all the distances covered by the object in each segment of its journey, regardless of direction. The total displacement, however, is the straight-line distance from the starting point to the final position, considering the direction of movement.
Can the average speed and average velocity of an object be different?
-Yes, the average speed and average velocity of an object can be different. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the time, while average velocity is the total displacement divided by the time. They can differ if the object changes direction during its motion.
What is an example of calculating the average velocity and speed for an object moving in a straight line with constant speed?
-If a car is moving at a constant speed of 72 km/h towards the east for a certain period, its average speed is 72 km/h. Its average velocity would also be 72 km/h in magnitude but would include the direction towards the east.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cinemática 05: Velocidade Média, Velocidade Escalar Média, Velocidade Instantânea

SPH3U 1.04:Speed and Velocity

FISIKA KELAS X: GERAK LURUS (PART 1) Jarak, Perpindahan, Kelajuan, Kecepatan, Percepatan
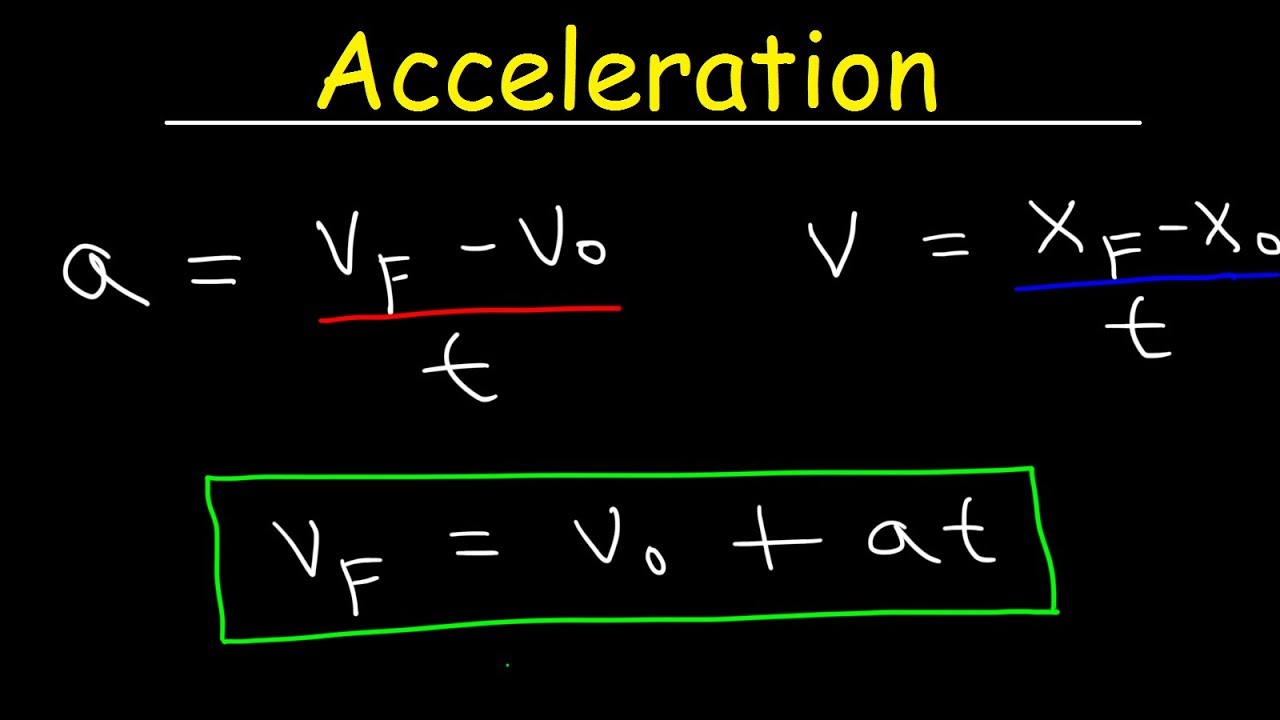
Physics - Acceleration & Velocity - One Dimensional Motion
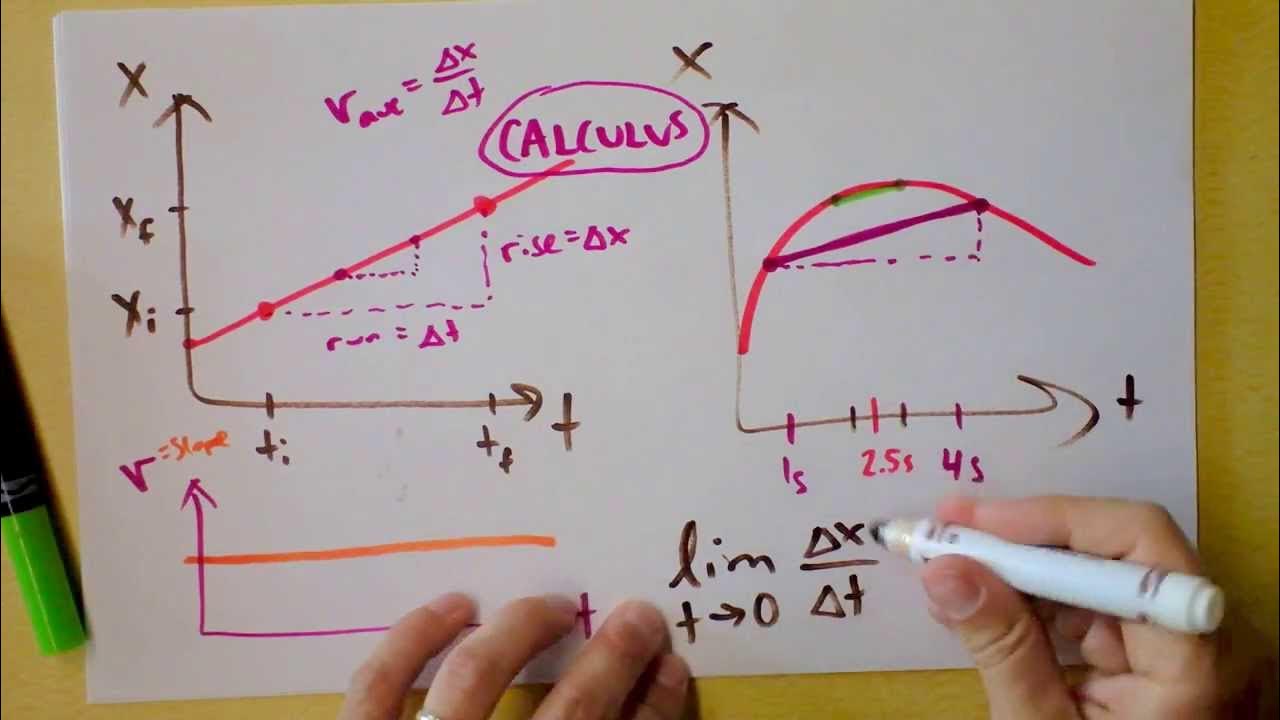
Instantaneous Velocity, Acceleration, Jerk, Slopes, Graphs vs. Time | Doc Physics

Distance displacement speed velocity acceleration for IGCSE Physics, GCE O level Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)