Converting Units
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script focuses on converting units of length, area, and volume within the metric system. It introduces conversion factors between kilometers, meters, centimeters, and millimeters, and demonstrates how to apply them in both directions. The script also covers compound measures such as speed, density, and pressure, explaining their formulas and providing examples to calculate each. The goal is to equip viewers with the ability to solve problems involving these measurements, enhancing their understanding of metric conversions and compound measures.
Takeaways
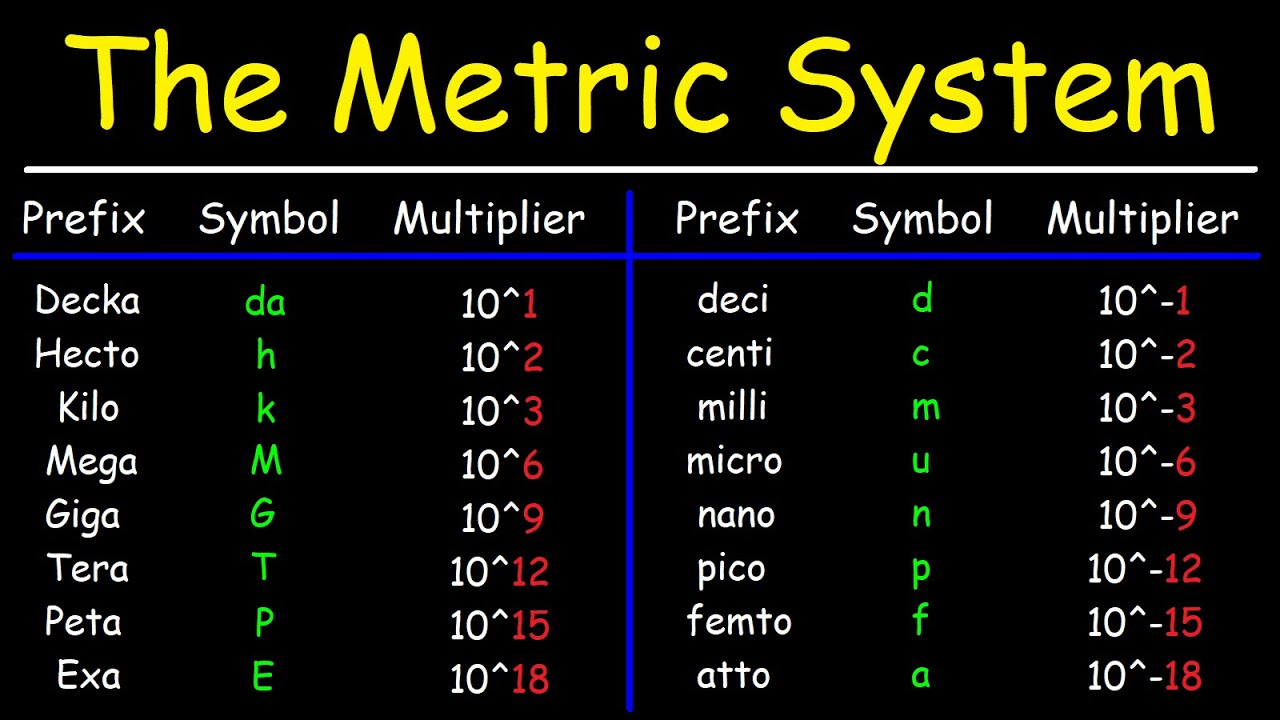
- 📏 Converting units of length involves understanding the metric system and using conversion factors such as multiplying by 1000 to convert kilometers to meters, by 100 to convert meters to centimeters, and by 10 to convert centimeters to millimeters.
- 🔄 To convert from smaller to larger units of length, divide by the conversion factor, for example, divide by 1000 to convert meters to kilometers, by 100 to convert centimeters to meters, and by 10 to convert millimeters to centimeters.
- 📐 For converting units of area, use the conversion factors between centimeters and meters squared, knowing that 1 cm equals 0.01 m and thus the area conversion involves squaring these conversion factors.
- 📦 When converting units of volume, such as cubic centimeters to cubic millimeters, multiply the given volume by the cube of the conversion factor between the units, in this case, 1000 (since 1 cm = 10 mm).
- 🔢 Compound measures are derived from two other measures, such as speed, density, and pressure, and require knowledge of the values and units of the two constituent measures.
- 🚗 Speed is a compound measure calculated by dividing a unit of distance by a unit of time, with common units being meters per second (m/s) and kilometers per hour (km/h).
- 📊 Density is a measure of mass per unit volume, calculated by dividing mass by volume, with units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).
- ⏳ Pressure is defined as force per unit area, with units like Newtons per square meter (N/m²) or Pascals (Pa), and is calculated using the formula pressure = force / area.
- 🔄 The script provides examples to illustrate the calculation of compound measures, such as calculating the average speed of a car, the density of a platinum bar, and the pressure exerted on a surface.
- 📘 The importance of using the correct formula and units when performing conversions and calculations is emphasized throughout the script to ensure accurate results.
Q & A
What is the main learning objective discussed in the script?
-The main learning objective is to be able to convert between metric units of length, area, and volume, as well as to understand and solve problems involving compound measures such as speed, density, and pressure.
What are the basic units of length mentioned in the script for conversion?
-The basic units of length mentioned are kilometers, meters, centimeters, and millimeters.
How do you convert kilometers to meters?
-To convert kilometers to meters, you multiply by 1,000.
What is the conversion factor from meters to centimeters?
-The conversion factor from meters to centimeters is 100, meaning you multiply by 100 to convert meters to centimeters.
How do you convert centimeters to millimeters?
-To convert centimeters to millimeters, you multiply by 10.
What is the conversion process when moving from smaller to larger units of length?
-When converting from smaller to larger units of length, you divide by the conversion factor: divide by 10 to convert millimeters to centimeters, by 100 to convert centimeters to meters, and by 1,000 to convert meters to kilometers.
Can you provide an example of converting meters to kilometers?
-An example given in the script is converting 33 meters to kilometers, which involves dividing 33 by 1,000, resulting in 0.033 kilometers.
What is the importance of a diagram when converting units of area?
-A diagram is useful for visualizing the conversion process, especially when changing the dimensions of a rectangle from centimeters to meters, to understand how area calculations are affected by unit conversion.
How do you convert cubic centimeters to cubic millimeters?
-To convert cubic centimeters to cubic millimeters, you multiply by 1,000 because 1 cm equals 10 mm, and volume conversion requires cubing the conversion factor (10^3).
What is a compound measure and why are they important in the script?
-A compound measure is a measure derived from two other measures, such as speed (distance over time), density (mass over volume), and pressure (force over area). They are important because they help in solving various physics and everyday problems.
Can you explain how to calculate the average speed given the distance and time?
-The average speed is calculated using the formula speed = distance / time. For example, if a car travels 100 kilometers in 2 hours, the average speed is 50 kilometers per hour.
How is the density of an object calculated?
-Density is calculated using the formula density = mass / volume. For instance, if a platinum bar has a mass of 840 grams and a volume of 40 cm³, the density is 840 / 40 = 21 grams per cm³.
What is the formula to calculate pressure and how is it applied in an example?
-Pressure is calculated using the formula pressure = force / area. In the example given, if a force of 820 Newtons is exerted on an area of 40 m², the pressure is 820 / 40 = 20.5 Newtons per m² or 20.5 pascals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

A beginners guide to the Metric System

High School Physics - Metric System

Modul Fisika Dimensi Untuk SMA (Murid)
The Metric System - Basic Introduction

2022 | Resumo da Aula | 1ª Série | Matemática | Aula 2 - Sistema Internacional de Unidades (SI) II

AP Chem Video 1.2 Measurement, metric system, and conversions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)