Gastrulação: Ectoderma, Mesoderma e Endoderma - Terceira Semana do Desenvolvimento (Embriologia)
Summary
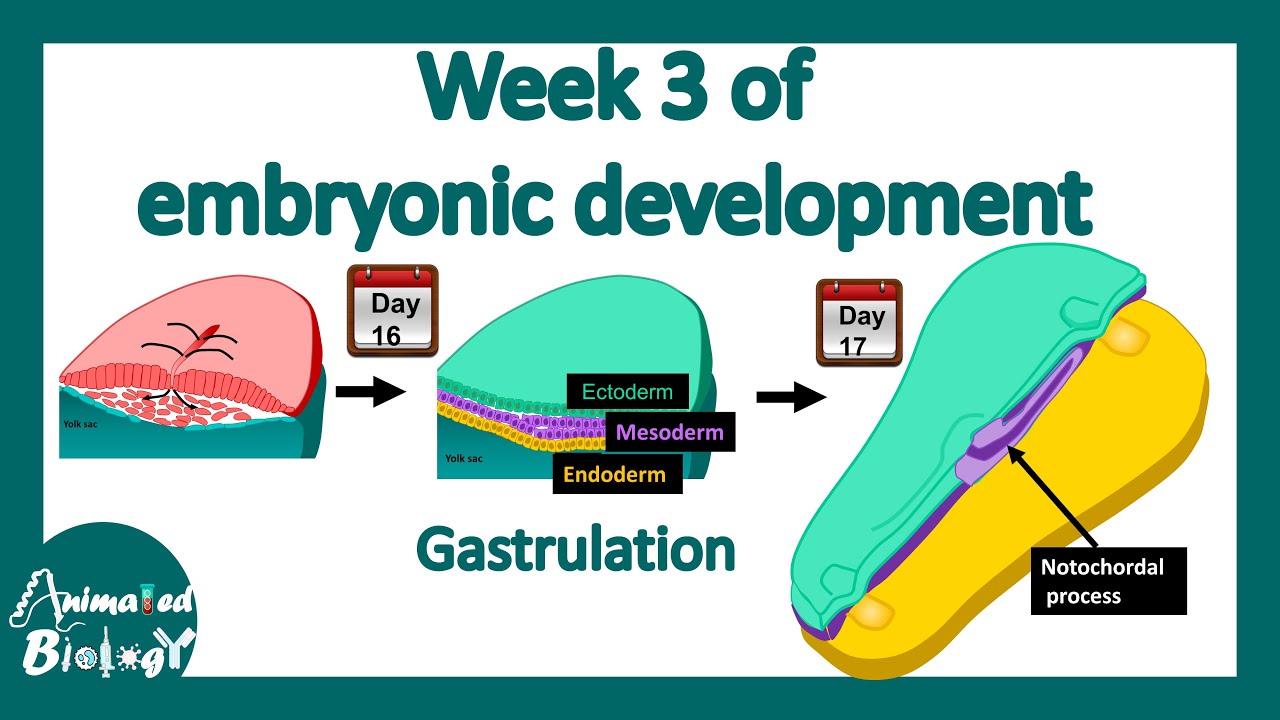
TLDRThis educational video script discusses the third week of embryonic development, focusing on gastrulation. It explains how the bilaminar embryonic disc transforms into a trilaminar disc, establishing the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. The gastrulation process is described, starting with the formation of the primitive streak from epiblast cells that migrate and invaginate to form the endoderm and mesoderm, with the remaining epiblast becoming the ectoderm. The script includes a visual aid to illustrate the process, aiming to clarify this crucial stage in embryonic development.
Takeaways
- 📅 The script discusses the third week of embryonic development, focusing on key events that occur during this period.
- 🌱 Gastrulation is introduced as the process that establishes the three germ layers in the embryo: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- 🔄 The gastrulation process begins with the formation of the primitive streak on the surface of the epiblast, where cells proliferate and migrate towards the embryo's median plane.
- 📍 The primitive streak grows from the caudal region towards the cephalic region, stopping at the primitive node.
- 🔍 Cells from the epiblast invaginate, or sink inwards, towards the hypoblast, which will eventually be replaced by the endoderm.
- 🔄 Some cells that migrate to the hypoblast replace it, forming the endoderm, while others concentrate in the middle to form a new layer called the mesoderm.
- 🌟 The remaining epiblast becomes the ectoderm, completing the formation of the trilaminar embryonic disc with ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm layers.
- 🧬 These germ layers are crucial as they give rise to all tissues and organs of the embryo.
- 📹 The script includes a visual demonstration of the gastrulation process, showing cells invaginating and forming the different germ layers.
- 🔑 The video script ends with a golden key takeaway, emphasizing the importance of understanding the gastrulation process in embryonic development.
- 👋 The presenter invites viewers to join the next video lesson, indicating a series of educational content on embryonic development.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video lesson?
-The main topic of the video lesson is the third week of embryonic development, specifically focusing on the process of gastrulation.
What significant transformation occurs during the third week of embryonic development?
-During the third week, the bilaminar embryonic disc transforms into a trilaminar disc, forming the three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
What is gastrulation?
-Gastrulation is the process that establishes the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) in the embryo, which will give rise to all tissues and organs.
What are the two membranes that appear in the epiblast at the end of the second week?
-The two membranes are the precordal plate, indicating the cephalic (head) region, and the cloacal membrane, indicating the caudal (tail) region.
How does the primitive streak form?
-The primitive streak forms when cells from the epiblast proliferate and migrate toward the midline, creating a visible line on the surface of the epiblast.
In which direction does the primitive streak grow?
-The primitive streak grows from the caudal (tail) region towards the cephalic (head) region.
What happens to the cells of the epiblast during gastrulation?
-During gastrulation, epiblast cells proliferate, migrate to the primitive streak, invaginate, and move toward the hypoblast, forming new germ layers.
What is the primitive groove?
-The primitive groove is an indentation formed by the invagination of epiblast cells at the primitive streak.
What happens to the hypoblast during gastrulation?
-During gastrulation, some invaginating epiblast cells displace the hypoblast cells, forming the endoderm.
What are the three germ layers formed by the end of gastrulation?
-The three germ layers formed are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
What role does the epiblast play in gastrulation?
-The epiblast plays a crucial role by contributing cells that form the primitive streak and subsequently differentiate into the three germ layers.
How can one visualize the process of gastrulation?
-The process of gastrulation can be visualized through diagrams and animations that show the movement and differentiation of cells within the embryo.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sistema Cardiovascular Primitivo e Alantoide - Terceira Semana do Desenvolvimento (Embriologia)
Week 3 of embryonic development | Gastrulation | Neural induction

Gastrulation - Embryology

Development of the Face and Palate

Embryology: from Fertilization to Gastrulation, Animation

Fase embrionik pertumbuhan dan perkembangan pada hewan - materi biologi sma kelas 12
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)