How does an Induction Motor work?
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the revolutionary impact of Nikola Tesla's induction motor, which still dominates global electric power consumption. It explains the motor's self-starting nature, the generation of a rotating magnetic field by a three-phase AC input in the stator, and the electromagnetic induction in the rotor that powers it. The script highlights the motor's advantages, including its simplicity, ease of speed control through frequency adjustment, and its dual role as a generator. This enduring technology is celebrated for its efficiency and adaptability in various applications, from industrial machinery to electric vehicles.
Takeaways
- ⚡ The induction motor, invented by Nikola Tesla, is over a hundred years old and remains the most common motor type, accounting for about 50% of global electric power consumption.
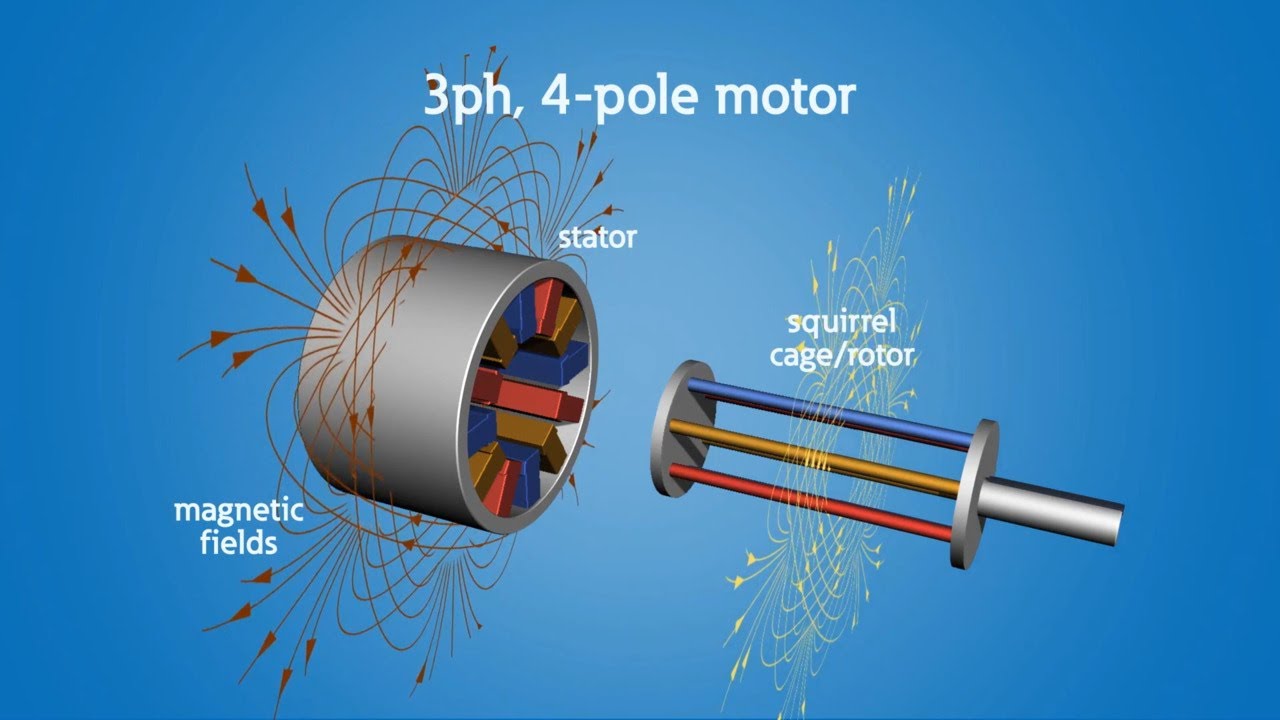
- 🔄 An induction motor consists of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is a three-coil winding connected to a three-phase AC power source.
- 🧲 The stator produces a rotating magnetic field (RMF) when a three-phase current passes through it. This RMF is what causes the rotor to turn.
- 🌪️ The rotational speed of the magnetic field is known as the synchronous speed. The rotor rotates at a speed slightly less than this, a phenomenon known as slip.
- 💡 The induction motor operates on electromagnetic induction, where electricity is induced in the rotor without a direct electrical connection.
- 🚀 Induction motors are inherently self-starting and do not require permanent magnets, brushes, commutator rings, or position sensors, unlike other electric motors.
- ⚙️ The speed of an induction motor can be easily controlled by adjusting the input power frequency using a variable frequency drive, making them suitable for applications like elevators, cranes, and electric cars.
- 🔄 An induction motor can also function as a generator when the rotor is moved by a prime mover, provided the RMF speed is less than the rotor speed.
- 📉 Induction motors minimize eddy current losses by using insulated iron core laminations within the rotor.
- 🎓 Induction motors continue to be popular in both domestic and industrial settings due to their simplicity, reliability, and efficiency.
Q & A
Who is credited with the invention of the induction motor?
-Nikola Tesla is credited with the invention of the induction motor.
What percentage of global electric power consumption is attributed to induction motors?
-Approximately 50% of global electric power consumption is due to induction motors.
What are the two main components of an induction motor?
-The two main components of an induction motor are the stator and the rotor.
What is the function of the stator in an induction motor?
-The stator in an induction motor is a three-coil winding that receives a three-phase AC power input and produces a rotating magnetic field.
How is the rotating magnetic field generated in an induction motor?
-The rotating magnetic field is generated by the interaction of the three-phase current with the stator's winding, which is arranged in a specific configuration and connected 120º apart.
What is the term used to describe the speed of the rotating magnetic field in an induction motor?
-The rotational speed of the magnetic field is known as the synchronous speed.
Why is the induction motor called an 'induction' motor?
-The induction motor is called so because electricity is induced on the rotor through electromagnetic induction rather than direct connection.
What is the purpose of the squirrel cage design in the rotor of an induction motor?
-The squirrel cage design in the rotor facilitates the induction of current in the bars, which are shorted by end rings, causing the rotor to rotate.
What is the term used to describe the difference between the synchronous and rotor speeds in an induction motor?
-The difference between the synchronous and rotor speeds is known as slip.
How can the speed of an induction motor be controlled?
-The speed of an induction motor can be easily controlled by varying the input power frequency, using a variable frequency drive.
What property of induction motors makes them suitable for applications like elevators, cranes, and electric cars?
-Induction motors are suitable for these applications because their speed can be easily controlled, and they have a high-speed range, allowing electric cars to run with a single speed transmission.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Induction Motor designed by Nikola Tesla | Induction Motor | nikola tesla inventions

Single Phase Induction Motor, How it works ?

How Three-Phase Induction Motors Work in Telugu | Understanding Three-Phase Induction Motors.

How a Tesla Coil Works ⚡ How to Make a Tesla Coil ⚡ Nikola Tesla

【全ては光】超天才ニコラテスラ 長年非公開だった 奇跡のインタビュー(ノーカット完全版) この世の真理
Motors 101
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)