Movimentos vegetais
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script by Tariq explores the fascinating world of plant movements, distinguishing between tropisms and nastiesm, which are directional growths in response to external stimuli, and tactisms, which involve the movement of organelles, cells, or unicellular organisms towards or away from external agents. Examples include plants growing around objects, water, or sunlight, and the closing of night-blooming flowers in response to light. The script also discusses how certain plants and bacteria move in response to chemicals, oxygen, and light, highlighting the surprising mobility of plants.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Plants move more than you might think, with movements classified into growth movements and locomotion movements.
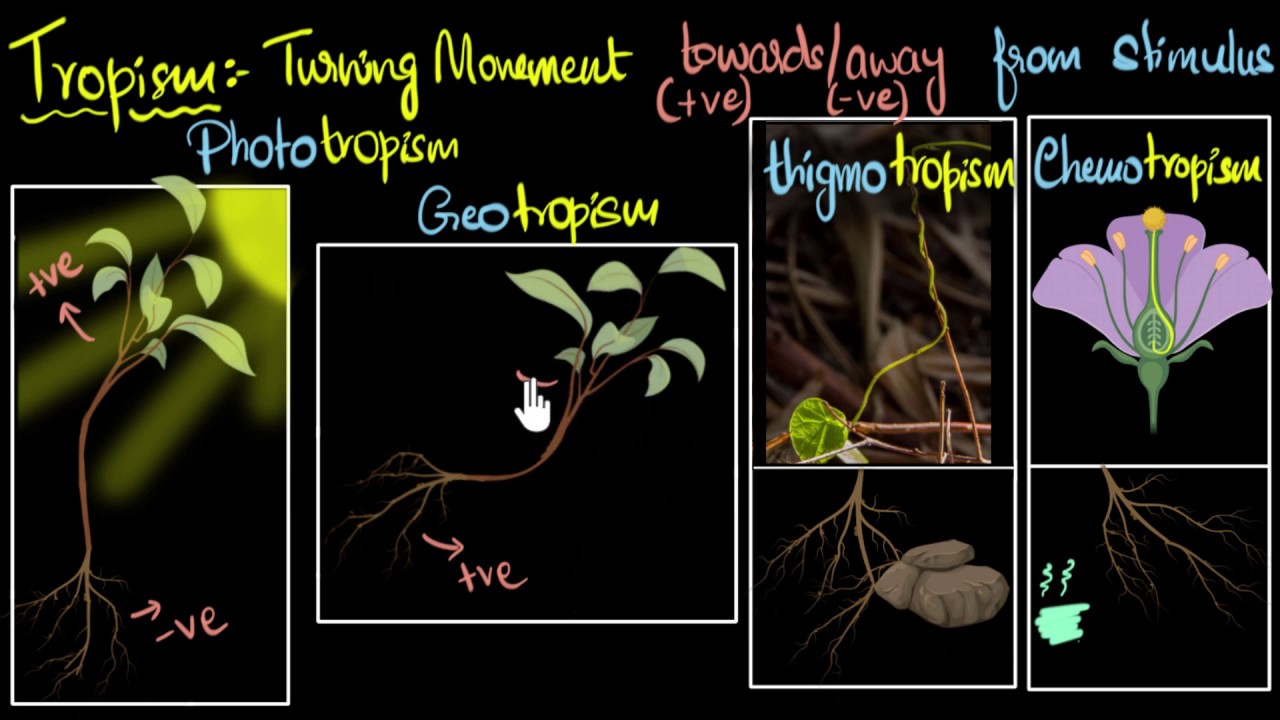
- 📏 Tropisms are directional growths in response to an external stimulus, which can be positive (towards the stimulus) or negative (away from it).
- 🌿 Thigmotropism is the growth around a solid object, such as in climbing plants or those with tendrils for support.
- 💧 Hydrotropism is the movement towards water, while geotropism is the movement towards the soil.
- ☀️ Heliotropism is the tracking of sunlight, as seen in sunflowers following the sun's rays.
- 🌗 Nasties are movements in response to external stimuli but differ from tropisms as they do not involve directional growth towards the stimulus.
- 🌜 Nyctinasty is the sleep movement of plants, caused by changes in the turgor of motor cells in the pulvinus at the base of the petiole.
- 🔍 Tactisms are movements of displacement of an organelle, cell, or unicellular organism in relation to an external agent, which can be positive or negative.
- 🌼 Chemotactism is the movement in relation to a chemical substance, such as pollen tubes growing towards the female organ in fertilization.
- 💨 Aerotaxis is the movement based on the chemical element oxygen, like bacteria moving towards oxygen.
- 🌞 Phototaxis is the movement in relation to sunlight, with chloroplasts moving towards or away from the cell wall in response to light intensity.
Q & A
What are the two main types of plant movements mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of plant movements mentioned are movements of curvature or growth, and movements of locomotion or displacement.
What is tropism and how does it relate to plant growth?
-Tropism is the directional growth of a plant in response to an external stimulus. It can be positive, meaning the plant grows towards the stimulus, or negative, meaning it grows away from the stimulus.
Can you give an example of thigmotropism?
-Thigmotropism occurs when a plant comes into contact with a solid object and starts to grow around it, such as in climbing plants or those with tendrils that coil for support.
What is the difference between hydrotropic and geotropic movements in plants?
-Hydrotropic movement is oriented towards water, while geotropic movement is directed towards the soil.
How does heliotropism affect plant growth?
-Heliotropism is the movement known for tracking sunlight. It causes plants, like sunflowers, to follow the sun.
What are nastic movements and how do they differ from tropisms?
-Nastic movements are responses to external stimuli but differ from tropisms in that the direction of the stimulus does not influence the plant's movement. Examples include nyctinasty and seismonastic movements.
What is nyctinasty and how does it relate to plant movement?
-Nyctinasty is the movement known as 'sleeping' of plants, which occurs due to changes in the turgor of motor cells in the pulvinus at the base of the petiole of a leaf.
What is tactism and how does it relate to plant locomotion?
-Tactism is a type of locomotion oriented towards the displacement of an organelle, cell, or unicellular organism in relation to an external agent. It can be positive or negative depending on the direction relative to the agent.
Can you provide an example of chemotactism in plants?
-Chemotactism is the movement of displacement in relation to a chemical substance. An example is when pollen from a flower's male organ comes into contact with the female organ of another flower, causing the sperm to grow towards the female organ.
What is aerotaxis and how does it relate to plant movement?
-Aerotaxis is the movement based on the chemical element oxygen. For instance, some bacteria move towards oxygen.
How do chloroplasts in plants respond to light through phototaxis?
-Chloroplasts move from the interior of the cell to the part closest to the cell wall in response to sunlight. When the light is too strong, they move away and back into the cell's interior.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Tropism (Types, positive & negative) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy

SISTEM GERAK PADA TUMBUHAN IPA KELAS 8 || TERLENGKAP

Bahan Ajar Iritabilitas Pada Tumbuhan Kelas XI (Fase F) Kurikulum Merdeka

EUKARYOTIC CELLS vs PROKARYOTIC CELLS | What's the difference?

BAB 5 Klasifikasi Makhluk Hidup - Karakteristik Makhluk Hidup || IPA Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka

A célula: definição, estrutura, funções e partes - Procariontes, eucariontes, animais, vegetais
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)