Bahan Ajar Iritabilitas Pada Tumbuhan Kelas XI (Fase F) Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRThis educational video on plant irritability explains how plants respond to stimuli like touch, light, water, temperature, and gravity. The presenter explores three types of plant movement: endonom, hygroscopic, and etionom movements. Endonom movements are internal, while hygroscopic movements are due to water content changes. Etionom movements, influenced by external factors, include tropic (directional) movements like phototropism, geotropism, and thigmotropism, nastic (non-directional) movements like thigmonasty, and taxis movements driven by stimuli like light and chemicals. The video aims to help students understand plant behavior and critical thinking through real-life phenomena.
Takeaways
- 😀 Plants exhibit irritability, which is their ability to respond to various stimuli such as touch, light, water, temperature, and gravity.
- 😀 The three types of plant movement are Endonom movement, Hygroscopic movement, and Etionom movement.
- 😀 Endonom movement is a response to internal stimuli within the plant, such as protoplasm flow in Elodia plants and chromosome division.
- 😀 Hygroscopic movement occurs due to the decrease in water content, such as the cracking of dry legumes and the opening of spore boxes in ferns.
- 😀 Etionom movement, also called esionom movement, is a response to external stimuli like physical, chemical, or mechanical forces.
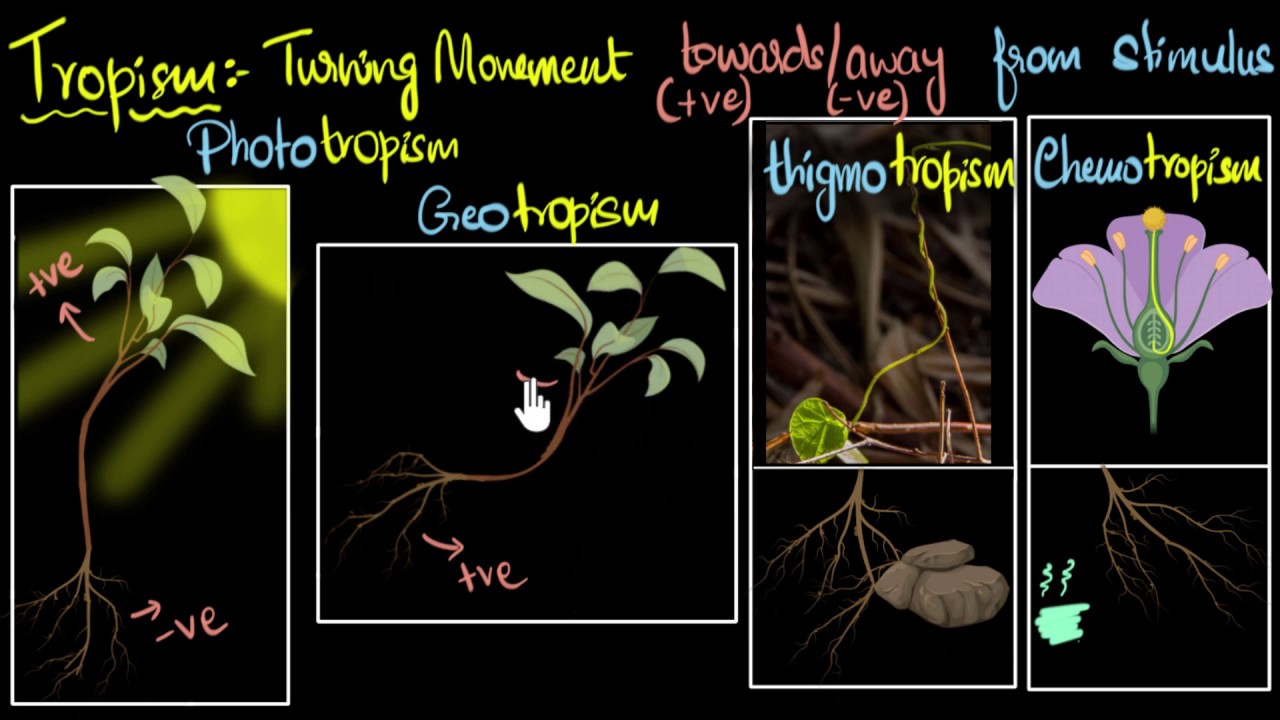
- 😀 Tropic movement, part of Etionom movement, occurs when a plant’s direction of movement is influenced by the stimulus, like phototropism or geotropism.
- 😀 Positive phototropism refers to plant parts moving towards light, while negative phototropism refers to roots growing away from light.
- 😀 Thigmotropism is the movement caused by touch, commonly seen in climbing plants like grapes, where tendrils wrap around objects.
- 😀 Nasti movement involves movement that is not influenced by the direction of the stimulus but rather by turgor pressure changes, like in the Mimosa pudica plant.
- 😀 Taxis movement involves the entire plant body moving in response to external stimuli, such as phototaxis (movement due to light) or chemotaxis (movement due to chemicals).
Q & A
What is plant irritability?
-Plant irritability refers to the ability of plants to respond to various stimuli such as touch, light, water, temperature, and gravity.
What are the three main types of plant movement based on the source of stimulation?
-The three main types of plant movement based on the source of stimulation are endonom movement, hygroscopic movement, and etionom (or esionom) movement.
Can you explain endonom movement with an example?
-Endonom movement occurs when the stimulus comes from within the plant itself. An example is the flow of protoplasm in the cells of the elodia plant, or the movement of chromosomes during cell division.
What is hygroscopic movement, and how does it occur?
-Hygroscopic movement is caused by a continuous decrease in water content, which leads to cracking of seeds or fruits. For instance, the cracking of dry legumes or the opening of spore boxes in ferns.
What types of stimuli influence etionom (or esionom) movement?
-Etionom (or esionom) movement is influenced by external stimuli, which can be physical (like temperature, light, and gravity), mechanical (like touch and wind), or chemical (such as poison or fertilizer).
What is tropism in plants, and how is it classified?
-Tropism is a plant's movement in response to external stimuli, with the direction of movement determined by the stimulus. Tropism is classified into types such as phototropism, geotropism, thigmotropism, chemotropism, and hydrotropism.
How does phototropism work in plants?
-Phototropism is the movement of plants in response to light. Generally, plant parts above the ground exhibit positive phototropism (moving towards light), while roots exhibit negative phototropism (moving away from light).
What is thigmotropism, and where does it occur?
-Thigmotropism is a movement in plants caused by touch. It typically occurs in climbing plants like grapes or cucumbers, where tendrils wrap around objects they touch due to uneven cell growth.
What are nastic movements in plants?
-Nastic movements are plant movements that are not directed by the stimulus but rather by changes in turgor pressure. Types of nastic movements include thigmonasty (touch), photonasty (light), nyctinasty (darkness), and thermonasty (temperature).
Can you give an example of a taxis movement in plants?
-Taxis movement in plants refers to a directional movement of the entire plant body in response to external stimuli. For example, phototaxis is the movement of chloroplasts toward light, or chemotaxis, which occurs when male gametes of moss move towards female gametes due to chemical signals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)