Biochemistry: Reactions of amino acids (Part-2)
Summary
TLDRThis video from the 'Learn at Ease' YouTube channel delves into the reactions of amino acids, focusing on those catalyzed by the amino group. It covers a range of reactions including acetylation, benzoylation, methylation, and the use of Sanger's reagent for color identification. The video also explores oxidative deamination, reactions with formaldehyde, aromatic aldehydes, ninhydrin, carbon dioxide, and the Verret reaction. It provides a comprehensive guide to the chemical behavior of amino acids, essential for understanding biochemistry.
Takeaways
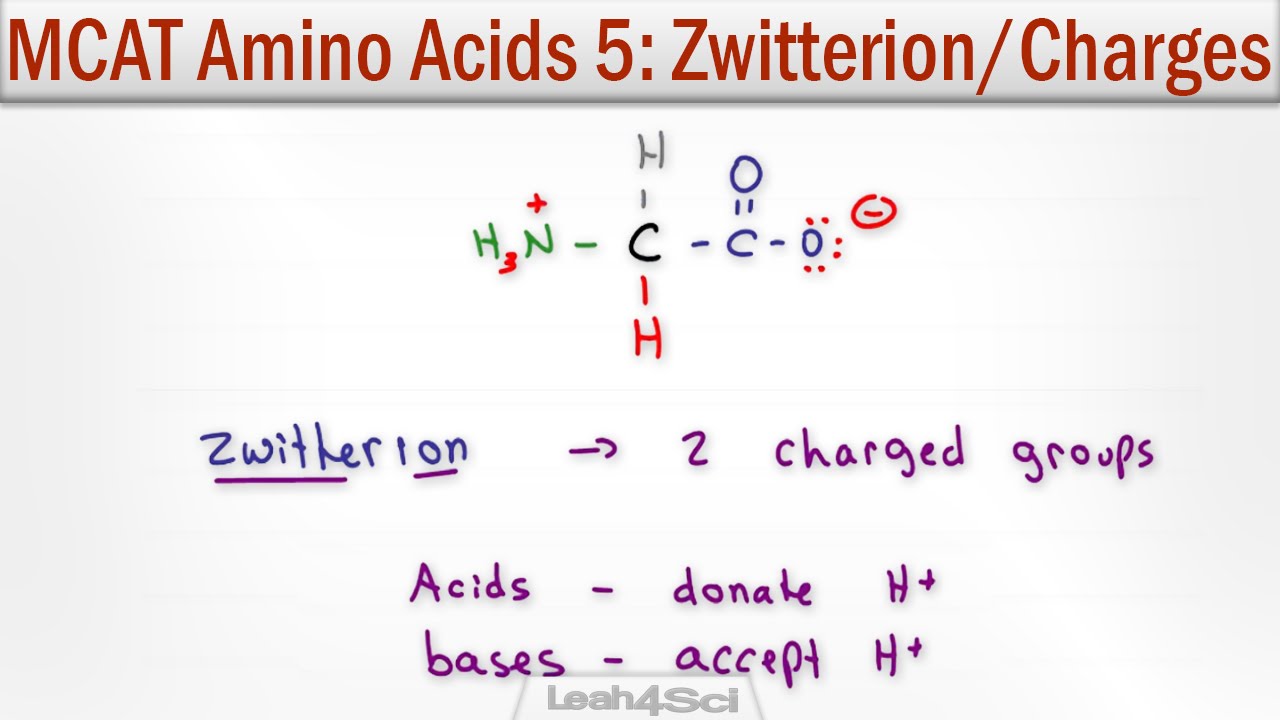
- 🧬 Amino acids are organic biomolecules with two oppositely charged functional groups, an amino group and a carboxylic group, attached to the same carbon atom, known as the alpha carbon.
- 🔍 This video is a continuation of a series discussing the reactions of amino acids, focusing on those that occur due to the involvement of the amino group alone.
- 🧪 The first reaction discussed is the acylation of amino acids, where the amino acid is isolated by dissolving it in cold alkali and then adding acetic anhydride to obtain an acetylated amino acid.
- 🌿 The second reaction is the benzoylation, where glycine reacts with benzoic acid to form hippuric acid, a detoxification process in the body.
- 🔑 The third reaction is methylation, where amino acids are treated with methyl iodide or dimethyl sulfate to obtain betaine, a methylated amino acid.
- 📚 The fourth reaction involves Sanger's reagent, which condenses with the free amino group to form a DNP amino acid, a bright yellow colored compound used for identification purposes.
- 💨 The fifth reaction is the reaction with nitrous acid (HNO2), leading to the formation of a hydroxyl acid and the release of nitrogen gas, useful for estimating free amino groups.
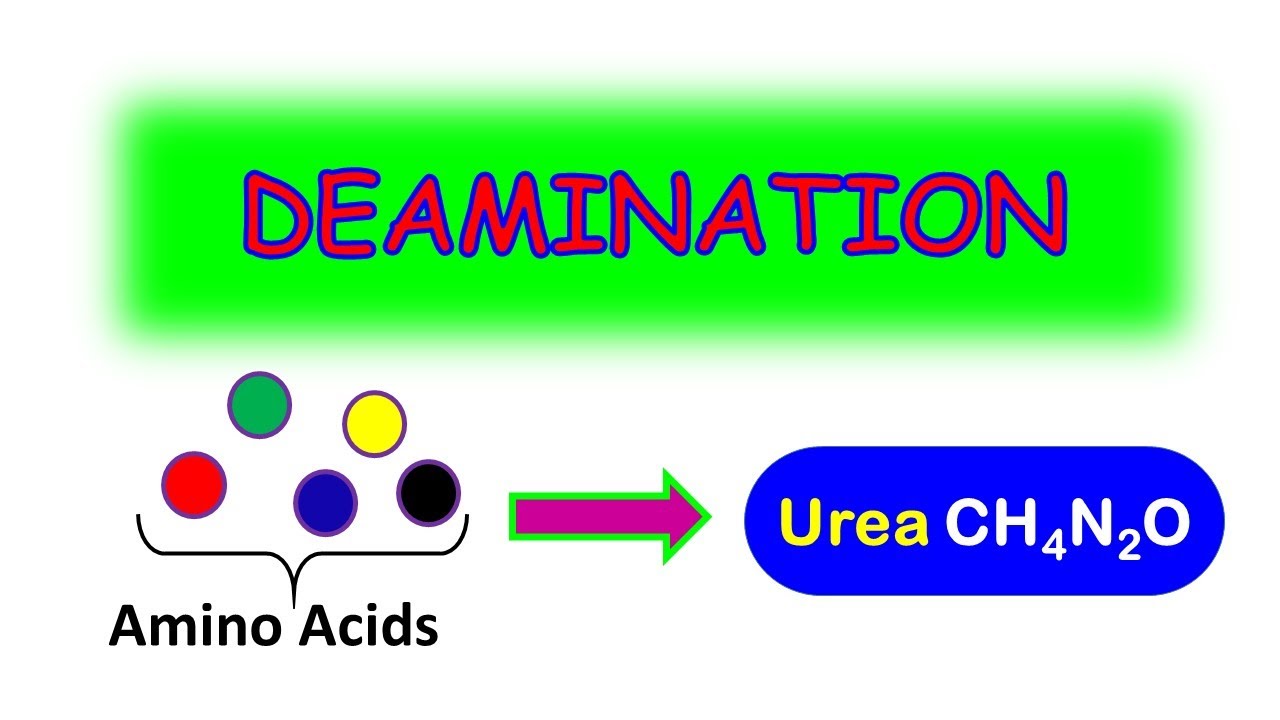
- 🔄 The sixth reaction is oxidative deamination, where amino acids are converted to keto acids and ammonia by oxidative enzyme systems, particularly in the liver and kidneys.
- 📊 The seventh reaction is the reaction with formaldehyde, where the amino group reacts to form dimethyl all amino acid, which is acidic in nature.
- 🌈 The eighth reaction is with aromatic aldehydes, leading to the formation of a Schiff base, a molecule with a C=N bond.
- 🟣 The ninth reaction is with ninhydrin, which forms a purple-colored compound known as Ruheim's purple, a color reaction of amino acids.
- 🔮 The tenth reaction is the reaction with carbon dioxide, resulting in the formation of N-carboxy amino acids through a condensation reaction.
- 🟪 The eleventh and final reaction discussed is the Biruté reaction, where copper ions react with the unshared electron pair of nitrogen to form a violet-colored complex, indicating the presence of two CoNH2 groups.
Q & A
What are amino acids and why are they important in biochemistry?
-Amino acids are organic biomolecules that contain an amino group and a carboxylic group attached to the same carbon atom, known as the alpha carbon. They are the building blocks of proteins and are crucial for various biological processes.
What are the two oppositely charged functional groups found in amino acids?
-The two functional groups are the amino group, which is positively charged, and the carboxylic group, which is negatively charged.
What is the significance of the alpha carbon in amino acids?
-The alpha carbon is significant because it is the carbon atom to which both the amino and carboxylic groups are attached, forming the backbone of the amino acid.
Can you explain the concept of 'isolation' in the context of amino acids?
-Isolation in this context refers to the process of separating an amino acid from a mixture when it is dissolved in cold alkali and then treated with acetic anhydride to form an acetylated derivative.
What is benzoyl elation and how does it relate to detoxification in the body?
-Benzoyl elation is the reaction where glycine reacts with benzoic acid to form hippuric acid. This is a detoxification process in the body that neutralizes the toxic benzoic acid.
What is methylation of amino acids and what is its purpose?
-Methylation of amino acids involves the treatment of amino acids with methyl iodide or dimethyl sulfate in an alkaline environment, resulting in the formation of betaines, which are methylated amino acids. This process is part of various biochemical reactions.
What is Sanger's reagent and how does it react with amino acids?
-Sanger's reagent, also known as 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (FDNB), reacts with the free amino group of an amino acid under alkaline conditions to form a DNP amino acid, which is a bright yellow-colored product used for the identification of amino acids.
How does nitrous acid (HNO2) react with amino acids and what is the outcome?
-Nitrous acid reacts with the free amino group of an amino acid, resulting in the formation of a hydroxyl acid, the release of nitrogen gas, and water. This reaction can be used to estimate the number of free amino groups in amino acids, peptides, or proteins.
What is oxidative deamination and what happens during this reaction?
-Oxidative deamination is a two-step reaction where an amino acid is converted to a keto acid and ammonia through the action of oxidative enzyme systems, particularly in the liver and kidneys.
What is the significance of the reaction between amino acids and formaldehyde?
-The reaction between amino acids and formaldehyde is significant because it allows the masking of the positive charge on the amino group by converting the amino acid to a dimethyl all amino acid, which is acidic in nature.
What is a Schiff base and how is it formed during the reaction with aromatic aldehydes?
-A Schiff base is a compound with a C=N double bond formed when an aromatic aldehyde reacts with an amino acid in the presence of an alkali, leading to the formation of a condensation intermediate that loses a water molecule to form the Schiff base.
What is the ninhydrin reaction and its significance in amino acid analysis?
-The ninhydrin reaction is a color reaction where ninhydrin reacts with an amino acid to form a purple-colored compound known as Ruheim's purple or dico hydride Aladin. This reaction is used for the detection and analysis of amino acids.
What is the Verret reaction and how does it relate to the detection of amino acids?
-The Verret reaction is a color reaction where compounds containing two NH2 groups react with copper sulfate to form a violet-colored complex. This reaction is used for the detection of amino acids and peptides.
What is the purpose of the video and who prepared it?
-The purpose of the video is to explain the various chemical reactions of amino acids, focusing on those involving the amino group. It was prepared by Dr. D. R. Paul and Goswami.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)