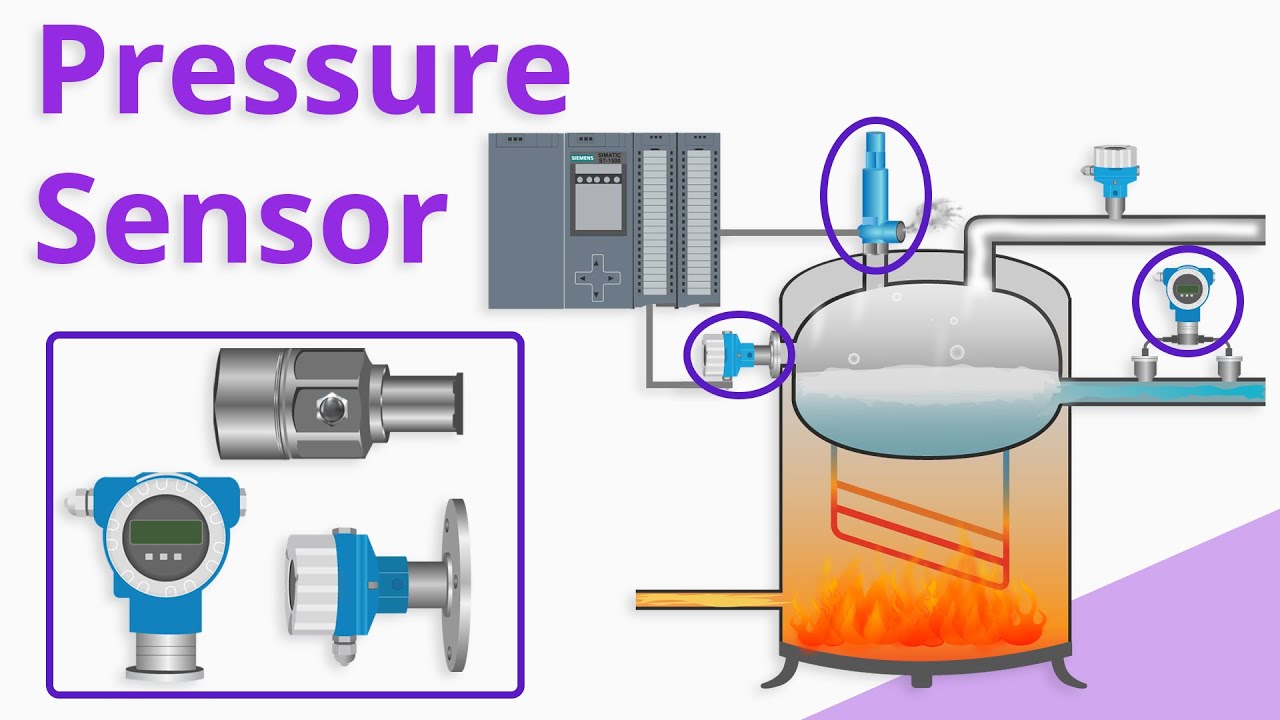
Electrochemical Sensors
Summary
TLDRThis session delves into electrochemical sensors, devices that detect analyte concentrations by converting electrode interactions into electrical signals. These sensors, also known as electrochemical cells, are categorized into potentiometric, amperometric, and conductometric types based on their signal transformation methods. Comprising a container with an electrolyte and three key electrodes—sensing, reference, and counter—these sensors are vital for applications such as dissolved oxygen detection, water and soil analysis, environmental monitoring, agricultural pesticide detection, clinical blood analysis, and defense against toxic gases and warfare agents.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Electrochemical sensors are devices used to detect the concentration of an analyte solution by converting electrode-analyte interactions into an electrical signal.
- ⚡ These sensors typically consist of a set of electrodes that act as transducers and are also known as electrochemical cells.
- 📏 Electrochemical sensors are classified into potentiometric sensors (measuring voltage), amperometric sensors (measuring current), and conductometric sensors (measuring conductivity).
- 🧪 An electrochemical sensor assembly usually includes a container filled with an electrolyte and immersed in three electrodes: sensing electrode, reference electrode, and counter electrode.
- 🛠 The sensing electrode is often attached with a hydrophobic membrane that allows only specific analytes to contact the electrode.
- 🔄 At least two electrodes are required to form a closed circuit for current flow, with one electrode acting as the reaction site, either undergoing oxidation or reduction.
- 📈 The current produced during oxidation or reduction at the sensing electrode is measured to determine important analyte data, such as concentration.
- 🌊 Applications of electrochemical sensors include detecting dissolved oxygen, water analysis, environmental monitoring, and measuring metal concentrations, pH, and various oxides in water.
- 🌱 These sensors are used in soil analysis and agricultural applications to detect pesticides.
- 🏥 In the clinical field, electrochemical sensors monitor blood glucose, calcium ions, iron ions, and uric acid levels.
- 🛡 Defense applications of electrochemical sensors include detecting toxic gases and warfare agents.
Q & A
What are electrochemical sensors?
-Electrochemical sensors are devices used to detect the concentration of analytes in a solution by converting electrode-analyte interactions, such as oxidation or reduction, into an electrical signal.
How are electrochemical sensors also known?
-Electrochemical sensors are also known as electrochemical cells because they consist of a set of electrodes that act as transducers.
What are the different types of electrochemical sensors based on signal transformation?
-Electrochemical sensors are classified into potentiometric sensors, which measure voltage; amperometric sensors, which measure current; and conductometric sensors, which measure conductivity.
What are the three main components of an electrochemical sensor assembly?
-The three main components of an electrochemical sensor assembly are a container filled with an electrolyte, a sensing electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode.
What is the purpose of the hydrophobic membrane attached to the sensing electrode?
-The hydrophobic membrane attached to the sensing electrode allows only a particular component of the analyte to be in contact with the sensing electrode, ensuring specificity in detection.
Why is a closed circuit necessary for an electrochemical sensor?
-A closed circuit is necessary for the flow of current in an electrochemical sensor, as it requires at least two electrodes to act as a transducer for the electrical signal.
What happens at the sensing electrode during the interaction with the analyte?
-During the interaction with the analyte, the sensing electrode undergoes oxidation if it is an anode or reduction if it is a cathode, enabling the flow of electrons and the production of a measurable current.
What are some applications of electrochemical sensors in environmental monitoring?
-Electrochemical sensors are used in environmental monitoring for the measurement of metal concentrations in water, pH levels, and detection of nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and carbon oxides.
How are electrochemical sensors used in agriculture?
-In agriculture, electrochemical sensors are used to detect the presence of pesticides, helping to ensure the safety and quality of crops.
What clinical applications do electrochemical sensors have?
-Electrochemical sensors are used in the clinical field for monitoring blood glucose, calcium ions, iron ions, and uric acid levels, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various health conditions.
How are electrochemical sensors utilized in defense applications?
-In defense applications, electrochemical sensors are used for the detection of toxic gases and warfare agents, providing crucial information for safety and security.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)