Cell Cycle | Biology MCAT
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the cell cycle, distinguishing between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and detailing the three categories of mammals: placental, marsupial, and monotreme. It explores DNA structure, the nucleus's role, and the significance of chromosomes and genes. The script explains the difference between somatic and germ cells, the process of DNA replication, and the transcription and translation into proteins. It breaks down the cell cycle into phases: G0, G1, S, G2, and M, highlighting the importance of each phase and the types of cells (permanent, stable, and labile). The video also touches on the clinical implications of the cell cycle, such as the effects of chemotherapy on rapidly dividing cells.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Organisms are categorized into prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with eukaryotes further divided into placental mammals, marsupials, and monotremes.
- 🧬 DNA, found in the nucleus, is a double helix composed of a sugar backbone, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases.
- 🔬 The human body is organized into systems, organs, tissues, and cells, each containing a nucleus with 46 chromosomes in somatic cells and 23 in germ cells.
- 🧬 Chromosomes contain genes, segments of DNA, which are essential for genetic inheritance.
- 👶 Determining sex involves analyzing the presence of XX (female) or XY (male) chromosomes.
- 🧬 Germ cells are either 22+X (ovum) or 22+Y (sperm), combining to form either a male (XY) or female (XX).
- 📚 Transcription is the process of DNA being made into RNA, and translation is the process of RNA being made into proteins.
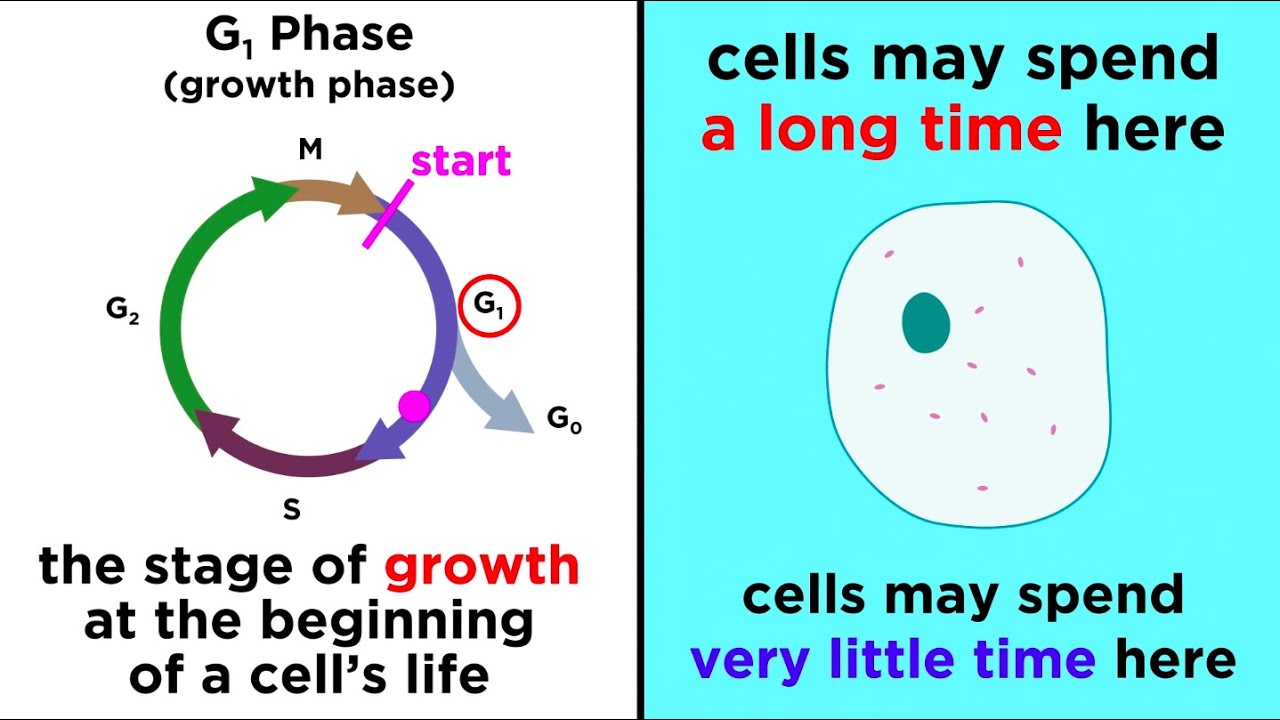
- 🔄 The cell cycle is divided into interphase (G0, G1, S, G2) and the M phase (mitosis), with interphase including growth, DNA replication, and preparation for mitosis.
- 🌱 G0 is a resting phase where cells are not dividing, while G1, S, and G2 are active phases of the cell cycle leading to cell division.
- 💊 Chemotherapy drugs work by inhibiting the cell cycle, affecting rapidly dividing cells, which can lead to side effects like hair loss and gastrointestinal issues.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of living organisms based on their cellular structure?
-The two main categories of living organisms are prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
How are eukaryotes subdivided in terms of mammals?
-Eukaryotes are subdivided into three categories: placental, marsupial, and monotreme.
What is the difference between a placental and a marsupial in terms of fetal development?
-In placental mammals, the fetus develops inside the mother's uterus until a late stage, whereas in marsupials, the early fetus develops in the uterus and then moves to a pouch (marsupium) where it continues to develop.
What is the unique feature of monotreme reproduction?
-Monotremes are unique because they lay eggs, and the young hatch from the eggs with underdeveloped features, often entering a pouch for further development.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
-The nucleus serves as the 'house' of the cell, containing the DNA, which is essential for the cell's genetic information and functions.
How is the DNA structure described in the script?
-DNA is described as a double helix made up of a sugar backbone, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases.
What are the two types of cells in the human body, and how do their chromosome numbers differ?
-The two types of cells in the human body are somatic cells and germ cells. Somatic cells have 46 chromosomes (diploid), while germ cells have 23 chromosomes (haploid).
What is the significance of the Barr body in determining the sex of an individual?
-The Barr body is an inactive X chromosome found in females. The presence of a Barr body indicates a female, while the absence indicates a male, as males have only one active X chromosome.
What is the process called when DNA is transcribed into RNA, and what is the subsequent process when RNA is made into proteins?
-The process of transcribing DNA into RNA is called transcription, and the process of making proteins from RNA is called translation.
What are the phases of the cell cycle, and what do the letters G, S, and M stand for?
-The phases of the cell cycle are G0, G1, S, G2, and M. G stands for growth, S stands for synthesis (DNA replication), and M stands for mitosis (cell division).
How do chemotherapeutic agents affect cancer cells and why might patients undergoing chemotherapy lose their hair?
-Chemotherapeutic agents are replication inhibitors that target rapidly dividing cells. They affect cancer cells by preventing them from dividing, which is beneficial. However, the side effect is that other rapidly dividing cells, like hair follicle cells, are also affected, leading to hair loss.
What are the three types of cells mentioned in the script, and how do they differ in terms of cell division?
-The three types of cells mentioned are permanent, stable, and labile cells. Permanent cells remain in G0 and do not divide, like neurons. Stable cells are quiescent in G0 but can divide when necessary, like hepatocytes. Labile cells are constantly dividing with little to no rest in G0, like hair follicle cells and bone marrow stem cells.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
The Cell Cycle and its Regulation

Protista adalah Jembatan Antar-Kingdom | Materi Biologi Kelas 10

Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells (Updated)

Materi Ciri Ciri Bakteri Dan Struktur Bakteri, Video Pembelajaran Biologi SMA Kelas 10 (Part 1/3)

Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | Biology | Khan Academy

Havo 5 | DNA | Basisstof 4 Genexpressie
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)