Linear Equations - Algebra
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script offers a comprehensive review of linear equations, focusing on three key forms: slope-intercept, standard, and point-slope. It explains how to calculate slopes using the rise-over-run method and identifies x and y-intercepts. The script also explores the concepts of parallel and perpendicular lines, their slopes, and provides step-by-step instructions for graphing linear equations in various forms, including slope-intercept, standard, and point-slope forms. It concludes with practical examples and exercises to solidify understanding.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is a review of linear equations, aimed at helping students prepare for tests.
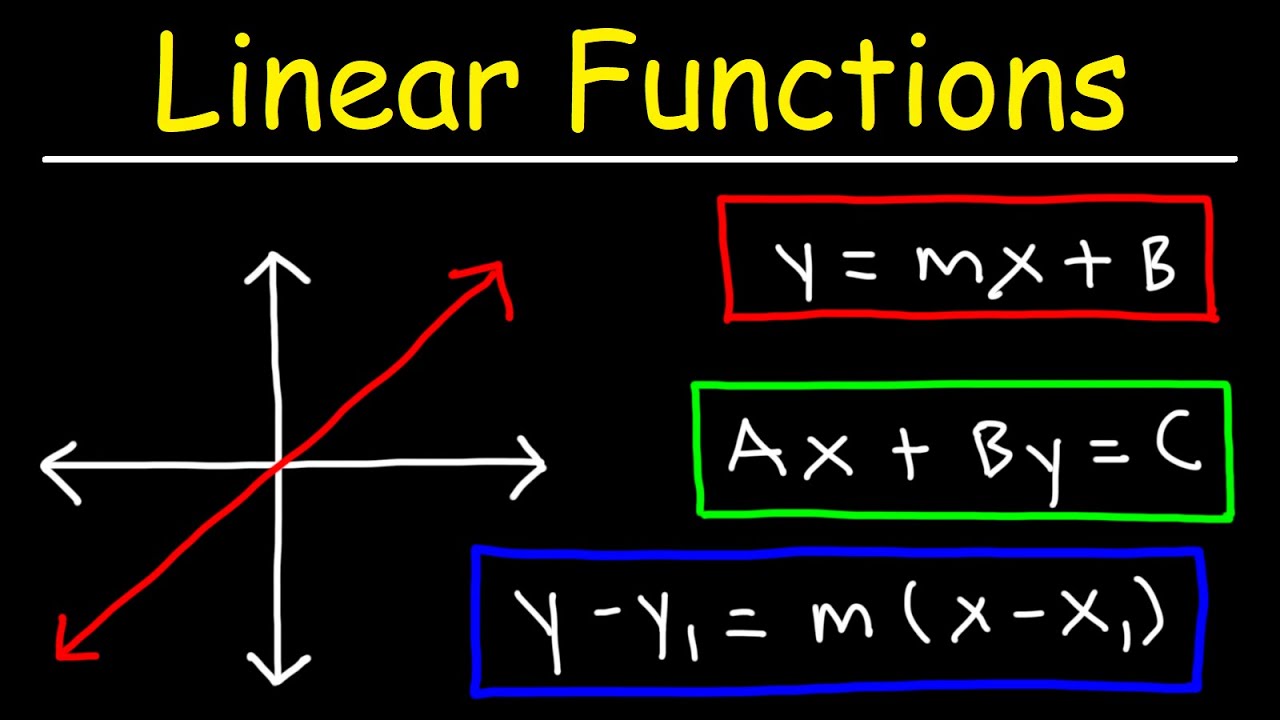
- 📈 There are three main forms of linear equations: slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), standard form (ax + by = c), and point-slope form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)).
- 📉 The slope-intercept form is characterized by 'm' representing the slope and 'b' representing the y-intercept.
- 🔍 In the standard form, 'a', 'b', and 'c' are coefficients, and 'x' and 'y' are variables.
- 📍 The point-slope form provides the slope (m) and a specific point (x1, y1) on the line.
- 🔢 The slope is calculated as the rise over the run, which can be positive, negative, or zero depending on the direction of the line.
- 📉 A line with a 45-degree angle has a slope of one, and the slope increases as the line becomes steeper.
- ↗️ Horizontal lines have a slope of zero, and vertical lines have an undefined slope.
- 🔍 To find the slope between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), use the formula (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1).
- 📍 X-intercepts are points where y = 0, and y-intercepts are points where x = 0.
- 🔄 Parallel lines have the same slope, and perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other.
Q & A
What are the three forms of a linear equation mentioned in the video?
-The three forms of a linear equation mentioned are slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), standard form (ax + by = c), and point-slope form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)).
What does 'm' represent in the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
-In the slope-intercept form of a linear equation (y = mx + b), 'm' represents the slope of the line.
What is the slope of a line that rises 4 units and runs 3 units?
-The slope of a line that rises 4 units and runs 3 units is calculated as rise over run, which is 4/3.
What is the relationship between the slopes of two parallel lines?
-The slopes of two parallel lines are equal, meaning if one line has a slope of 'm', the other line will also have a slope of 'm'.
How do you find the slope of a line given two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)?
-You can find the slope of a line given two points by using the formula: slope (m) = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1).
What is an x-intercept and how do you find it?
-An x-intercept is a point where the line crosses the x-axis, which means the y-value is zero. To find the x-intercept, set y to zero in the equation and solve for x.
What is a y-intercept and how is it related to the 'b' value in the slope-intercept form?
-A y-intercept is the y-coordinate of the point where the line crosses the y-axis, which occurs when x is zero. In the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), 'b' represents the y-intercept.
How do you graph a linear equation in slope-intercept form?
-To graph a linear equation in slope-intercept form, first plot the y-intercept, then use the slope to find another point by moving up by the rise and to the right by the run, and finally draw a line through the points.
What is the slope of a horizontal line?
-The slope of a horizontal line is zero because it does not rise or fall as it moves from left to right.
What is the slope of a vertical line?
-The slope of a vertical line is undefined because it represents an infinite rate of change as it moves from bottom to top without a horizontal displacement.
How do you determine if two lines are perpendicular?
-Two lines are perpendicular if the product of their slopes is -1, meaning if one line has a slope of 'm', the other line will have a slope of -1/m.
What is the process of graphing a linear equation in standard form?
-To graph a linear equation in standard form, find the x-intercept by setting y to zero and solving for x, find the y-intercept by setting x to zero and solving for y, plot these intercepts, and then draw a straight line through them.
How do you graph a linear equation in point-slope form?
-To graph a linear equation in point-slope form, identify the point (x1, y1) and the slope 'm'. Plot the point, then use the slope to find another point by moving up by the rise and to the right by the run, and draw a line through these points.
What does it mean if a linear equation is given in the form y = a constant?
-If a linear equation is given in the form y = a constant, it represents a horizontal line at the y-value of the constant, with a slope of 0.
What does it mean if a linear equation is given in the form x = a constant?
-If a linear equation is given in the form x = a constant, it represents a vertical line at the x-value of the constant, with an undefined slope.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)