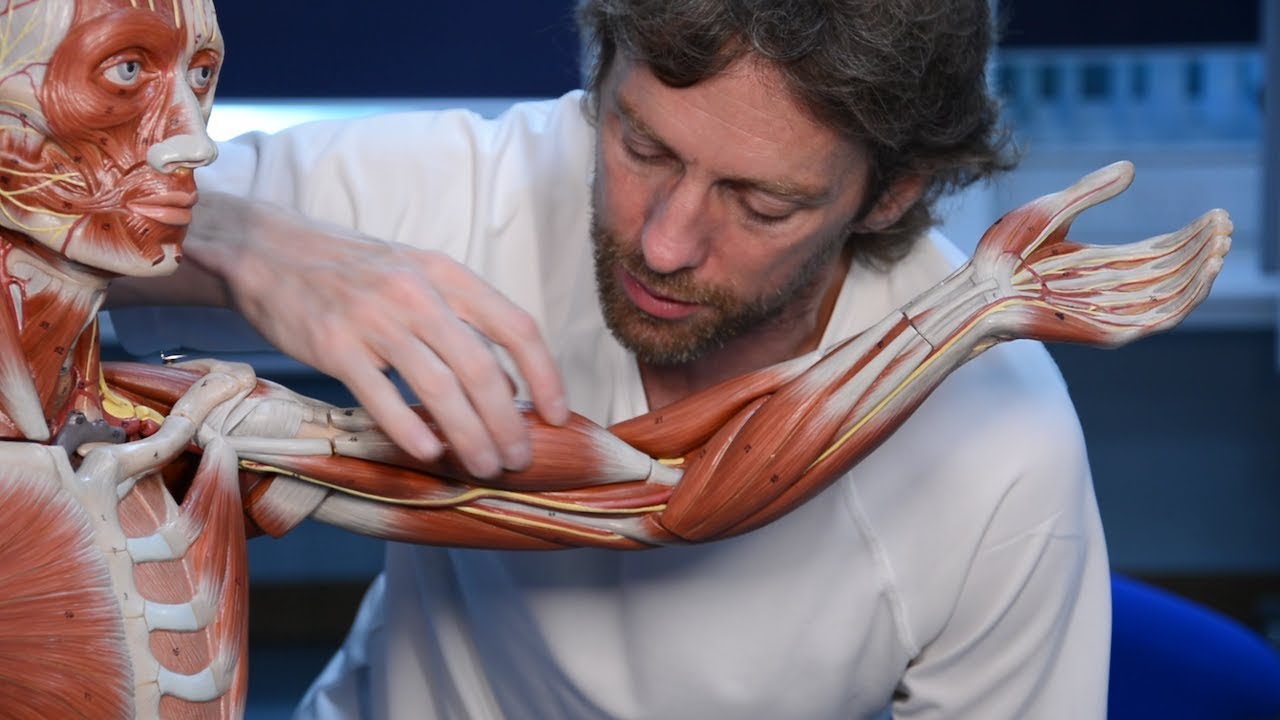
Posterior forearm muscles (identifying)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script discusses the muscles of the posterior forearm, focusing on their identification and functions. It explains the process of determining muscle names and actions, such as flexion, extension, and deviation of the wrist and fingers. The script also covers the muscles involved in thumb movements, emphasizing the importance of understanding muscle attachments and actions for accurate identification.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses the muscles of the posterior forearm, focusing on their identification and function.
- 🏋️♂️ The process involves understanding where the muscles go and what actions they perform, often using Greek and Latin roots to deduce their names.
- 🤔 The posterior forearm is more complex than the anterior, but the same principles apply in identifying the muscles.
- 📍 Key landmarks include the humerus, radius, ulna, and carpal bones, with the thumb being a distinctive feature.
- 💪 The brachioradialis muscle is highlighted as a muscle that crosses the elbow and is involved in flexing the elbow against resistance.
- 🔍 The extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis are identified as muscles that extend the wrist, with the longus having a longer tendon.
- 👆 The extensor digitorum muscle is responsible for extending the fingers, with additional muscles like extensor indicis and extensor digiti minimi providing more control over the index and little fingers.
- 🤚 The muscles of the thumb are also discussed, with the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis longus being key in thumb movements.
- 🔄 The supinator muscle is mentioned as a muscle that wraps around the radius, aiding in pronation and supination of the forearm.
- 👨🏫 The video emphasizes the importance of understanding muscle attachments and actions to correctly identify them, rather than just memorizing names.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The main focus of the video script is to identify and understand the muscles of the posterior forearm, their functions, and how they contribute to various movements.
What are the key principles used to identify muscles in the script?
-The key principles used to identify muscles are determining where the muscle goes (its attachment points) and what action it performs (e.g., flexion, extension, abduction).
What is the significance of the radial and ulnar deviation in the context of the forearm muscles?
-Radial and ulnar deviation refer to the movements of the wrist. Radial deviation involves the wrist bending towards the thumb side (radius), while ulnar deviation involves bending towards the little finger side (ulna). These movements are important for understanding the actions of the forearm muscles.
What is the role of the brachioradialis muscle?
-The brachioradialis muscle is involved in flexing the elbow, especially when the thumb is pointing upwards. It is also known as the 'beer-drinkers muscle' as it becomes prominent when flexing the elbow against resistance in this position.
How are the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis muscles distinguished from each other?
-The extensor carpi radialis longus has a longer tendon that goes further, while the extensor carpi radialis brevis has a shorter tendon. Both muscles are involved in extending the wrist but originate from different parts of the humerus.
What is the function of the extensor digitorum muscle?
-The extensor digitorum muscle is responsible for extending the fingers. It has a single layer in the posterior forearm and sends tendons to the digits.
Why are there separate muscles for the index finger and little finger in the extensor compartment?
-Separate muscles for the index finger (extensor indicis) and little finger (extensor digiti minimi) allow for more individual control and movement of these fingers, similar to the control provided by the muscles of the thumb.
What is the role of the extensor carpi ulnaris and anconeus muscles?
-The extensor carpi ulnaris is involved in extending the wrist towards the ulnar side (little finger side). The anconeus muscle, located next to the extensor carpi ulnaris, helps in stabilizing the elbow joint and assists in forearm rotation.
How do the muscles of the thumb differ from those of the fingers in terms of movement?
-The thumb moves in a plane that is at 90 degrees to that of the fingers. It has its own set of muscles for flexion, extension, and abduction, which are distinct from the flexor and extensor muscles of the fingers.
What is the significance of the supinator muscle in the script?
-The supinator muscle is involved in the rotation of the forearm, specifically in supination (rotating the palm forward). It wraps around the radius and pulls on it to facilitate this movement.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)