Israel-Palestine conflict: What’s the two-state solution? | Realpolitik
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the resurgence of the Palestine question in West Asia's geopolitics following Hamas's attack on Israel and the ongoing conflict. It explains the two-state solution's history, from the Peel Commission to the Oslo Accords, and the current obstacles to its implementation, including disputed borders, the presence of Israeli settlers, the status of Jerusalem, and the right of Palestinian refugees to return. The script highlights the challenges and the complex geopolitical landscape that hinders lasting peace in the region.
Takeaways
- 📜 The two-state solution proposes dividing historical Palestine into an Arab state and a Jewish state for lasting peace.
- 🏛 The Peel Commission in 1936 first suggested partitioning Palestine, which was rejected by Arabs but accepted by the Jewish community.
- 🌍 The UN Special Commission on Palestine (UNSCOP) in 1947 proposed dividing Palestine into three territories, including an international territory for Jerusalem.
- 🇮🇱 Israel was unilaterally declared on May 14, 1948, leading to the first Arab-Israeli war and subsequent territorial gains beyond the UN plan.
- 🕊 The Oslo process in the 1990s saw the PLO recognizing Israel and agreeing to a Palestinian state within the 1967 borders, which was about 22% of historical Palestine.
- 🔄 The 1967 Six-Day War resulted in Israel capturing the West Bank, East Jerusalem, Gaza Strip, and other territories, effectively controlling all of historical Palestine.
- 🏢 The Palestinian National Authority was established as a self-governing body in the West Bank and Gaza, but with limited powers and Israel maintaining control over certain areas.
- 🚫 The assassination of Yitzhak Rabin and the rise of right-wing leadership in Israel contributed to the derailment of the peace process.
- 🛑 Structural factors such as undefined borders, the status of settlers, Jerusalem, and the right of refugees to return complicate the two-state solution.
- 🏙️ Israel's current right-wing leadership shows no willingness to make concessions, aiming to maintain the status quo of occupation.
- 🌐 Recognition of Palestine by European countries and the international community signifies support for a future Palestinian state.
Q & A
What is the main topic of discussion in the 'Real Politic' episode featuring Stanley and Johnny?
-The main topic is the Palestine question and the two-state solution in the context of recent events, including Hamas's attack on Israel and Israel's ongoing conflict with Gaza.
How many people were reported to have been killed in the conflict mentioned in the script?
-The script reports that 37,000 people were killed in the conflict.
What is the two-state solution in the context of the Israel-Palestine conflict?
-The two-state solution refers to the idea of dividing historical Palestine into two separate states: an Arab state and a Jewish state, with the aim of achieving lasting peace in the region.
What was the Peel Commission's proposal regarding the partition of Palestine in 1937?
-The Peel Commission proposed dividing Palestine into a Jewish state and an Arab state, with the West Bank, Gaza, and Negev desert for the Arab state, and the coastal and fertile Galilee region for the Jewish state.
What was the outcome of the UN General Assembly Resolution 181?
-Resolution 181 adopted the partition plan for Palestine into a Jewish state, an Arab state, and an international territory for Jerusalem. However, the plan was never implemented due to Arab rejection and the subsequent declaration of the state of Israel by the Zionist leadership.
What territories did Israel capture during the 1967 Six-Day War?
-During the Six-Day War, Israel captured the West Bank and East Jerusalem from Jordan, the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt, and the Golan Heights from Syria.
What was the Oslo Process and what did it aim to achieve?
-The Oslo Process was a series of agreements in the 1990s aimed at establishing a framework for peace in the Middle East, including the recognition of Israel by the PLO and the creation of a Palestinian state within the 1967 borders.
What are the structural factors mentioned in the script that make the two-state solution currently unachievable?
-The structural factors include the lack of a clearly demarcated border, the status of settlers in the West Bank and East Jerusalem, the status of Jerusalem, and the right of Palestinian refugees to return to their homes.
How many Jewish settlers are currently living in the West Bank and East Jerusalem according to the script?
-The script mentions that there are approximately 700,000 Jewish settlers living in the West Bank and East Jerusalem.
What was the role of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) in the Oslo Process?
-The PLO, under the leadership of Yasser Arafat, initially demanded the liberation of all of Palestine but later recognized the state of Israel and agreed to the creation of a Palestinian state within the 1967 borders.
What is the current stance of Israel's right-wing leadership on the two-state solution as described in the script?
-The script describes Israel's right-wing leadership as showing no willingness to make concessions to the Palestinians and wanting to maintain the status quo of occupation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Israel attacks explained in Hindi | Israel vs Palestine | Abhi and Niyu

इज़राइल की हवा टाइट• हर जगह मिल रही हार•अमरीकी-इज़राइली रिपोर्ट में इज़राइल की हार•सबसे ख़ास रिपोर्ट

Geopolitik Indonesia dalam Merespon Persoalan Dunia

فلسطين في دقيقة (٥٣) | يافا ! | ١٦-٢٥ يوليو ٢٠٢٤

Hamas's October 7 Attack: A Minute-by-Minute Breakdown
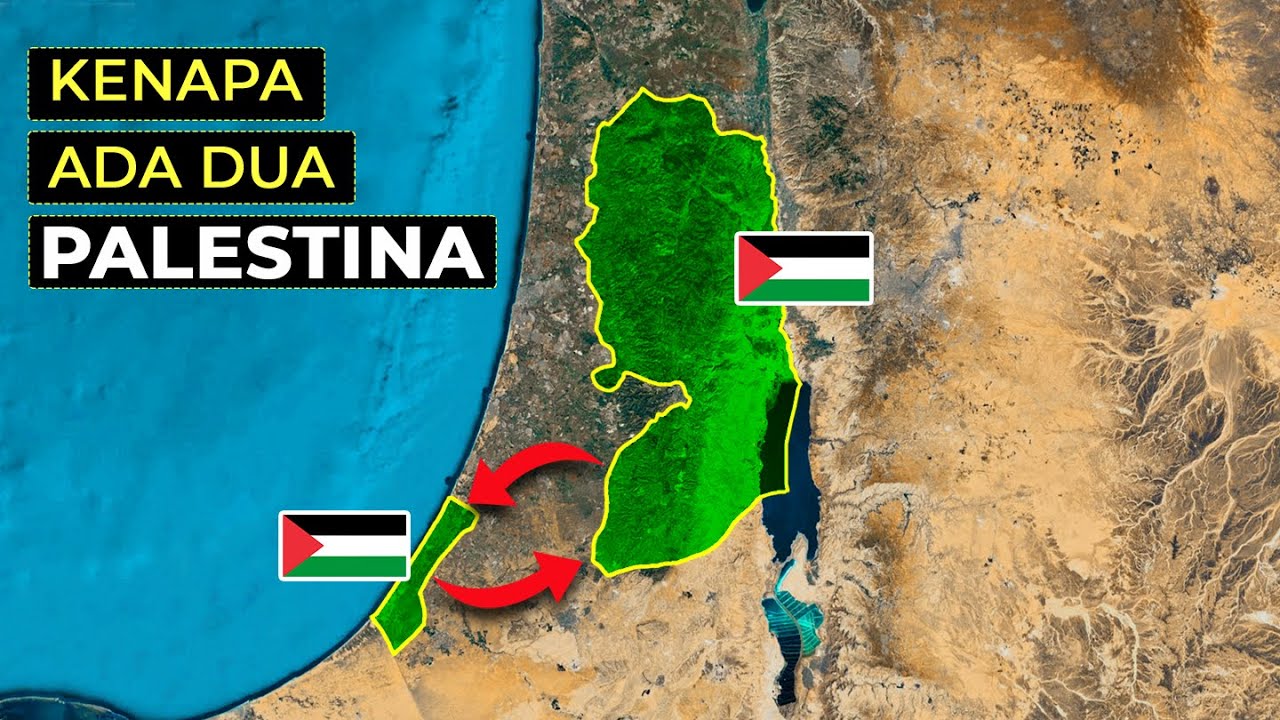
Kenapa Wilayah Palestina terbagi dua?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)