Next Generation Sequencing - A Step-By-Step Guide to DNA Sequencing.
Summary
TLDRThe video script details the evolution of genome sequencing from the 32-year Human Genome Project to the rapid Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) that now takes just a day. NGS, enabled by the human reference DNA sequence, sequences billions of DNA strands simultaneously, unlike the Sanger method used previously. The script explains the process of library preparation, sequencing by synthesis on Illumina instruments, and the importance of read depth and coverage in various applications, from diagnosing diseases to ecological research.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The Human Genome Project sequenced 3.2 billion bases of the human genome, taking 32 years from 1990 to 2003 to complete.
- 🚀 Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) can sequence a person's entire genome in just one day, a significant advancement from the 32-year timeline of the Human Genome Project.
- 🔬 NGS allows for the simultaneous sequencing of billions of DNA strands, in contrast to Sanger sequencing which sequences only one strand at a time.
- 🌟 The success of NGS is built upon the foundation of the human reference DNA sequence established by the Human Genome Project.
- 🧩 NGS involves cutting DNA into small pieces and sequencing them, then assembling the sequences based on the reference genome.
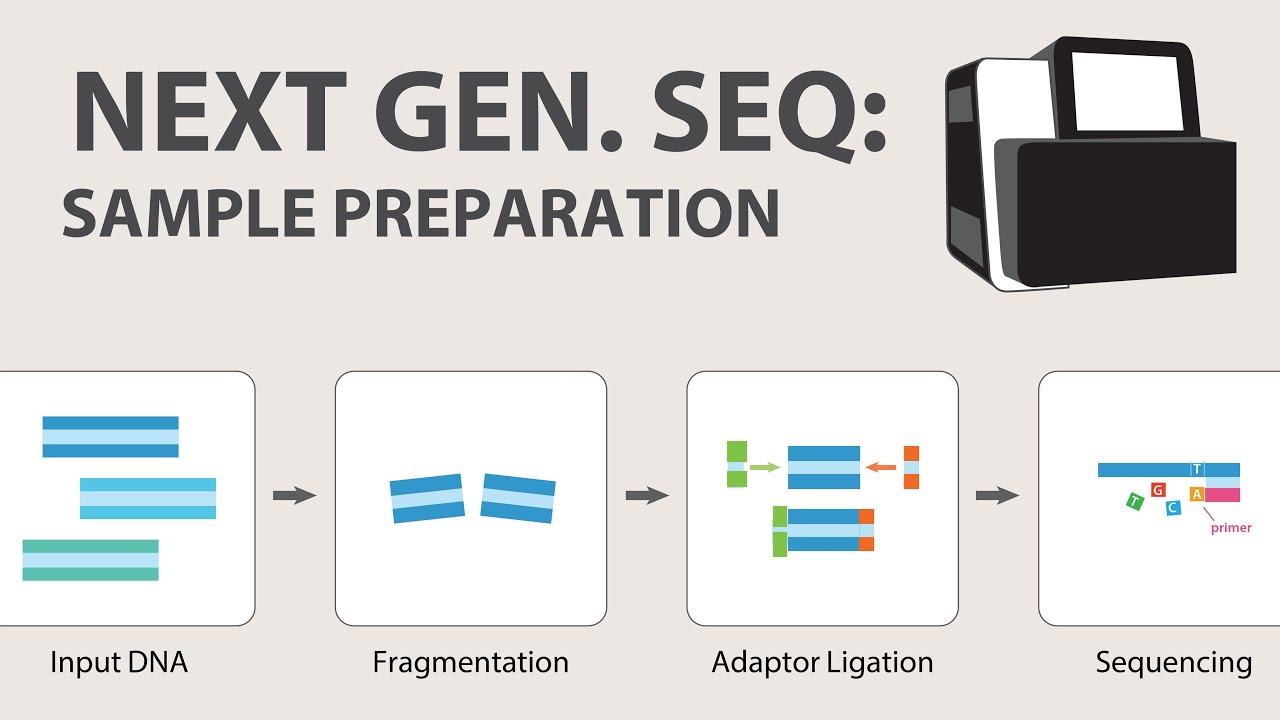
- 🧪 The process begins with sample collection and purification of DNA or RNA, with RNA needing to be reverse-transcribed into DNA before sequencing.
- 📚 A 'library' of short DNA fragments is prepared from the purified DNA, cut to a specified size and tagged with adapters for sequencing.
- 🔄 The sequencing process on Illumina instruments uses 'sequencing by synthesis' on a flow cell, where DNA fragments are amplified to form clusters for detection.
- 🔍 Each sequencing cycle involves the addition of fluorescently tagged nucleotides, recording their color to determine the DNA sequence, and repeating until complete.
- 🧬 Paired-end sequencing provides two reads from the same DNA fragment, improving alignment confidence and analysis of longer stretches of DNA or RNA.
- 📊 Read depth and coverage are key metrics in sequencing, with different applications requiring different depths for effective analysis.
- 🌐 NGS has a wide range of applications, from diagnosing diseases and guiding treatments to various research fields, and can sequence various types of RNA and DNA, including non-coding RNAs and methylation sites.
Q & A
What was the duration of the Human Genome Project from its start to the completion of 85 percent of the first genome?
-The Human Genome Project started in 1990 and took until 2003 to complete 85 percent of the first genome, which is a duration of 13 years.
How long did it take to fully sequence the human genome after the initial 85 percent was completed?
-After completing 85 percent of the first genome in 2003, it took an additional 19 years to fully sequence the human genome by 2022.
What is the difference in sequencing time between the methods used during the Human Genome Project and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
-The Human Genome Project took 32 years to sequence the human genome, whereas with Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), it takes only a day to sequence a person's entire genome.
How does Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) differ from Sanger sequencing in terms of the number of DNA strands sequenced at once?
-With Sanger sequencing, only one DNA strand can be sequenced at a time, whereas NGS allows for the simultaneous sequencing of billions of DNA strands.
What is the significance of the human reference DNA sequence in the context of NGS?
-The human reference DNA sequence, created by the Human Genome Project, is crucial for NGS as it provides a basis for assembling the sequences of the small pieces of DNA that are cut and sequenced.
What is the process of creating a library in NGS and why is it necessary?
-A library in NGS is a collection of short DNA fragments from a long stretch of DNA. It is created by cutting the DNA into short pieces of a specified size, adding adapter sequences to each fragment, and removing any non-bound adapters. This process is necessary to prepare the DNA for sequencing and to include an index for sample identification.
What is the purpose of the PCR step in the NGS process and when is it used?
-The PCR step in the NGS process is used to increase the library amount. It is applied depending on the application when a higher quantity of the library is required for sequencing.
Which company's sequencing instruments are predominantly used in NGS, and what method do they employ?
-Illumina's sequencing instruments are predominantly used in NGS, and they employ a method called sequencing by synthesis.
What is the purpose of the clonal amplification step in the NGS sequencing process?
-The clonal amplification step is necessary to increase the signal of each unique library fragment to a level that is detectable by the sequencing instrument. It is achieved through a PCR process that forms clusters of identical DNA fragments.
How does the sequencing by synthesis method work in Illumina's NGS instruments?
-In the sequencing by synthesis method, fluorescent nucleotides with different color tags and terminators are added to the flow cell along with DNA polymerase. Only one nucleotide is sequenced at a time, and the complementary base binds to the sequence before the camera records the color of each cluster. The process repeats for the number of reads set on the sequencer.
What are the two essential metrics in sequencing mentioned in the script, and what do they represent?
-The two essential metrics in sequencing mentioned in the script are read depth and coverage. Read depth is the number of reads for a nucleotide, and average read depth is the average depth across the region sequenced. Coverage refers to the aim of having no missing areas across the target DNA.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)