Metabolism | Cholesterol Metabolism
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the intricate world of cholesterol metabolism, highlighting its vital role in the synthesis of essential compounds like bile salts, steroid hormones, and cell membrane integrity. It explains the liver's endogenous cholesterol production from acetyl CoA and the significance of enzymes like HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins to manage high cholesterol levels. The script also touches on cholesterol's multifaceted uses, including its structural contributions to cell membranes and its transformation into various hormones, emphasizing the balance needed to prevent health issues.
Takeaways
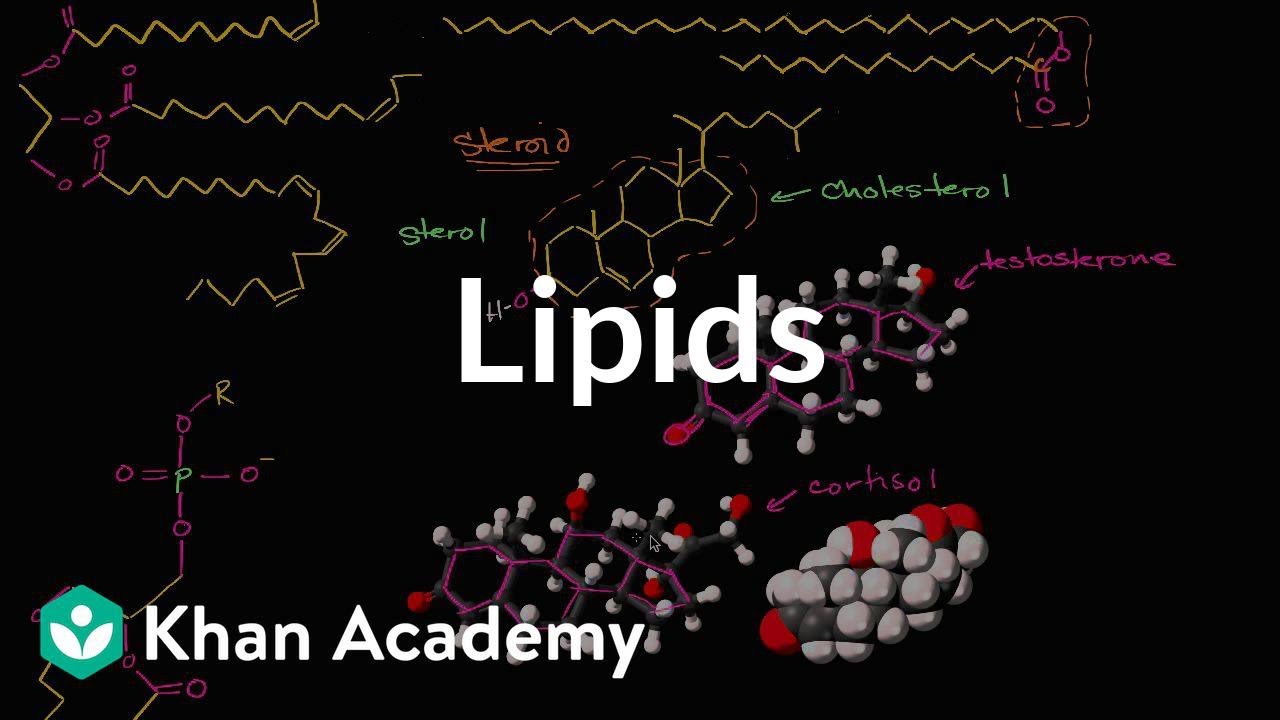
- 🧬 Cholesterol metabolism is crucial for various bodily functions, including the production of bile salts, steroid hormones, and as a component of cell membranes.
- 🚀 Cholesterol synthesis primarily occurs in the liver and involves the conversion of acetyl CoA into cholesterol through a series of enzymatic steps.
- 🔬 The rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis is catalyzed by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is highly regulated and targeted by statin drugs like Lipitor to lower cholesterol levels.
- 💊 Statins work by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, thus reducing cholesterol synthesis for individuals with high cholesterol.
- 🔄 Cholesterol is also obtained through an exogenous pathway by ingesting food and transported to different tissues via chylomicrons.
- 🌀 Cholesterol plays a significant role in cell membranes, affecting fluidity and preventing drastic phase transitions, as well as being part of lipid rafts for signaling pathways.
- 🚀 Cholesterol is a precursor for the synthesis of various steroid hormones, including testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and corticosteroids.
- 🧴 Bile salts, synthesized from cholesterol in the liver, are essential for emulsifying fats, making them more soluble and easier to digest.
- 🚛 Lipoproteins are molecules that transport cholesterol and other lipids through the bloodstream to different tissues, including LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein).
- 🔑 Insulin is an anabolic hormone that stimulates cholesterol synthesis, while glucagon opposes it, promoting the use of cholesterol for energy production or glucose synthesis.
- 🌿 NADPH is required as a reducing agent in the cholesterol synthesis pathway, highlighting its importance in various biosynthetic processes within the body.
Q & A
What is the primary role of cholesterol in the body?
-Cholesterol serves as a basic unit for various functions in the body, including the synthesis of bile salts, steroid hormones such as testosterone, progesterone, estrogen, and cortisol, and as an integral component of cell membranes. It is also involved in the transport of cholesterol via lipoproteins.
Where does cholesterol metabolism mainly occur?
-Cholesterol metabolism primarily occurs in the liver, although cholesterol can be ingested through food and transported to different tissues via chylomicrons.
What is the significance of acetyl CoA in cholesterol synthesis?
-Acetyl CoA is the basic unit used for cholesterol synthesis. It undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions to form cholesterol.
What is the role of insulin in cholesterol metabolism?
-Insulin is the main anabolic hormone in the body and plays a crucial role in cholesterol metabolism by stimulating the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in cholesterol synthesis.
What are bile salts and why are they important?
-Bile salts are molecules derived from cholesterol that aid in the emulsification of large fat globules, making them more soluble in water and easier to digest. They are crucial for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats.
What is the function of HMG-CoA reductase in cholesterol synthesis?
-HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. It catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, which is a crucial step in the production of cholesterol.
How do statins like Lipitor help in managing high cholesterol levels?
-Statins, including Lipitor, inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, thus reducing the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver and lowering overall cholesterol levels in the body.
What is the purpose of incorporating cholesterol into cell membranes?
-Cholesterol in cell membranes helps regulate fluidity, making the membrane less fluid and more rigid. It also prevents drastic phase transitions and is involved in the formation of lipid rafts, which are important for cell signaling processes.
What are lipoproteins and how are they related to cholesterol transport?
-Lipoproteins are complexes of lipids and proteins that transport cholesterol and other lipids through the bloodstream to different tissues. Examples include VLDL, LDL, and HDL, each with specific roles in lipid transport and metabolism.
Why is the synthesis of cholesterol regulated?
-The synthesis of cholesterol is highly regulated because excessive cholesterol can lead to health problems such as atherosclerosis. The body controls cholesterol levels through feedback mechanisms involving HMG-CoA reductase and the influence of hormones like insulin and glucagon.
What is the role of NADPH in cholesterol synthesis?
-NADPH acts as a strong reducing agent and is required in the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate during cholesterol synthesis. It provides the necessary reducing power for this reaction to occur.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)