Lipids (Part 11 of 11) - Sterols / Steroids
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the world of lipids, focusing on sterols and steroids, which share a common steroid nucleus structure. It explains their roles as membrane components and signaling molecules, with cholesterol being a key player in maintaining membrane fluidity. The script also covers bile acids' role in fat emulsification and the significance of steroid hormones, such as testosterone and estradiol, in the body. It touches on corticosteroids, including cortisol and aldosterone, and their impact on stress response and mineral balance. The video concludes with synthetic corticosteroids like prednisone, highlighting their anti-inflammatory properties and potential risks.
Takeaways
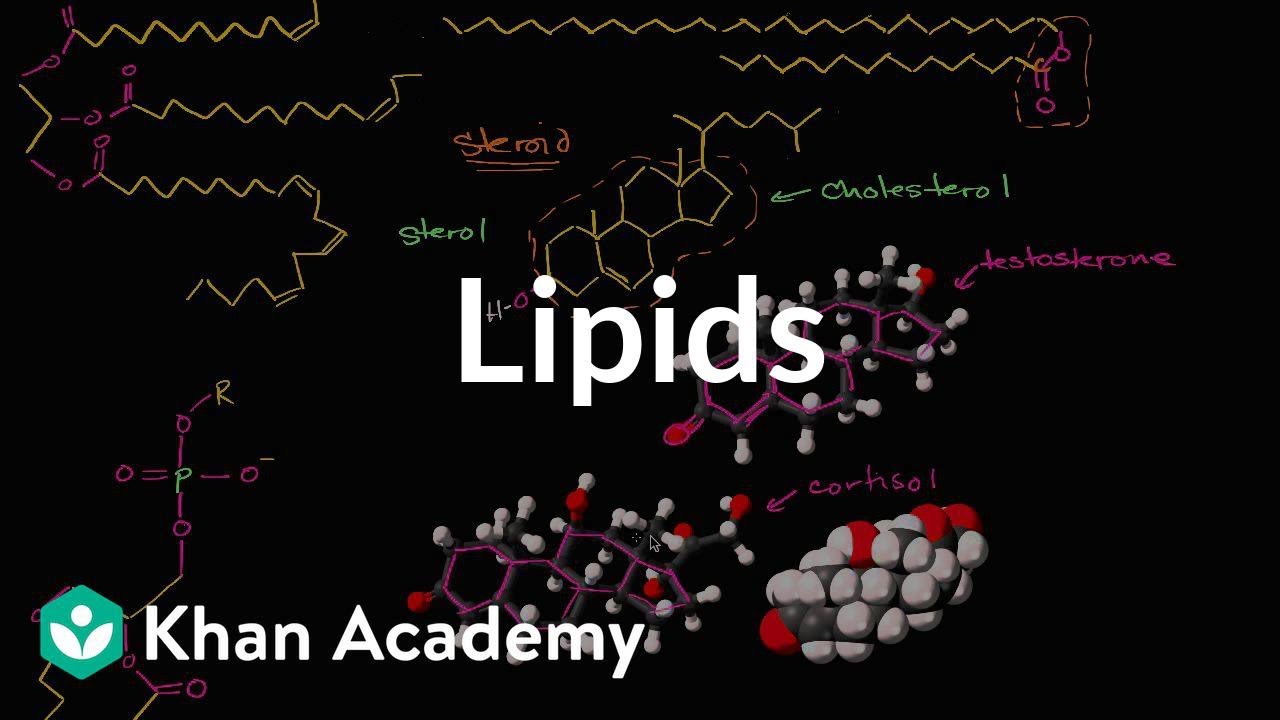
- 🌟 Sterols and steroids are lipids with a basic structure based on a steroid nucleus, which includes four rings: three six-membered rings and one five-membered ring.
- 🔍 Steroids function as membrane components and signaling molecules, such as hormones.
- 🧬 Cholesterol is the major sterol in animals, playing a crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and serving as a precursor to other steroid molecules.
- 🔢 The numbering system of cholesterol is important for understanding enzyme names and their functions in converting one steroid molecule to another.
- 🍗 Bile acids, a type of steroid, help emulsify fats from our diet, making them more accessible for lipases to break down further.
- 🚹🚺 Sex steroids, such as testosterone and estradiol, are produced in the reproductive organs and are involved in various physiological processes.
- 🌡 Corticosteroids, including glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are produced in the adrenal cortex and have effects on blood glucose levels and mineral balance in the body.
- 💊 Synthetic corticosteroids, like prednisone, are used to treat anti-inflammatory diseases and have immunosuppressive effects, which can increase susceptibility to infections.
- 🔬 Steroid hormones, including sex steroids and corticosteroids, exert their effects by altering gene transcription within cells.
- 📚 Understanding the structure and function of steroids is essential for studying various biological pathways and their roles in health and disease.
- 📈 The video aims to provide a comprehensive wrap-up of lipids, focusing on the importance of sterols and steroids in biological systems.
Q & A
What is the basic structure of all steroids?
-The basic structure of all steroids is based on a steroid nucleus, which consists of four rings: three six-membered rings (A, B, and C rings) and one five-membered ring (D ring). This structure is nearly planar.
What roles do sterols and steroids play in biological membranes?
-Sterols and steroids function as membrane components and help maintain membrane fluidity. They prevent the membrane from becoming too rigid or too fluid, thus maintaining optimal fluidity levels.
What is the primary sterol found in animals and what is its main function?
-The primary sterol in animals is cholesterol. It plays a crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and serves as a precursor to other steroid molecules.
How does cholesterol's amphipathic nature contribute to its function in biological membranes?
-Cholesterol's amphipathic nature, with both polar and non-polar portions, allows it to interact with the phospholipids in the membrane, contributing to the membrane's fluidity and stability.
Why is the numbering system of cholesterol important in understanding steroid metabolism?
-The numbering system of cholesterol is important because it helps in identifying the carbon atoms involved in enzymatic reactions that convert one steroid molecule to another, which is essential for understanding steroid metabolism pathways.
What is the function of bile acids in the human body?
-Bile acids function to emulsify fats from our diet, breaking them down into smaller molecules that lipases can act upon for further digestion.
Can you explain the difference between sex steroids and corticosteroids?
-Sex steroids, such as testosterone and estradiol, are produced in the reproductive organs and are involved in sexual development and function. Corticosteroids, on the other hand, are produced in the adrenal cortex and are involved in stress response and regulation of blood glucose and mineral balance.
What is the role of aldosterone in the body?
-Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid that plays a role in regulating sodium levels in the body, which in turn affects blood pressure and fluid balance.
What is the purpose of synthetic corticosteroids like prednisone in medical treatments?
-Synthetic corticosteroids like prednisone are used to treat anti-inflammatory diseases and act as immunosuppressants, reducing inflammation and immune responses.
Why might patients taking synthetic corticosteroids be more susceptible to infections?
-Patients taking synthetic corticosteroids may be more susceptible to infections because these drugs suppress the immune system, reducing the body's ability to fight off pathogens.
How do steroid hormones exert their effects within the body?
-Steroid hormones exert their effects by altering gene transcription within the nucleus of cells, leading to changes in cellular function and response.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Lipid overview | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
Cellteorin (Biologi 2)

Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids

Struktur dan Fungsi Lipid | Biomolekul #3

NEW 2025 EXAM - IB Biology B1.1 - Carbohydrates & Lipids [SL/HL] - Interactive Lecture

Lipids - Structure Of Lipids - Structure Of Fats - Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Prostaglandins
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)