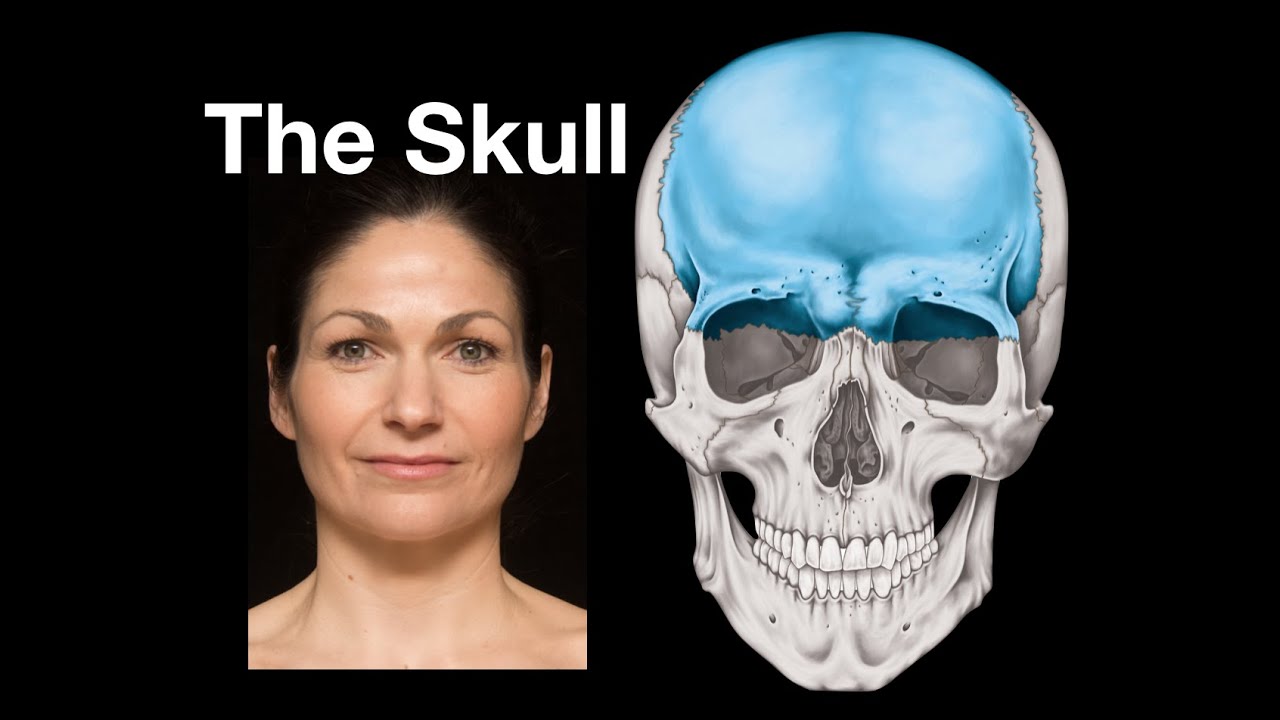
Bones of the skull and more skull anatomy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the intricacies of the human skull, focusing on sutures and bony landmarks. It explains the purpose of sutures like the coronal, sagittal, and lambdoid, and highlights features such as fontanels, which allow for brain growth and ease of childbirth. The script also covers various bony processes and fossae, emphasizing their roles in muscle attachment and housing blood vessels and nerves. The goal is to familiarize viewers with anatomical terms and structures, enhancing their understanding of the skull's complex architecture.
Takeaways
- 💀 The video discusses the anatomy of the human skull, focusing on sutures and bony landmarks.
- 🔍 The sutures are the seams between the bones of the skull, including the coronal, sagittal, lambdoid, and squamosal sutures.
- 👶 Fontanels are soft spots in the skull of infants, allowing for brain growth and facilitating birth.
- 🦴 The skull has various bony processes, such as the mastoid process and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone, which are important for muscle and ligament attachments.
- 👂 The external acoustic meatus is the opening for the ear, located near the mastoid process.
- 👁️ The sphenoid bone is a key part of the skull, with various sutures connecting it to other bones, such as the frontal and parietal bones.
- 🦷 The mandible articulates with the temporal bone at the mandibular fossa, with the condylar process being the articulating part.
- 🧠 The cranial fossae are depressions in the skull that house different parts of the brain, including the anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae.
- 🩺 The internal structures of the skull, such as the sella turcica, are important for the location of the pituitary gland and passage of blood vessels.
- 🦷 The palate is formed by the maxilla, palatine bones, and the sphenoid bone, with the hard palate being a significant structure.
- 🕳️ Foramina in the skull, such as the greater and lesser palatine foramina, are passageways for nerves and blood vessels.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The main focus of the video script is to discuss the anatomy of the skull, specifically the sutures and various bony landmarks, as well as the anatomical terms associated with them.
What are sutures in the context of the skull?
-Sutures are the fibrous joints between the bones of the skull that allow for growth and provide protection to the brain. They are immovable and have a tight interdigitated structure.
What does the term 'coronal suture' refer to?
-The coronal suture is the suture that separates the frontal bone from the two parietal bones and lies in the coronal plane.
What is the sagittal suture, and what does its name signify?
-The sagittal suture is the suture that separates the two parietal bones in the midline. Its name comes from 'Sagittarius the Archer,' symbolizing the straight path of an arrow, which is similar to the suture's direction.
What is the significance of the lambda and bregma in the skull?
-Lambda is the point where the lambdoid suture meets and forms a Y-shape, while bregma is where the sagittal suture meets the coronal suture, forming a T-shape. These points are important anatomical landmarks on the skull.
What are fontanels, and why are they important in infants and fetuses?
-Fontanels are large spaces between the bones of the skull in infants and fetuses, allowing for the rapidly expanding brain to grow without the bones impeding its growth. They also facilitate the molding of the skull during birth for easier passage through the birth canal.
What is the function of the mastoid process and the styloid process in the skull?
-The mastoid process is a bony projection from the temporal bone, and the styloid process is a thin, elongated projection that serves as an attachment point for various muscles and ligaments, including the stylohyoid ligament to the hyoid bone.
What is the purpose of the sphenoid bone in the skull?
-The sphenoid bone is a central bone in the skull that forms part of the眼眶 and the base of the skull. It also houses the pituitary gland and provides attachment points for various structures, including the tentorium cerebelli.
What are the anterior and posterior cranial fossae, and what do they contain?
-The anterior cranial fossa is the space above the sphenoid bone, housing the frontal lobes of the brain. The posterior cranial fossa is located at the back of the skull, containing the cerebellum and brainstem.
What is the function of the pterygoid plates in the skull?
-The pterygoid plates are parts of the sphenoid bone that serve as attachment points for the muscles of mastication, including the lateral and medial pterygoid muscles.
What are the ethmoid bone and its significance in the skull?
-The ethmoid bone is a light, spongy bone located in the orbit of the skull, forming the upper part of the nasal cavity and contributing to the formation of the eye socket.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)