Amides, anhydrides, esters, and acyl chlorides | Organic chemistry | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the chemistry of carboxylic acid derivatives, focusing on the transformations of acetic acid. It explains the systematic and common naming conventions for various derivatives, including amides, esters, anhydrides, and acyl halides. The script provides examples and illustrates the process of substituting the hydroxyl group with different functional groups, highlighting the structural and nomenclature changes that occur.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Carboxylic acids can be transformed into various derivatives by altering the functional groups attached to the carbon chain.
- 📚 Acetic acid, with the systematic name 'ethanoic acid', serves as a base example for discussing carboxylic acid derivatives.
- 🔍 The process of naming derivatives involves identifying the longest carbon chain and the type of functional group attached to the acyl group.
- 🍃 Amides are formed when the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced with an amine, and are named based on the carbon chain length and amine substituents.
- 🧬 Esters result from the replacement of the hydroxyl group with an alkoxide group, and are named as 'ate' derivatives of the parent carboxylic acid.
- 🔗 Anhydrides are formed by the linkage of two acyl groups through an oxygen atom, and are named by appending 'anhydride' to the carboxylic acid name.
- ⚔️ Acyl halides, specifically acyl chlorides, are created by substituting the hydroxyl group with a halogen, and are named as 'yl halide' of the acyl group.
- 🔑 The systematic naming of derivatives involves using the prefix based on the carbon chain length, such as 'ethan-' for two carbons, followed by the type of derivative.
- 🌐 When different substituents are present on the nitrogen in amides, the naming reflects the positions and types of these groups, like 'N-methyl' or 'N-propyl'.
- 📉 Anhydrides typically consist of the same type of carboxylic acid linked together, but can occasionally have different carbon chain lengths if from different acids.
- 🚀 The script promises a follow-up discussion on the relative stabilities of these derivatives and their implications on reaction directions in future videos.
Q & A
What is the common name and systematic name for the molecule discussed in the script?
-The common name for the molecule is acetic acid, and its systematic name is ethanoic acid.
What happens when you replace the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid with an amine?
-When the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced with an amine, the resulting compound is called an amide.
What is the systematic name for the amide formed from acetic acid and a simple amine?
-The systematic name for the amide formed from acetic acid and a simple amine is ethanamide.
How do you name an amide when there are additional carbon chains or groups attached to the nitrogen?
-You start naming with the group attached to the nitrogen, such as 'N-methyl', and then name the acyl group based on the carbon chain length, like 'propanamide'.
What is the common name for the ester formed when an acyl group is bonded to a methyl group?
-The common name for the ester formed when an acyl group is bonded to a methyl group is acetate.
What is the systematic name for the ester derived from acetic acid?
-The systematic name for the ester derived from acetic acid is ethanoate.
What is an anhydride and how is it formed?
-An anhydride is a molecule formed when two acyl groups are joined by an oxygen atom, essentially two carboxylic acids joined together.
What is the name of the anhydride derived from acetic acid?
-The anhydride derived from acetic acid is called acetic anhydride, with the systematic name being ethanoic anhydride.
How do you name an anhydride when the carbon chains on either end have different lengths?
-In the unusual case where the carbon chains have different lengths, you list each of them, such as 'ethanoic propanoic anhydride'.
What is an acyl halide and what is its most common form?
-An acyl halide is a compound where an acyl group is bonded to a halogen atom, with the acyl chloride being the most common form.
What is the systematic name for the acyl chloride derived from acetic acid?
-The systematic name for the acyl chloride derived from acetic acid is ethanoyl chloride.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Asam karboksilat dan ester
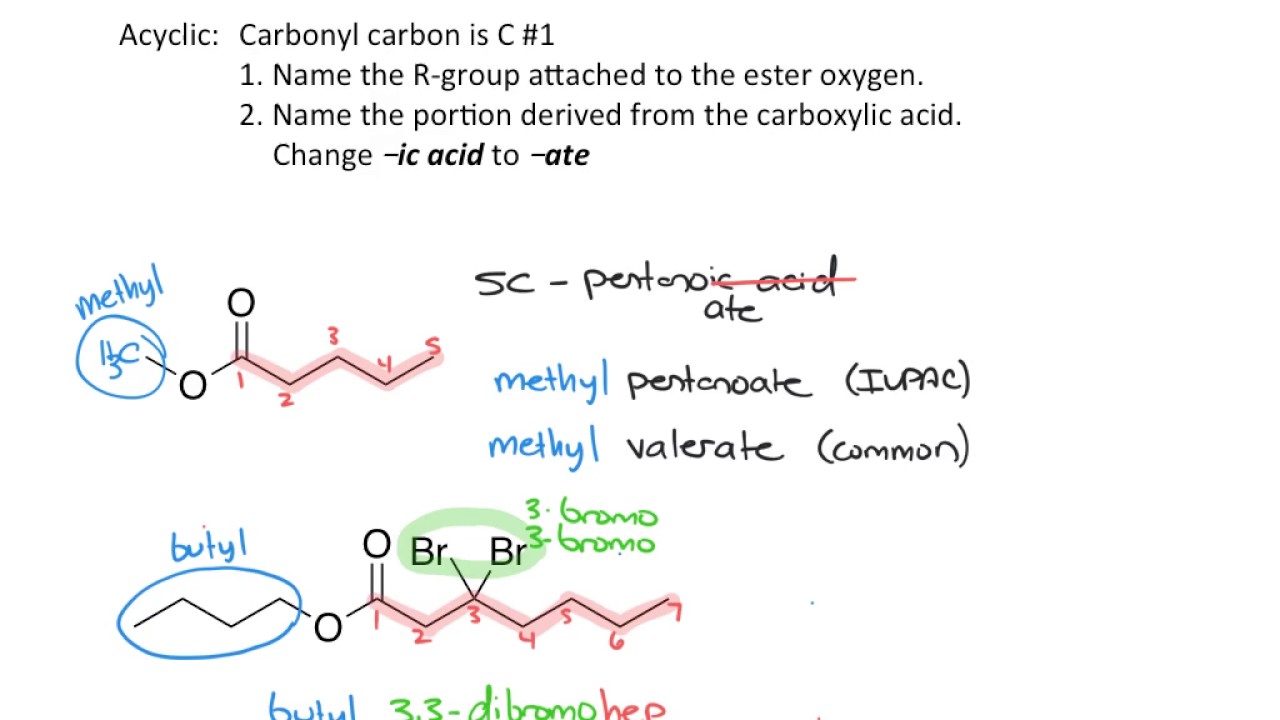
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives

Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - Interconversion & Organometallics: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #32

Les transformations acide-base / BAC Terminale Spécialité Physique Chimie

Carboxylic Acid & Ester - Tagalog

Asam Karboksilat dan Ester | KIMIA KELAS 12
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)