The Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Jacob Clifford explores the Demographic Transition Model (DTM), illustrating how economic development impacts birth and death rates over time. Starting with a historical perspective on the US and Western Europe, the video explains the four stages of DTM, from high birth and death rates in agrarian societies to the current situation where some countries face population decline. Clifford also addresses misconceptions about population growth and the environmental challenges posed by increasing consumption in developing nations, urging viewers to rethink their understanding of economic progress and its global implications.
Takeaways
- 🧐 Hans Rosling often asked his audience questions to reveal their misconceptions about the world's current state.
- 🌍 People commonly underestimate the rate at which the world's population growth is slowing down and the extent to which extreme poverty is decreasing.
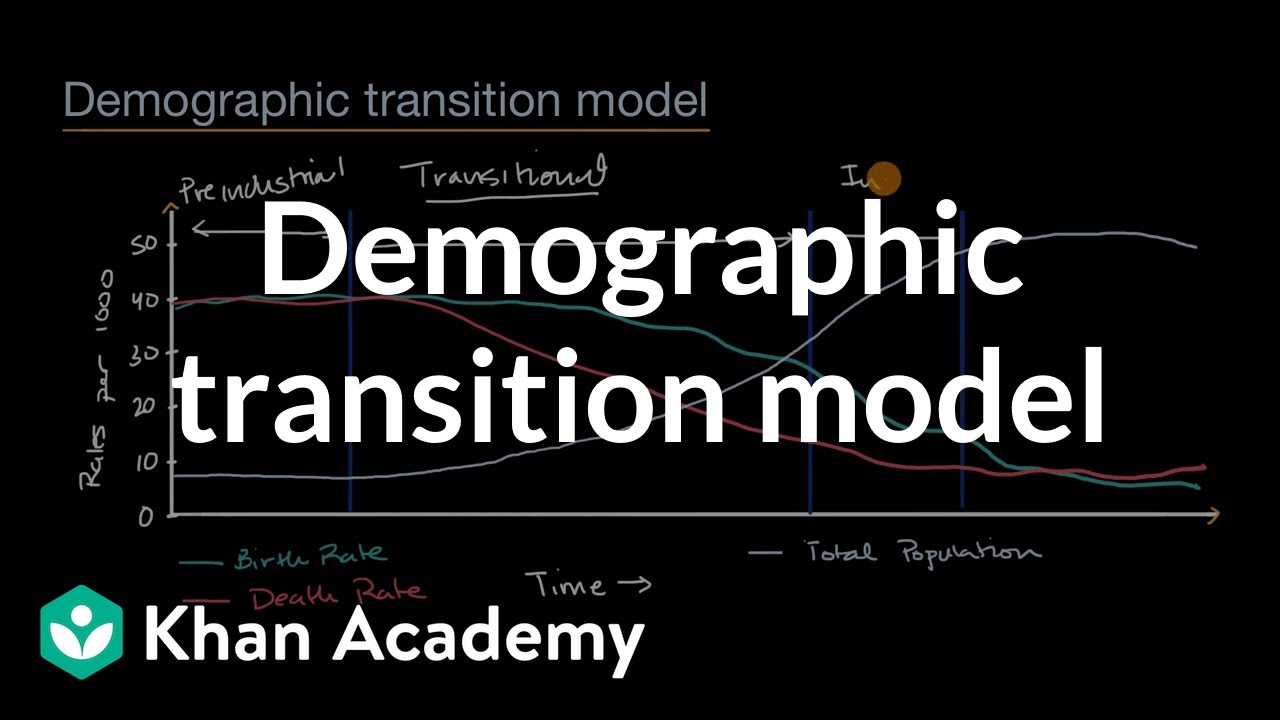
- 📈 The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) illustrates changes in birth rates, death rates, and total population over time.
- 🏭 The Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift in production, leading to better healthcare, education, and sanitation, which in turn lowered the death rate.
- 🌾 Initially, population growth was exponential due to the belief that having more children was economically beneficial, despite a falling death rate.
- 🏙️ Urbanization and industrialization contributed to a decrease in the birth rate as families no longer needed as many children for economic support.
- 🌟 Stage 3 of the DTM is characterized by industrialized countries with a decreasing rate of population growth due to lower fertility rates.
- 🛠️ Post-industrial economies in Stage 4 focus on service industries, have low birth and death rates, and experience zero population growth.
- 🌱 Not all countries are at the same stage of development; some are still in Stage 2 with high birth and death rates, while others are in Stage 4 with stable or declining populations.
- 🌳 The DTM predicts that the global population will eventually stabilize, addressing common fears about overpopulation.
- 🌳 The real challenge may not be overpopulation, but rather the environmental impact of increasing consumption by a growing number of affluent individuals.
Q & A
Who is the main subject of the video script?
-The main subject of the video script is the late great Hans Rosling, a statistician and global health professor, and his approach to understanding the world's economic and demographic changes through the Demographic Transition Model (DTM).
What did Hans Rosling discover about people's perceptions of the world?
-Hans Rosling discovered that most people have preconceived ideas about the world, often thinking it is the same as it was 50 or 20 years ago. They tend to get questions about global trends wrong due to these outdated perceptions.
What is the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
-The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) is a model that explains the transformation in a country's population from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as it undergoes economic growth and industrialization.
What are the four stages of the Demographic Transition Model?
-The four stages of the DTM are: Stage 1 - High birth and death rates with a low population growth; Stage 2 - Decreasing death rates but high birth rates leading to increasing population growth; Stage 3 - Decreasing birth rates with still high population growth but at a decreasing rate; Stage 4 - Low birth and death rates with zero population growth.
Why did Thomas Malthus predict a future of widespread starvation?
-Thomas Malthus predicted widespread starvation because he observed that food production grows at a linear rate, while population grows exponentially, leading him to conclude that eventually, there would not be enough food to sustain the population.
How did the Industrial Revolution impact the Demographic Transition?
-The Industrial Revolution brought about technological advancements that changed food production and economic systems. It led to better healthcare, education, and sanitation, which decreased the death rate. It also caused people to move from rural areas to urban areas, reducing the economic need for large families and thus starting to decrease the birth rate.
What economic activities characterized the first stage of the DTM?
-In the first stage of the DTM, economic activities were primarily subsistence farming, where people grew food for themselves rather than for sale. There was little to no economy beyond this due to the high death rates and low life expectancy.
What are the characteristics of a post-industrial economy as described in the script?
-A post-industrial economy, as described in the script, focuses on service industries such as finance, insurance, and healthcare. It is characterized by low birth and death rates, zero population growth, high life expectancy, gender equality, and high living standards.
Which countries are currently in the fourth stage of the DTM according to the script?
-Countries like China, Canada, and the United States are in the fourth stage of the DTM, characterized by very little population growth and high living standards.
What is the theoretical fifth stage of the DTM, and which countries exemplify it?
-The theoretical fifth stage of the DTM is characterized by a population that is actually falling. Countries like Germany and Japan exemplify this stage.
What is the script's perspective on the issue of overpopulation?
-The script suggests that the problem is not overpopulation itself, but rather the impact of increasing consumption by a growing number of affluent individuals on resources and the environment. It implies that the focus should be on sustainable development and resource management rather than limiting population growth.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Unit 2 - Demographic Transition and Population Pyramids

Demografiska transitionen

APES Video Notes 3.9 - Demographic Transition
Demographic transition model| Human populations| AP Environmental science| Khan Academy

IGCSE Geography: 1.1 Population Dynamics

Animation of the demographic transition model and population growth & decline
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)