Ukuran frekuensi penyakit (Prevalens, Insidens, IMR, MMR, CDR, ASDR)
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides an in-depth exploration of descriptive epidemiology, focusing on key concepts such as incidence and prevalence. It explains how prevalence measures the disease burden in a population at a specific point (point prevalence) or over a period (period prevalence), while incidence assesses the risk of disease development. The script also covers essential mortality rates, such as infant mortality rate (IMR), maternal mortality rate (MMR), and case fatality rate (CFR), alongside the concept of crude death rate (CDR). Furthermore, it highlights the importance of these metrics for disease surveillance, public health planning, and understanding disease dynamics in populations.
Takeaways
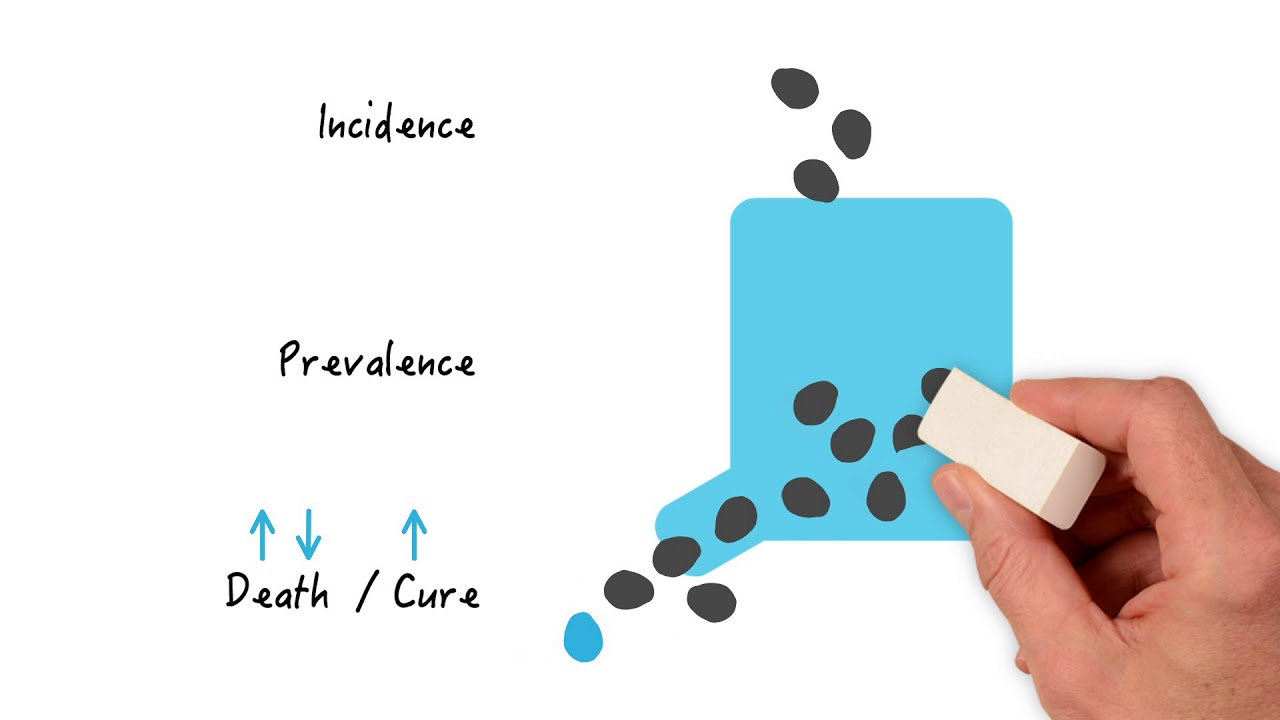
- 😀 Prevalence measures the burden of disease in a population at a specific point in time, while incidence reflects the risk of disease occurrence over time.
- 😀 Point prevalence measures the proportion of a population that has a disease at a specific time, whereas period prevalence accounts for the occurrence of disease over a specified period.
- 😀 Incidence is divided into two types: cumulative incidence (measuring the probability of developing a disease during a specific time) and incidence rate (measuring disease occurrence in terms of person-time).
- 😀 Prevalence can be impacted by both the incidence of new cases and the duration of the disease, especially for chronic conditions with long durations.
- 😀 Point prevalence is ideal for understanding the burden of diseases that persist over time, like chronic illnesses, while period prevalence is better for capturing overall disease exposure during a specific timeframe.
- 😀 Cumulative incidence is useful for calculating the risk of disease in a population and excludes those who are already sick at the beginning of the study.
- 😀 The incidence rate (density) measures how many new cases occur in a population over a given time frame, taking into account the varying durations of observation among individuals.
- 😀 Mortality rates like Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) and Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) are key metrics in descriptive epidemiology, helping measure deaths in relation to live births and pregnancy-related conditions.
- 😀 The Crude Death Rate (CDR) is a broad measure of mortality, representing the number of deaths in a given population during a specific time period, typically expressed per 1,000 people.
- 😀 Age-specific mortality rates (ASMR) provide a more detailed understanding of mortality by focusing on specific age groups within a population, helping identify at-risk groups for certain conditions.
Q & A
What is the difference between prevalence and incidence in epidemiology?
-Prevalence refers to the total number of cases of a disease in a population at a specific point in time, showing the burden of the disease. Incidence, on the other hand, measures the occurrence of new cases within a specific period, indicating the risk of developing the disease.
What is point prevalence, and how is it calculated?
-Point prevalence measures the proportion of individuals in a population who have a specific disease at a single point in time. It is calculated by dividing the number of existing cases by the total population at that time.
What is period prevalence, and how is it different from point prevalence?
-Period prevalence measures the number of individuals who have a disease during a defined time period, such as a year. Unlike point prevalence, which looks at a specific moment, period prevalence takes into account cases over a range of time.
How is incidence rate different from cumulative incidence?
-Incidence rate (or incidence density) measures the rate at which new cases of a disease occur, considering the varying time periods each individual is at risk. Cumulative incidence, however, is the proportion of a population that develops a disease over a fixed time period, assuming all individuals are observed for the same duration.
What is the formula for calculating cumulative incidence?
-Cumulative incidence is calculated by dividing the number of new cases of a disease by the population at risk at the beginning of the observation period.
What is the significance of using incidence rate (or density) in epidemiological studies?
-Incidence rate is crucial for understanding how quickly a disease spreads in a population and accounts for different observation times across individuals. It helps in assessing the burden of a disease more accurately, especially when individuals contribute varying amounts of risk time.
What are the main advantages of using period prevalence over point prevalence?
-Period prevalence captures a broader picture of disease occurrence over time, including both new and existing cases during a specific period. It is especially useful for understanding diseases with long durations or chronic conditions.
What role does the duration of illness play in determining prevalence?
-The duration of illness significantly affects prevalence. If the illness lasts longer, individuals remain part of the prevalence count for a longer time, leading to higher prevalence rates. Chronic diseases with long durations tend to have higher prevalence.
What is the difference between infant mortality rate (IMR) and maternal mortality rate (MMR)?
-Infant mortality rate (IMR) refers to the number of infant deaths per 1,000 live births, whereas maternal mortality rate (MMR) refers to the number of maternal deaths due to pregnancy-related causes per 100,000 live births.
How is the crude death rate (CDR) calculated, and what are its limitations?
-Crude death rate (CDR) is calculated by dividing the total number of deaths in a population by the mid-year population and multiplying by 1,000. Its limitation is that it does not account for age or other demographic factors, which can vary greatly in different populations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Incidence vs Prevalence: Understanding Disease Metrics

Medidas de Associação - Resumo - Epidemiologia

4. Ukuran Frekuensi dalam Epidemiologi (Iwany Amalliah)

DESCRIPTIVE TEXT LENGKAP (CONTOH TEKS, PURPOSE, ANALISIS GENERIC STRUCTURE, LANGUAGE FEATURES)

DISTRIBUSI FREKUENSI - STATISTIK DESKRIPTIF | BAB 2

VIDEO PEMBELAJARAN BAHASA JAWA KELAS X - TEKS DESKRIPSI RUMAH ADAT JAWA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)