Alternator, How it works?
Summary
TLDRAn alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. It typically operates with a rotating magnetic field and a stationary armature. The rotor produces a rotating magnetic field, which induces alternating current (AC) in the armature coils. The frequency of the induced EMF is linked to the rotor speed and the number of poles in the rotor. Alternators use automatic voltage regulators to maintain a constant terminal voltage, adjusting the field current based on load variations. Salient pole rotors are commonly used for low-speed prime movers to minimize mechanical failure due to centrifugal forces.
Takeaways
- 😀 An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, producing alternating current (AC) electricity through electromagnetic induction.
- 😀 There are two types of alternators: one with a rotating magnetic field and a stationary armature, and another with a rotating armature and stationary magnetic field.
- 😀 The most common type of alternator uses a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.
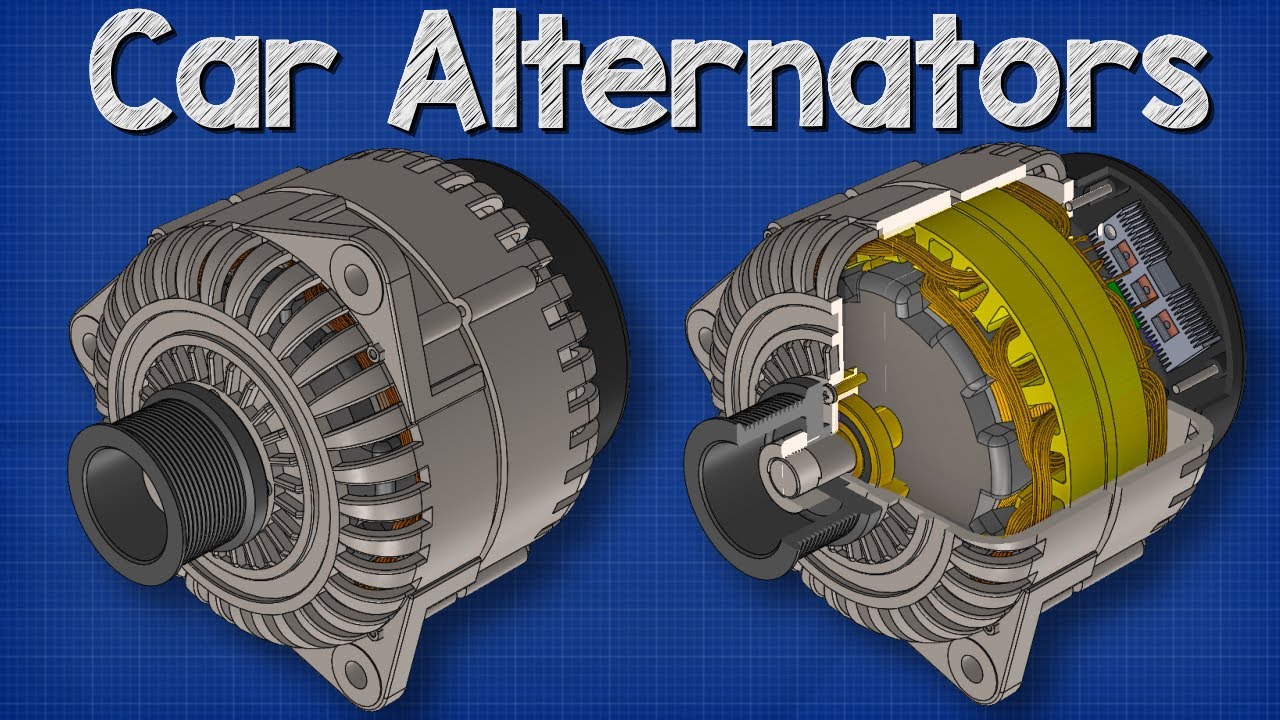
- 😀 The main components of an alternator are the rotor, stator, bearings, slip-rings, voltage regulator, DC generator, and pulley.
- 😀 The rotor creates a rotating magnetic field, which induces electricity in the stationary armature coils.
- 😀 In a typical alternator setup, the rotor's rotating magnetic flux intersects the armature coils, generating an alternating electromagnetic force.
- 😀 The frequency of the induced EMF is directly proportional to the number of poles in the rotor and its rotational speed.
- 😀 For producing three-phase AC current, three armature coils are placed in the stator, each with a 120-degree phase difference.
- 😀 To produce 60 Hz electricity, the rotor speed should be around 1000-800 rpm, but this requires a large number of poles to reduce mechanical failure from centrifugal force.
- 😀 Salient pole rotors, commonly used in alternators, have between 10 to 40 poles, which reduce the need for high rpm and are ideal for prime movers that rotate at lower speeds (120-400 rpm).
- 😀 Alternators use slip rings to supply DC current to the rotor, which in turn creates the rotating magnetic field. These slip rings are designed to handle low voltage DC current.
- 😀 Voltage regulation in alternators is achieved using an automatic voltage regulator, which adjusts the field current to maintain the desired terminal voltage as the load varies.
Q & A
What is the primary function of an alternator?
-An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current (AC) electricity through electromagnetic induction.
What are the two types of alternators used to generate electricity?
-The two types of alternators are: Type 1, which uses a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature, and Type 2, which uses a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field.
Which type of alternator is most commonly used?
-The most commonly used alternator type is the rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature (Type 1).
What are the main parts of an alternator?
-The main parts of an alternator include the rotor, stator, bearings, slip rings, regulator, DC generator, pulley, and outer cover.
What role does the rotor play in an alternator?
-The rotor generates a rotating magnetic field, which induces electricity in the stationary armature coils through electromagnetic induction.
How does the rotor's rotation influence the generated electricity?
-As the rotor turns, the magnetic flux associated with it intersects the stationary armature coils, inducing alternating electromagnetic force (EMF) and generating electricity.
What is a salient pole rotor, and why is it used?
-A salient pole rotor is a type of rotor with poles that protrude outward. It is used in alternators to produce a rotating magnetic field, and it is commonly used in alternators where lower speeds (120 to 400 rpm) are required.
How does the number of poles in the rotor affect the frequency of the induced EMF?
-The frequency of the induced EMF is directly proportional to both the number of poles in the rotor and the rotor speed. The relationship between these variables determines the output frequency of the generated electricity.
Why do alternators with a four-pole rotor require higher rotational speeds to generate electricity?
-A four-pole rotor requires higher rotational speeds (1000-1800 rpm) to generate 60 Hz electricity. At these speeds, the induced EMF takes one complete cycle for every half-revolution of the rotor.
What is the purpose of the automatic voltage regulator in an alternator?
-The automatic voltage regulator ensures that the terminal voltage of the alternator remains within a specified limit by adjusting the field current. If the voltage drops below the desired value, the regulator increases the field current to raise the voltage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

AC Generator 3D animation | Electromagnetic Induction | Electric generator | Working of AC Generator

Principle of Operation of a DC Generator | Electrical & Electronics Engineering

AC Generator
How Alternators Work - Automotive Electricity Generator
Motor VS Generator VS Alternator || How Generator, Motor And Alternator Works || In Hindi

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 9 Bab 4 Magnet
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)