Airway Anatomy - 3D Tutorial
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the structure and function of the human respiratory system, detailing the upper and lower respiratory tracts, including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. It emphasizes the role of alveoli in gas exchange, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are transferred between the lungs and bloodstream. The video also covers key anatomical features such as the pleura, bronchial tree, and alveolar cells, providing a comprehensive overview of how air moves through the respiratory system and how diffusion supports breathing. The video is designed to clarify the complexity of respiratory anatomy in a clear and engaging manner.
Takeaways
- 😀 The respiratory system is divided into the upper and lower respiratory tracts. The upper includes the nose, pharynx, and larynx, while the lower includes the trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs.
- 😀 The pharynx is a passageway extending from the base of the skull to the sixth cervical vertebra, serving both the respiratory and digestive systems.
- 😀 The pharynx is divided into three regions: nasopharynx (posterior to the nasal cavity), oropharynx (posterior to the oral cavity), and laryngopharynx (extends to the larynx).
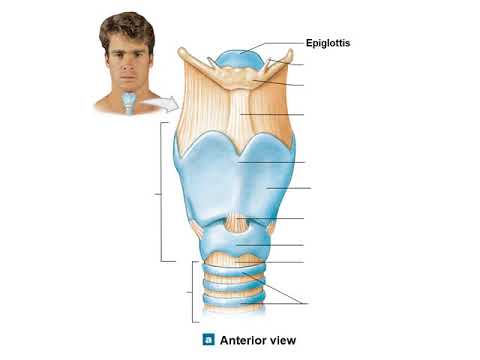
- 😀 The larynx, or voice box, plays a crucial role in speech, where vocal cords vibrate as air from the lungs passes through. It also prevents food from entering the larynx with the help of the epiglottis.
- 😀 The trachea, also known as the windpipe, divides into the right and left bronchi, which channel air into each lung. The trachea is reinforced with hyaline cartilage to prevent collapse.
- 😀 The bronchial tree branches out from the trachea into smaller passageways, eventually leading to tiny air sacs called alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
- 😀 The lungs are spongy organs filled with air spaces and are separated by the mediastinum, which contains the heart. The lungs are attached at the hilum where bronchi and blood vessels enter.
- 😀 The right lung is broader and has three lobes, while the left lung is longer, narrower, and has two lobes. The left lung also has a cardiac notch for the heart.
- 😀 Alveoli are tiny air sacs that facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and blood. They are made up of type 1 pneumocytes (for gas exchange) and type 2 pneumocytes (secrete surfactant).
- 😀 Diffusion of gases occurs in the alveoli: oxygen moves from the alveoli into the capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be expelled from the body.
- 😀 The pleura is a double-layered serous membrane surrounding the lungs, with the visceral pleura attached to the lung and the parietal pleura lining the thoracic wall. The pleural cavity between the layers contains a lubricating fluid.
Q & A
What are the two main divisions of the respiratory system?
-The respiratory system is divided into the upper respiratory tract, which includes the nose, pharynx, and larynx, and the lower respiratory tract, which includes the trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs.
What is the function of the pharynx?
-The pharynx serves both the respiratory and digestive systems. It receives air from the nasal cavity and food, air, and water from the oral cavity. It also connects to the larynx and esophagus.
How is the pharynx divided?
-The pharynx is divided into three regions: the nasopharynx (posterior to the nasal cavity), the oropharynx (posterior to the oral cavity), and the laryngopharynx (extends from the hyoid bone to the lower margin of the larynx).
What is the role of the larynx?
-The larynx, or voice box, acts as a passageway for air between the pharynx and trachea. It also plays a crucial role in sound production when the vocal cords vibrate as air passes through.
What is the structure of the trachea and how does it function?
-The trachea, or windpipe, is the main airway to the lungs. It divides into the right and left bronchi at the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra. Its walls are supported by hyaline cartilage to prevent collapse, and the posterior soft tissue allows the esophagus to expand.
What happens as the bronchial tree branches into smaller passageways?
-As the bronchial tree branches, the amount of hyaline cartilage in the walls decreases, and smooth muscle increases. The mucous membrane also transitions from ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium to simple cuboidal and eventually simple squamous epithelium.
What is the function of the alveoli in the respiratory system?
-The alveoli are responsible for gas exchange in the respiratory system. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli to be expelled from the body.
What types of cells make up the alveoli, and what are their functions?
-The alveoli contain Type 1 pneumocytes, which facilitate gas exchange, and Type 2 pneumocytes, which secrete surfactant to prevent alveolar collapse. Alveolar macrophages are immune cells that clean debris and bacteria.
How do the lungs function during inhalation and exhalation?
-During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, creating negative pressure that causes the alveoli to expand. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes, and the alveoli recoil to expel air.
How does surfactant help the alveoli function?
-Surfactant helps maintain the shape and surface tension of the alveoli, increasing the surface area available for gas exchange. This enables efficient diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide out of the body.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sistema Respiratório 2/6: Vias Aéreas Superiores
Anatomi Sistem Respirasi | Materi Kedokteran Dasar

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 8 Bab 2: Sistem Pernapasan

Respiratory System Anatomy (v2.0)

IMAT Biology Lesson 6.6 | Anatomy and Physiology | Respiratory System

SISTEMA RESPIRATÓRIO - AULA COMPLETA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)