Multiplexing Tutorial - TDM, STDM, FDM Explained
Summary
TLDRIn this detailed presentation, Jake Swick explores the concept of multiplexing and its evolution in communication technology. He explains how multiplexing allows multiple signals to share a single transmission line, reducing the need for excessive wiring. Highlighting three main types of multiplexing—TDM, STDM, and FDM—Jake compares their efficiencies, with FDM being the most effective due to its ability to transmit multiple signals simultaneously. He also discusses the historical impact of multiplexing, from the early messy telephone systems to modern streamlined communications, emphasizing its transformative role in shaping our technological landscape.
Takeaways
- 😀 Multiplexing allows multiple signals to be sent over a single communication line, reducing the need for numerous wires and improving efficiency.
- 😀 Emile Baudot coined the term 'multiplexing' in the 1800s to reduce the clutter and cost of communication lines by allowing multiple messages on one wire.
- 😀 Multiplexing works by combining several signals into a single stream for transmission, which is later separated by a demultiplexer.
- 😀 The main types of multiplexing discussed are TDM (Time Division Multiplexing), STDM (Statistical Time Division Multiplexing), and FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing).
- 😀 TDM assigns equal time slots to all signals, which can result in inefficiencies when some signals are idle.
- 😀 STDM improves on TDM by allocating time slots based on the priority and workload of the signals, making it more efficient.
- 😀 FDM is the most efficient type of multiplexing because it uses different frequencies to send multiple signals simultaneously without interference.
- 😀 FDM is the best option for high-bandwidth communication because it enables simultaneous signal transmission over multiple channels.
- 😀 The progression of multiplexing has drastically improved modern communication, including telephone lines, Ethernet, and cable systems.
- 😀 The historical shift from cluttered wiring systems (like in 1909 NYC) to cleaner, more efficient multiplexing systems demonstrates the transformative impact of this technology.
- 😀 Overall, multiplexing has revolutionized the way we transmit data, improving speed, reducing costs, and creating more efficient communication networks.
Q & A
What is multiplexing and why is it important?
-Multiplexing is a process that allows multiple signals to travel over a single communication line or wire. It is important because it reduces the need for multiple wires, making communication more efficient, cheaper, and easier to manage, thus revolutionizing how data is transmitted over long distances.
Who first introduced the concept of multiplexing and when?
-The concept of multiplexing was first introduced by Emile Baudot, who is credited with coining the term. It became practical in the year 1910 when George Owens Squire worked on improving the system by reducing the number of wires in New York City, making communication lines more efficient.
What were the issues with communication lines before multiplexing?
-Before multiplexing, communication systems were cluttered with multiple wires for different signals, which made systems inefficient, messy, and expensive. For example, in early New York City, each telephone had its own wire, leading to a chaotic and visually overwhelming scene of cables everywhere.
How does multiplexing improve cable management?
-Multiplexing simplifies cable management by reducing the number of wires needed to transmit multiple signals. Instead of each signal having its own dedicated wire, multiple signals can travel over a single wire, making it easier to organize and manage communication infrastructure.
What are the main types of multiplexing discussed in the presentation?
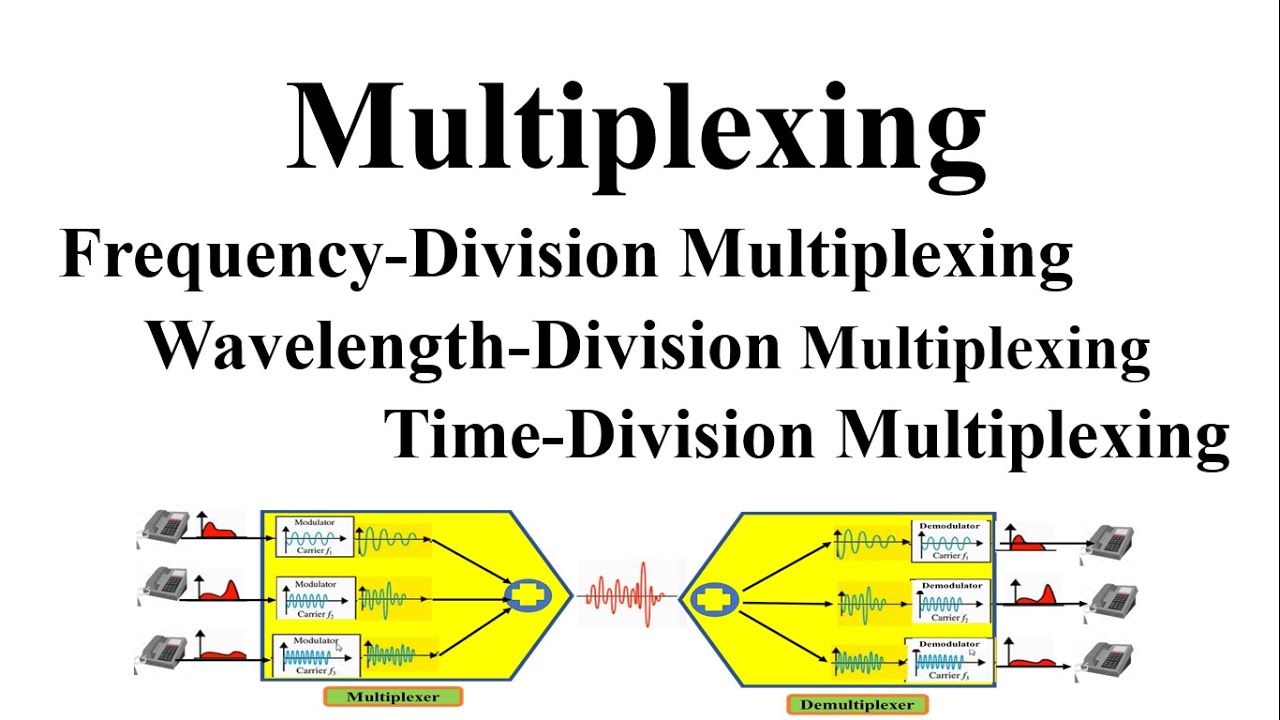
-The presentation discusses three main types of multiplexing: Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (STDM), and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM). Each has its own method of handling multiple signals over a single communication line.
What is Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and how does it work?
-Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) divides time into slots and assigns each signal a specific time slot. Signals are transmitted one after another in a fast, repeating cycle. TDM does not prioritize signals, so it simply sends data in equal time intervals, which can be less efficient in some cases.
How does Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (STDM) improve upon TDM?
-STDM improves upon TDM by allocating time slots based on the priority or workload of each signal. Instead of assigning equal time slots to each signal, STDM prioritizes the busiest or most important signals, making it more efficient and flexible than TDM.
What is Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) and how is it different from TDM and STDM?
-Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) divides the bandwidth of a communication line into multiple channels, allowing several signals to be sent simultaneously over different frequencies. Unlike TDM and STDM, which send signals sequentially, FDM transmits multiple signals at the same time, using different frequency bands to avoid interference.
What are the efficiency rankings of the different types of multiplexing?
-The efficiency ranking of the three types of multiplexing is as follows: FDM is the most efficient because it allows for simultaneous transmission of multiple signals with minimal interference. STDM comes next because it prioritizes signals based on need or workload. TDM is ranked lowest due to its lack of signal prioritization, sending all signals in equal time slots regardless of importance.
How has multiplexing impacted technology and communication systems?
-Multiplexing has had a significant impact on technology and communication systems. It has made data transmission more efficient and affordable, transforming technologies like Ethernet, phone lines, and cable systems. It reduced the clutter of wires and increased the speed and capacity of communication networks, leading to advancements in many areas of technology.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Frequency division multiplexing|Time division multiplexing|FDM|WDM| TDM| computer networks in detail

2.2 - MULTIPLE ACCESS - FDMA/TDMA/CDMA/OFDMA

SISTEM INFORMASI MANAJEMEN|KELOMPOK 5| COMPUTING AND COMMUNICATIONS RESOURCES

LAPORAN TUGAS VIDEO_KELOMPOK1

Media Pembelajaran Kelas 5 "Teknologi Untuk Kehidupan"
Principios del Multiplexado PSA Peugeot Citroën (Peugeot 206)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)