(OLD VIDEO) Why RNA is Just as Cool as DNA
Summary
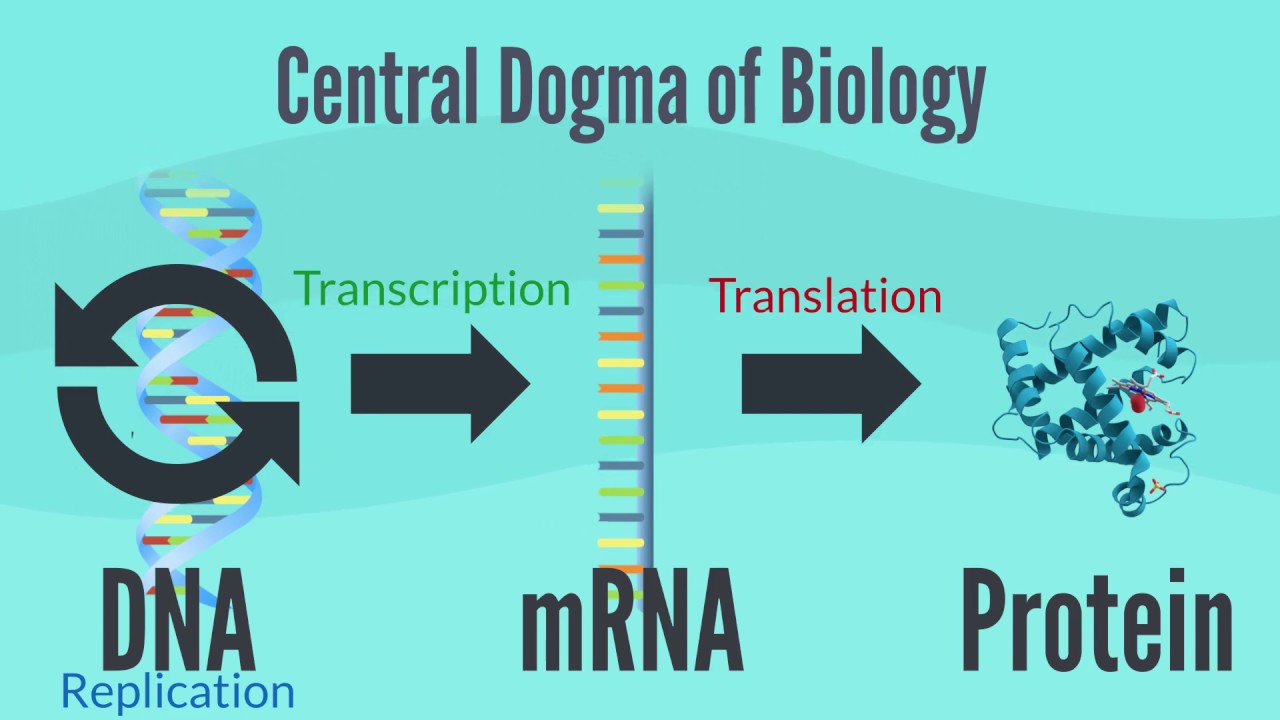
TLDRThis video explores the crucial roles of DNA and RNA in cells, highlighting that while DNA stores genetic information, RNA is essential for translating that information into proteins. It explains the structural differences between DNA and RNA, including their sugars, strands, and bases, and introduces helpful mnemonics for base pairing. The video also breaks down the three types of RNA—mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA—detailing their roles in protein synthesis. By understanding these differences, viewers gain a clear foundation for grasping how genetic information is expressed in cells, making RNA just as important as DNA in the process of creating proteins.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA is important as it codes for traits, but RNA is equally crucial as it helps carry the genetic message to cells for protein production.
- 😀 DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, and RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. Both are types of nucleic acids.
- 😀 DNA is double-stranded and has a double helix shape, while RNA is single-stranded.
- 😀 DNA uses adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) as its nitrogenous bases, while RNA replaces thymine (T) with uracil (U).
- 😀 The mnemonic for remembering DNA base pairs is 'Apples in the Tree' (A-T) and 'Car in the Garage' (C-G). RNA uses 'Apples Under' (A-U).
- 😀 DNA is primarily found in the nucleus of the cell, whereas RNA starts in the nucleus but moves out to carry the genetic message.
- 😀 There are three types of RNA: mRNA (messenger RNA), tRNA (transfer RNA), and rRNA (ribosomal RNA), each with distinct functions.
- 😀 mRNA carries the genetic message from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
- 😀 tRNA is responsible for transferring the amino acids to the ribosome to help build proteins.
- 😀 rRNA is a component of the ribosome and plays a vital role in protein synthesis.
- 😀 Understanding the roles of RNA and DNA is essential for grasping the process of protein synthesis.
Q & A
What is the primary role of RNA in protein synthesis?
-RNA is essential in protein synthesis because it helps carry the genetic message from DNA to the cells, enabling the production of proteins.
How does DNA contribute to the creation of proteins?
-DNA contains the genetic code that provides instructions for creating proteins, which are responsible for traits and functions in an organism.
What is the key difference between DNA and RNA in terms of structure?
-DNA is double-stranded and has a double helix structure, while RNA is single-stranded and has a simpler structure.
What are the key components that make up DNA?
-DNA is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate groups, and four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA, and how do they differ from DNA?
-RNA contains adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The key difference is that RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T), which is found in DNA.
How do the bases pair up in DNA and RNA?
-In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. In RNA, adenine pairs with uracil, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What is the function of messenger RNA (mRNA)?
-mRNA carries the genetic message from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place.
What role does transfer RNA (tRNA) play in protein synthesis?
-tRNA's job is to transfer amino acids to the ribosome, matching them to the codons in the mRNA sequence to help form a protein.
What is ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and why is it important?
-rRNA is a component of ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis. Ribosomes use rRNA to help link amino acids together into proteins.
Where does RNA start and end its journey in the cell?
-RNA starts in the nucleus, where it is transcribed from DNA. It then travels to the cytoplasm, where it aids in protein synthesis at the ribosome.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)