linked list in plain english
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a clear and practical introduction to linked lists, a fundamental data structure in programming. Using relatable examples of storing friends' names and ages, it explains how each data record contains information and a pointer to the next record. The video covers essential operations such as inserting new elements in order, traversing the list to search for specific items, and deleting elements by updating pointers. By walking through step-by-step scenarios with multiple entries, the explanation demystifies how linked lists manage dynamic collections of data, making the concept accessible and easy to understand for beginners.
Takeaways
- 😀 A linked list is a data structure where each element (node) contains data and a pointer to the next node.
- 😀 Each node typically stores the information you want, such as a name and age, along with a 'next' pointer.
- 😀 The head pointer is used to keep track of the start of the linked list.
- 😀 The last node in a linked list points to null, marking the end of the list.
- 😀 Adding a new node involves updating pointers to insert the node at the correct position in the list.
- 😀 To insert a node between two nodes, set the new node's next pointer to the following node, and the previous node's next pointer to the new node.
- 😀 Traversing a linked list requires starting from the head and following next pointers until the desired node is found or the end is reached.
- 😀 Deleting a node involves adjusting the previous node's pointer to skip the node being removed.
- 😀 Linked lists allow dynamic memory management, making insertion and deletion easier than in arrays.
- 😀 Operations on linked lists—such as insertion, deletion, and searching—rely heavily on pointer manipulation to maintain the chain between nodes.
- 😀 The structure of linked lists makes them flexible for organizing elements in a sequence without needing contiguous memory allocation.
Q & A
What is a linked list?
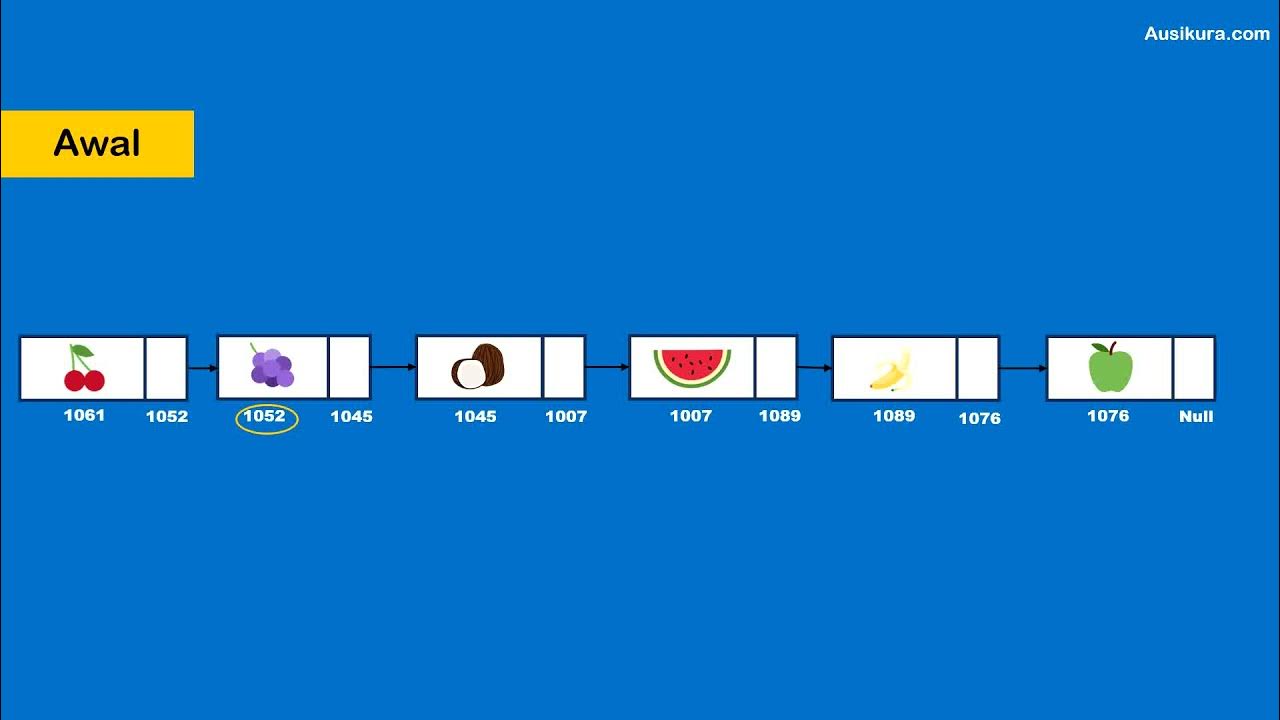
-A linked list is a data structure where elements, called nodes, are connected sequentially using pointers. Each node contains data and a reference to the next node in the sequence.
What are the main components of a linked list node?
-Each node in a linked list typically has two main components: the data fields (e.g., name and age) and a pointer to the next node in the list.
What is the role of the 'head' in a linked list?
-The head is a pointer that references the first node in the linked list. Traversals and searches always start from the head.
How do you traverse a linked list to find an element?
-To traverse a linked list, start at the head and check each node's data. If it doesn't match the target, follow the next pointer to the next node, repeating until the element is found or the end of the list is reached.
How is a new node inserted into a linked list?
-To insert a new node, first find its correct position. Update the new node's next pointer to point to the next node, then update the previous node's next pointer to point to the new node, effectively linking it into the list.
How would you insert a node at the end of a linked list?
-For insertion at the end, set the new node's next pointer to null and update the previous last node's next pointer to reference the new node.
How is a node deleted from a linked list?
-To delete a node, traverse the list to find it. Then, update the previous node's next pointer to skip the node being deleted and point to the next node, effectively removing it from the list.
What happens if you traverse a linked list and reach a null pointer?
-Reaching a null pointer indicates the end of the linked list, meaning there are no further nodes to traverse.
Why might a linked list be preferred over an array?
-A linked list allows dynamic memory allocation and easy insertion or deletion of elements without shifting other elements, unlike arrays which have fixed sizes and require shifting.
In the provided example, how are nodes ordered alphabetically?
-Nodes are ordered alphabetically by comparing the names of the people as they are inserted. The new node is placed between two existing nodes if its name comes between theirs alphabetically.
What is the significance of the 'next' pointer in a linked list?
-The next pointer connects nodes together, forming the chain-like structure of the linked list. It allows traversal and insertion/deletion operations to navigate and modify the list efficiently.
How does inserting a node between two existing nodes work?
-To insert a node between two nodes, set the new node's next pointer to the second node, and then update the first node's next pointer to point to the new node, linking it into the list.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

#1 Introduction to Lists | List Manipulation | Class 11 CBSE Computer Science and IP
Pengenalan Linked List - struktur Data (Animasi)

DATA STRUCTURES VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS | DATA STRUCTURES Interview QUESTIONS with ANSWERS

Linked List Data Structure | Illustrated Data Structures

ENTENDA LISTAS ENCADEADAS EM C EM POUCOS MINUTOS!

2.2 Types of Linked List in Data Structures | DSA Full Course
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)