What is Mechanics of Materials and why it is important in engineering?
Summary
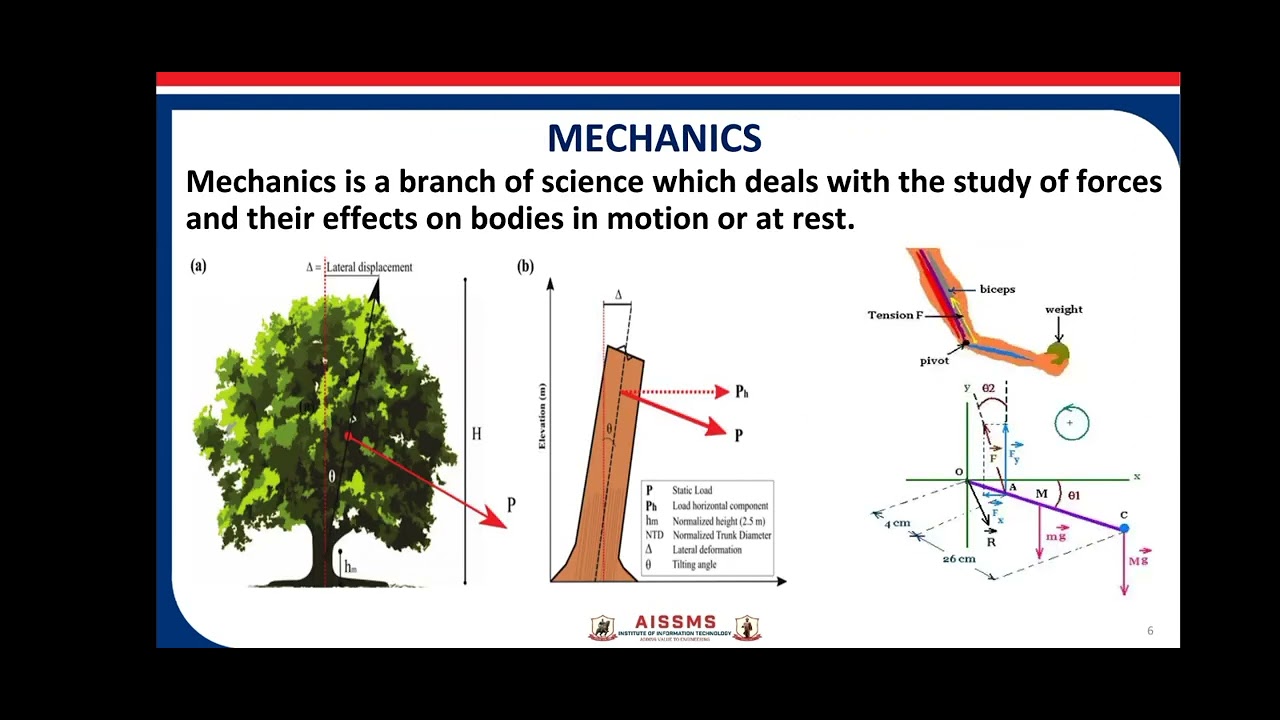
TLDRMechanics of materials, a core branch of engineering mechanics, studies how real-world objects deform and respond to forces. Unlike statics and dynamics, which assume rigid bodies, it focuses on internal forces (stress) and deformations (strain) in structures like beams, shafts, and pressure vessels. The subject is vital for designing safe and functional load-bearing objects, ensuring strength, stiffness, and stability. Success in learning mechanics of materials relies on a solid understanding of statics, mathematics, and problem-solving skills. By studying it, engineers gain essential insights into material behavior and develop critical problem-solving abilities applicable across diverse engineering fields.
Takeaways
- 🛠️ Mechanics of materials studies how real-world objects deform and react under applied forces, unlike statics and dynamics which assume rigid bodies.
- ⚖️ Statics focuses on the equilibrium of forces on bodies at rest, while dynamics studies the motion of bodies under forces.
- 📱 Mechanics of materials examines internal stresses and deformations, for example, when a cell phone hits the ground.
- 🏗️ Engineers use mechanics of materials to design safe and functional load-carrying structures such as bridges, buildings, and vehicles.
- 💪 Strength is a key design criterion, ensuring components withstand predicted loads without failure or fracture.
- 📏 Stiffness is another criterion, reflecting a structure's resistance to excessive deformation under load.
- ⚠️ Stability ensures that structures do not fail suddenly, such as through buckling, before reaching maximum strength.
- 🔍 Key concepts include stress (internal forces) and strain (deformation), which are analyzed in components like beams, shafts, pipes, and pressure vessels.
- 📐 Prerequisites for studying mechanics of materials include knowledge of statics, free body diagrams, section properties, and mathematical tools like derivatives, integrals, and limits.
- 🧠 Problem-solving skills are essential in mechanics of materials, as engineers must analyze new and challenging scenarios to design safe structures.
- 🎓 Undergraduate courses cover the fundamentals, while advanced topics are typically taught at the senior or graduate level.
Q & A
What is mechanics of materials?
-Mechanics of materials is a branch of engineering mechanics that studies how real-world objects deform under applied forces, focusing on the distribution of internal forces (stress) and resulting deformation (strain).
How does mechanics of materials differ from statics and dynamics?
-Statics and dynamics assume objects are rigid. Statics studies forces on stationary objects, while dynamics studies forces on moving objects. Mechanics of materials, however, studies deformable objects and how they respond internally to applied forces.
Why is mechanics of materials important for engineers?
-It is important because engineers need to design safe and functional load-bearing structures like bridges, vehicles, buildings, and machines. Understanding stress, strain, and material behavior ensures components meet strength, stiffness, and stability requirements.
What are the three main criteria engineers must consider when designing structures?
-The three main criteria are strength (ability to carry loads without failure), stiffness (resistance to excessive deformation), and stability (resistance to sudden failure before reaching maximum strength).
What is stress and why is it important?
-Stress is the internal force per unit area within a material. It is important because it helps engineers determine how forces are distributed inside a component and whether it can safely carry the applied loads.
What is strain and why is it studied?
-Strain is the measure of deformation in a material caused by applied forces. Studying strain allows engineers to understand how much an object will deform under a load, ensuring it remains functional and safe.
Can you give an example illustrating the difference between statics, dynamics, and mechanics of materials?
-A cell phone on a table: Statics studies the equilibrium of the phone at rest. Dynamics studies its motion if it falls. Mechanics of materials studies how the phone deforms, how internal forces are distributed, and whether it breaks upon impact.
What topics are typically covered in an undergraduate mechanics of materials course?
-Undergraduate courses cover stress and strain, axial members, torsional elements, beams, shafts, pipes, pressure vessels, stress and strain transformations, and basic failure theories, preparing students for advanced study.
What skills and knowledge are required to be successful in mechanics of materials?
-Success requires strong understanding of statics (equilibrium equations, free body diagrams, centroid, and moment of inertia), mathematical skills (calculus including derivatives, integrals, and limits), and problem-solving abilities to tackle new and challenging problems.
What is instability failure and how does it differ from material fracture?
-Instability failure occurs when a structure suddenly fails under load before reaching its maximum strength, such as a buckling ruler. It differs from material fracture, where the material itself breaks or cracks under load.
Why is stiffness an important criterion in design even if a structure can carry the load?
-Stiffness is important because excessive deformation can make a structure unusable, like a sagging floor or a swaying suspension bridge, even if the material has not fractured and can still carry the load.
How does studying mechanics of materials enhance an engineer’s problem-solving skills?
-Mechanics of materials involves analyzing stress, strain, and deformation in various components, often requiring new approaches and calculations. This practice strengthens analytical and problem-solving abilities, which are essential for engineering work.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Introduction to Engineering Mechanics

Statics: Crash Course Physics #13

Introduction to Engineering Mechanics

Statika Partikel 3D (1/5): Komponen Gaya dalam Tiga Dimensi

Introduction to Semiconductor Physics and Devices

Atomic Structure and Bonding Explained | Chapter 2 – Materials Science and Engineering
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)