Body Cavities and Serous Membranes | Corporis
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Patrick Kelly dives into the fascinating organization of the human body, focusing on body cavities, the organs they contain, and the protective membranes that surround them. He explains the dorsal cavity housing the brain and spinal cord, and the ventral cavity containing lungs, heart, digestive organs, and reproductive organs. The video also covers subdivisions like the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities, and highlights serous membranes that minimize friction between organs. Using relatable analogies and memory aids, Patrick makes complex anatomy concepts accessible and engaging, helping viewers understand both the structure and function of the body’s internal spaces.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The human body is organized into cavities, which are empty spaces that contain and protect vital organs.
- 🦴 The dorsal cavity, located at the back, houses the brain in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the vertebral cavity.
- 🛡️ The brain and spinal cord are protected by three layers of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid, providing cushioning similar to a padded helmet.
- 💓 The ventral cavity, at the front of the body, contains organs like the lungs, liver, intestines, and reproductive organs, and has less rigid protection.
- 🏋️♂️ The ventral cavity is divided into the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity, separated by the diaphragm.
- ❤️ The thoracic cavity contains the pericardial cavity for the heart and the pleural cavities for the lungs.
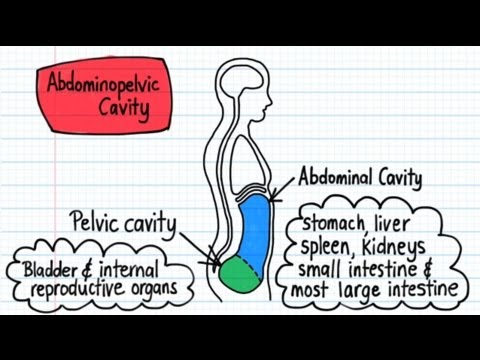
- 🍽️ The abdominopelvic cavity holds most of the digestive system and some immune system components, extending down into the pelvis.
- 👀 Other smaller cavities include the orbital cavities for the eyes and the oral cavity for the mouth and tongue.
- 🫧 Serous membranes line body cavities and organs, reducing friction and providing lubrication with a small amount of serous fluid.
- 🧩 Each serous membrane has a parietal layer (lining the cavity), a visceral layer (wrapping organs), and sometimes specialized names like pericardium or pleura.
- 🩺 The heart’s layers include a fibrous outer layer, parietal layer, serous fluid space, and visceral layer (epicardium), following the same basic structure as other cavities.
- 📚 Understanding body cavities and membranes helps explain organ positioning, protection, and interactions during both healthy and pathological conditions.
Q & A
What is the main concept introduced at the beginning of the video regarding the human body?
-The video introduces the idea that the human body can be seen as a 'squishy meat sack' composed of fluid-filled bundles of cells, most of which occupy empty space, organized into body cavities containing important organs.
How are body cavities different from sinuses?
-Body cavities contain important organs, while sinuses are typically empty spaces filled with mucus, fluid, or air and do not house major organs. Sinuses can fill during conditions like sinus headaches or swelling.
What are the two main body cavities, and where are they located?
-The two main body cavities are the dorsal cavity located at the back, containing the brain and spinal cord, and the ventral cavity located at the front, containing organs such as the lungs, liver, intestines, and reproductive organs.
What protective structures are found in the dorsal cavity?
-The dorsal cavity protects the brain and spinal cord with bony structures (skull and vertebral column), three layers of meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid to cushion and protect these delicate structures.
How is the ventral cavity organized, and why is it less rigid?
-The ventral cavity is less rigid and more flexible, which allows organs like the lungs, spleen, and uterus to change size and shape. It is divided into the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity, separated by the diaphragm.
Which cavities are found within the thoracic cavity, and what do they contain?
-The thoracic cavity contains the pericardial cavity, which houses the heart, and the pleural cavities, which house the two lungs.
What is the significance of the abdominopelvic cavity extending into the pelvis?
-Including the pelvis in the abdominopelvic cavity ensures that all contents from the abdomen down to the pelvic floor muscles are accounted for, including parts of the digestive and immune systems, as well as reproductive organs.
What are serous membranes, and what role do they play?
-Serous membranes are layers of epithelial tissue that line body cavities and wrap around organs. They secrete a small amount of serous fluid to minimize friction and prevent organs from rubbing against each other.
What is the difference between parietal and visceral membranes?
-The parietal membrane lines the walls of a body cavity, while the visceral membrane wraps directly around individual organs. Between them is a small space containing serous fluid for lubrication.
Can you give examples of specialized names for serous membranes?
-Yes. The pericardium surrounds the heart, and the pleura surrounds the lungs. Despite different names, their basic structure and function are similar, consisting of parietal and visceral layers with serous fluid in between.
What analogy does the video use to explain the organization of body cavities?
-The video compares the body to an 'organized meat sack' and likens the arrangement of organs and cavities to a nightclub, where serous membranes act like lubrication to prevent friction between crowded organs.
What additional content does the video mention for further learning about tissue types?
-The video references a separate video dedicated to different tissue types, such as epithelial and connective tissue, explaining how to identify and differentiate them.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Body Cavities and Membranes: Drawn and Defined [Anatomy Physiology]

Body Cavities and Membranes (Dorsal, Ventral)- Anatomy and Physiology

LA CELLULE : UNE VILLE MAGNIFIQUE - BMShow
Body Cavities - Drawn & Defined

Tissues of Human Body | Animation | Simple Explanation

◣มสธ.◢ 50102 รายการที่ 1 ตอนที่ 1 ความรู้เกี่ยวกับร่างกายมนุษย์ (1)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)