6 Hallmarks of Cancer | What you need to know
Summary
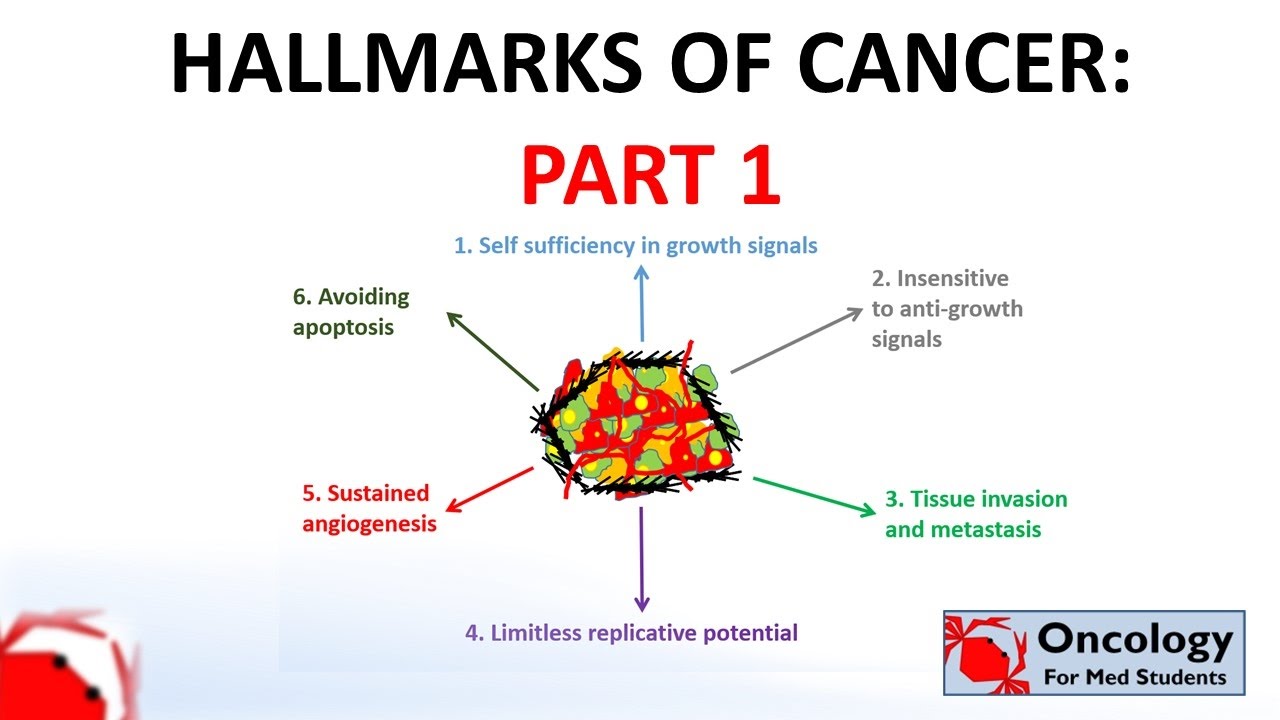
TLDRThe Hallmarks of Cancer, first described by Dr. Robert Weinberg in 2000, outline key biological traits of cancer cells that drive tumor growth and progression. These traits include uncontrolled cell proliferation, evasion of apoptosis (cell death), unlimited replication (immortalization), tissue invasion and metastasis, and angiogenesis (blood vessel formation). Cancer cells manipulate both intrinsic and extrinsic signals to bypass normal regulatory mechanisms, enabling continuous growth and spread. Understanding these processes has been crucial for advancing cancer research and developing therapeutic strategies.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Hallmarks of cancer, first described by Dr. Robert Weinberg in 2000, represent the core biological properties that contribute to cancer development and progression.
- 😀 The regulation of cell proliferation is tightly controlled in normal tissues by both internal mechanisms and external signals, but cancer cells can bypass these controls.
- 😀 Cancer cells can sustain uncontrolled proliferation, even under unfavorable conditions, by producing their own growth factors or signaling to nearby cells.
- 😀 In normal cells, external anti-growth signals and internal checkpoints prevent unnecessary cell division, but cancer cells often disrupt these control mechanisms.
- 😀 Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a critical mechanism for eliminating abnormal cells, but cancer cells often evade this process, allowing them to survive.
- 😀 Cancer cells can bypass internal mechanisms that limit the number of divisions, leading to their immortalization and enabling indefinite cell replication.
- 😀 Normal tissues maintain a defined architecture that is essential for organ function, but cancer cells can disrupt this structure, leading to invasion and metastasis.
- 😀 Metastasis allows cancer cells to invade surrounding tissues, enter the bloodstream, and spread to distant sites, contributing to disease progression and severity.
- 😀 Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is essential for tumor growth, as it provides necessary nutrients and oxygen to support continuous cell division.
- 😀 The disruption of normal biological mechanisms by cancer cells is responsible for their ability to thrive, invade other tissues, and metastasize, ultimately worsening the disease.
Q & A
What are the Hallmarks of cancer as described by Dr. Robert Weinberg?
-The Hallmarks of cancer are six distinct biological properties of cancer cells that contribute to the cancer phenotype. These features were first described in 2000 by Dr. Robert Weinberg and are still relevant today in understanding cancer development and progression.
How is normal cell proliferation controlled?
-Normal cell proliferation is tightly regulated through the cell cycle, a process governed by internal mechanisms and external signals from the cellular environment. This balance ensures proper cell division, promoting growth under favorable conditions and halting it when conditions are unfavorable.
What mechanisms do cancer cells use to sustain proliferation?
-Cancer cells can sustain proliferation even in unfavorable conditions by producing their own growth factors or signaling to nearby cells. They can also have dysregulated cell surface receptors that become hypersensitive to growth signals or remain in an active state continuously.
What happens when the cell cycle checkpoints and anti-growth signaling pathways are disrupted in cancer cells?
-In cancer cells, the loss or disruption of cell cycle checkpoints and anti-growth signaling pathways leads to uncontrolled and persistent cell division, bypassing the normal regulation mechanisms that prevent excessive cell proliferation.
What is apoptosis, and how do cancer cells avoid it?
-Apoptosis is programmed cell death, a regulated process that eliminates damaged cells to maintain the health of the organism. Cancer cells often accumulate mutations that allow them to bypass apoptosis, enabling them to survive despite abnormal or damaged conditions.
Why is cell immortality a significant feature of cancer cells?
-Cell immortality refers to the ability of cancer cells to divide indefinitely. This occurs because cancer cells lose the mechanisms that control the number of divisions, allowing them to replicate without the normal limits on lifespan, a feature crucial for tumor formation and progression.
How do cancer cells invade neighboring tissues and metastasize?
-Cancer cells activate signaling pathways that allow them to invade surrounding tissues, enter the bloodstream, and travel to distant organs. This process, known as metastasis, enables cancer cells to form new tumors at secondary sites, worsening the disease's severity.
What is angiogenesis, and why is it important for tumor growth?
-Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues. Tumors also require angiogenesis to sustain growth, as the newly formed blood vessels provide the necessary resources for continuous cell division and metastasis.
What role does the microenvironment play in cancer cell growth?
-The cancer cell microenvironment plays a crucial role in tumor progression. Cancer cells can influence nearby cells in their environment to support tumor growth by providing growth factors, increasing blood supply through angiogenesis, and allowing cells to evade normal growth controls.
How does the failure of apoptosis contribute to cancer progression?
-The failure of apoptosis in cancer cells allows abnormal or damaged cells to survive and continue dividing. This evasion of cell death contributes to the accumulation of mutations and the unchecked growth of the tumor, leading to cancer progression.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
4. Hallmarks of Cancer (part 1)

5. Hallmarks of cancer (part 2)

7. Proto-oncogenes and Oncogenes

Cell Cycle and Cancer: Phases, Hallmarks, and Development

"시원하게 암세포 녹습니다" 암 치료 12년 의사가 뽑은 시한부 살리고 암세포 씨말리는 인생 최고의 건강 음식 (김지호 원장 1부)

Breaking Myths: What Really Fuels Cancer Growth, with Dr. Fung and Dr. Seyfried | TCP Ep. 71
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)