Characteristics of Minerals
Summary
TLDRThis lesson explores the characteristics of minerals, focusing on the five key criteria that define a mineral: natural occurrence, solid state, definite chemical composition, orderly atomic arrangement, and being inorganic. Students learn how to distinguish minerals from non-minerals, with examples like gold, pearls, and salt. The lesson also delves into mineral categorization by chemical and physical properties, highlighting their uses in electronics, cosmetics, transportation, and even nutrition. The goal is for students to identify and explain minerals based on these defining characteristics.
Takeaways
- 😀 A mineral is defined by five essential characteristics: naturally occurring, solid, definite chemical composition, orderly structure, and inorganic.
- 😀 To be considered a mineral, an object must meet all five characteristics; rocks are made of minerals.
- 😀 Minerals must be naturally occurring, meaning they are not man-made (e.g., a feather or shell is naturally occurring, but a pen is not).
- 😀 A mineral must be a solid, not a liquid or gas, in order to qualify as a mineral.
- 😀 Minerals have a definite chemical composition, meaning their chemical makeup is consistent (e.g., fluorite always contains calcium and fluorine in a specific ratio).
- 😀 Minerals must have an orderly atomic structure, not a random arrangement.
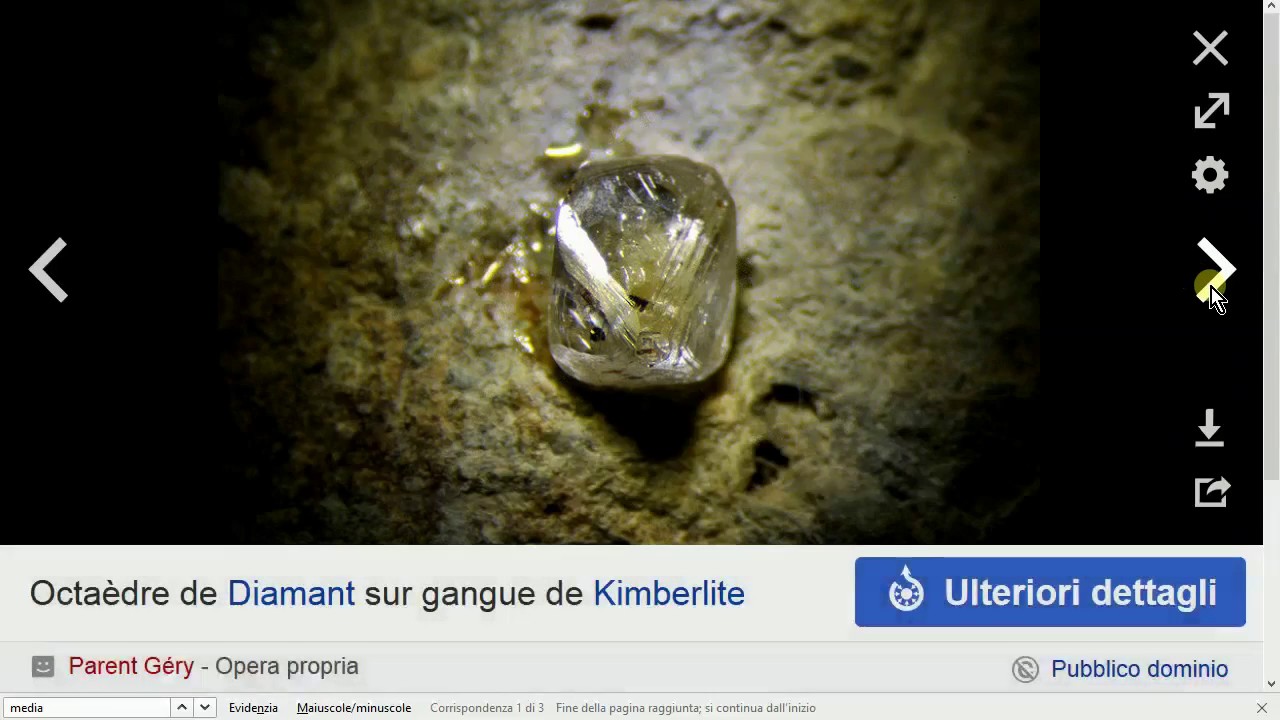
- 😀 A mineral is inorganic, meaning it was never alive (e.g., diamonds are minerals but fossils are not).
- 😀 Pearls are not minerals because, despite being naturally occurring, they are organic and created by living organisms (oysters).
- 😀 Table salt (NaCl) is a mineral because it meets all five characteristics: naturally occurring, solid, definite chemical composition, orderly structure, and inorganic.
- 😀 Minerals are categorized into groups based on their chemical and physical properties, such as silicates, carbonates, and sulfides.
- 😀 Minerals are used in everyday products, such as electronics, cosmetics, transportation materials, and are essential for nutrition (e.g., fortified cereals).
Q & A
What are the five characteristics that all minerals must have in common?
-The five characteristics that all minerals must have are: 1) Naturally occurring, 2) Solid, 3) Definite chemical composition, 4) Ordered atomic structure, 5) Inorganic.
Why is it important to understand the characteristics of minerals before studying rocks?
-It is important because all rocks are made of minerals. Understanding the characteristics of minerals helps us understand the properties of rocks and how they are formed.
What does it mean for a mineral to be 'naturally occurring'?
-A mineral is considered 'naturally occurring' if it is not man-made and is formed through natural processes, like those found in the earth's crust.
Why can't a mineral be a liquid or gas?
-A mineral must be a solid because its atoms are arranged in an orderly pattern, which would not be possible in a liquid or gas. Liquids and gases do not have a fixed atomic structure.
Can you provide an example of a mineral with a definite chemical composition?
-An example is fluorite, which has the chemical composition of calcium fluoride (CaF2). For every calcium atom, there are two fluorine atoms.
What is the significance of a mineral being 'inorganic'?
-Being 'inorganic' means the mineral was never alive. For example, diamonds are minerals made from carbon that underwent extreme pressure, while organic materials like dinosaurs are not minerals.
Why are pearls not considered minerals?
-Although pearls are solid, naturally occurring, and have a definite chemical composition, they are organic because they are created by living organisms (oysters), so they do not meet the 'inorganic' criterion for minerals.
How can we determine if something is a mineral or not?
-To determine if something is a mineral, you need to check if it meets the five characteristics: naturally occurring, solid, definite chemical composition, ordered atomic structure, and inorganic.
What are some common uses for minerals in everyday life?
-Minerals are used in electronics, cosmetics, transportation, and construction materials. For example, mica and quartz are used in electronics, while hematite is used for iron in cars.
What is the most abundant type of mineral on Earth?
-Silicate minerals are the most abundant, making up 90% of Earth's crust. They contain silicon and oxygen.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)