Nuclear Chemistry vs Traditional Chemistry
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the key differences between traditional chemistry and nuclear chemistry. In traditional chemistry, atoms remain the same, only rearranging through chemical reactions, with energy changes relatively small. However, nuclear chemistry involves altering the atomic nucleus, leading to significant changes in the atom's type and mass. The video highlights different nuclear reactions such as fission, fusion, and decay, which release massive amounts of energy. These energy changes are far larger than in chemical reactions, and due to the mass-energy relationship, nuclear reactions don't conserve mass like chemical ones do.
Takeaways
- 😀 In chemistry, the focus is on electrons because they hold atoms together in bonds, and chemical reactions involve rearranging these bonds.
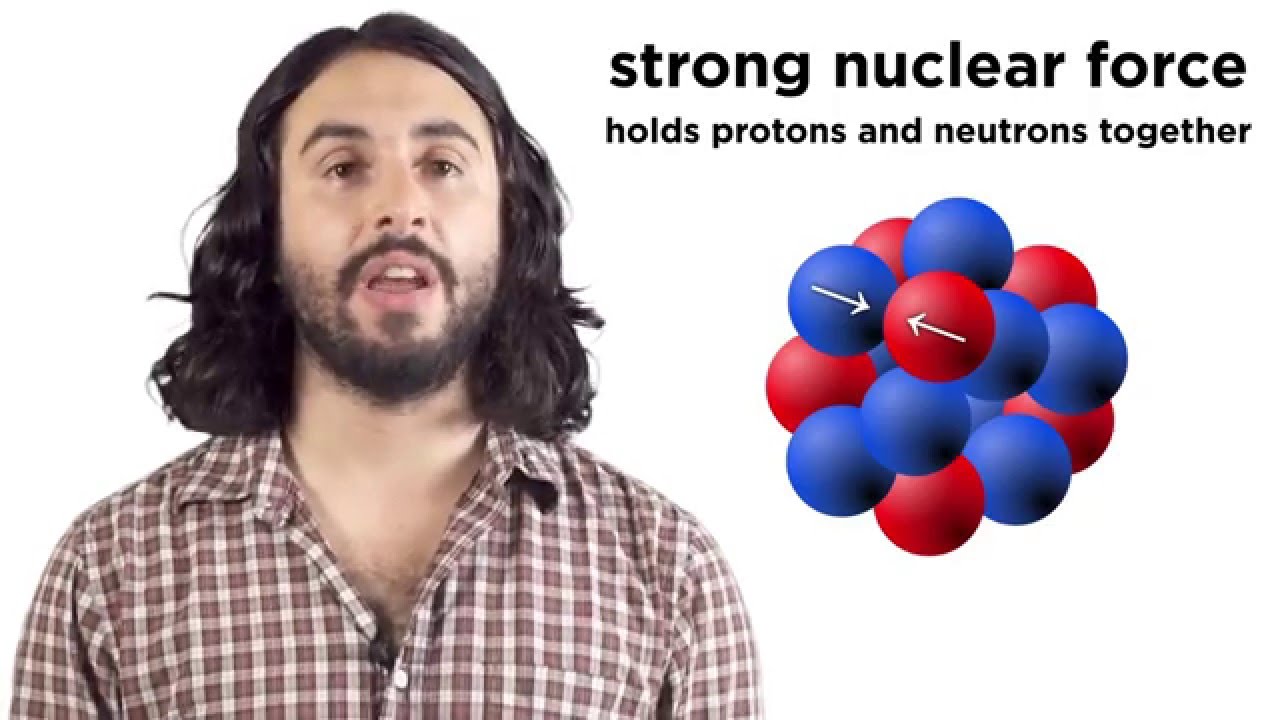
- 😀 Nuclear chemistry differs from traditional chemistry as it involves changes to the nucleus of atoms, affecting the number of protons and thus the type of atom.
- 😀 In nuclear reactions, atoms are transformed into different elements, a process not seen in chemical reactions.
- 😀 Fission reactions occur when a single nucleus splits into multiple smaller atoms, while fusion reactions involve the combining of multiple nuclei into one atom.
- 😀 Nuclear decay processes involve an atom spontaneously converting into a different type by emitting a subatomic particle.
- 😀 Nuclear reactions result in massive energy changes, much larger than in typical chemical reactions, often tens or hundreds of thousands of times greater.
- 😀 Due to the immense energy changes, nuclear reactions lead to measurable mass differences between the reactants and products.
- 😀 The relationship between mass and energy in nuclear reactions is explained by Einstein’s theory of relativity, where energy changes can lead to mass differences.
- 😀 Unlike chemical reactions, where mass is conserved, nuclear reactions do not conserve mass, reflecting a significant difference in the nature of the reactions.
- 😀 The key distinction between nuclear and chemical reactions is that nuclear reactions change the type of atom, whereas chemical reactions only rearrange atoms.
Q & A
What is the main focus in chemistry when studying compounds?
-In chemistry, the main focus is on the electrons in a compound, as they are responsible for holding atoms together in bonds. Chemical reactions involve breaking and making bonds, but the number and types of atoms remain the same—only their arrangement changes.
How do nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions?
-Nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions in that they involve changes to the nucleus of atoms, altering the number of protons and, therefore, the type of atom. In contrast, chemical reactions do not change the type of atoms; they merely rearrange them.
What happens during a fission reaction?
-During a fission reaction, a single nucleus splits into multiple smaller nuclei, releasing a significant amount of energy.
What occurs during a fusion reaction?
-In a fusion reaction, multiple smaller nuclei come together to form a larger, single atom. This process also releases a large amount of energy.
What is nuclear decay?
-Nuclear decay is a process in which an unstable atom spontaneously transforms into a different type of atom by emitting a subatomic particle, such as an alpha or beta particle.
Why are energy changes in nuclear reactions much larger than in chemical reactions?
-Energy changes in nuclear reactions are tens or hundreds of thousands of times larger than in chemical reactions because nuclear changes involve the nuclei of atoms, which are much more tightly bound and energy-rich than the electrons involved in chemical bonding.
How does mass change during nuclear reactions?
-In nuclear reactions, there is a measurable change in mass between the products and reactants. This is due to the relationship between mass and energy, as described by the theory of relativity. The mass lost is converted into energy.
What is the significance of Einstein's theory of relativity in nuclear chemistry?
-Einstein's theory of relativity, which states that mass and energy are interchangeable, explains why nuclear reactions do not conserve mass. Instead, mass is converted into a large amount of energy during nuclear reactions.
How does mass conservation differ in chemical and nuclear reactions?
-In chemical reactions, the mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products, meaning mass is conserved. However, in nuclear reactions, mass is not conserved because some of it is converted into energy, as described by the theory of relativity.
What is the key difference between traditional chemistry and nuclear chemistry?
-The key difference is that in traditional chemistry, atoms are conserved and only rearranged, whereas in nuclear chemistry, atoms change their type due to changes in their nucleus, altering the number of protons and thus the element itself.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)