GCSE Physics - Atomic Structure, Isotopes & Electrons Shells #32
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a clear overview of atomic structure, covering key concepts in chemistry. It explains the components of an atom—protons, neutrons, and electrons—and how they interact within the nucleus and energy levels. The video also explores isotopes, highlighting how elements can have variations in neutron numbers. It details how electrons move between energy levels, becoming excited and emitting radiation. The concept of ionization, where electrons can be ejected from atoms, is also introduced. Perfect for beginners, this video helps demystify atomic structure and basic nuclear chemistry.
Takeaways
- 😀 Atoms consist of a nucleus made up of protons (positive charge) and neutrons (neutral charge), with electrons (negative charge) orbiting in energy levels.
- 😀 The number of protons in an atom determines the element, and the number of protons and electrons is always equal in a neutral atom.
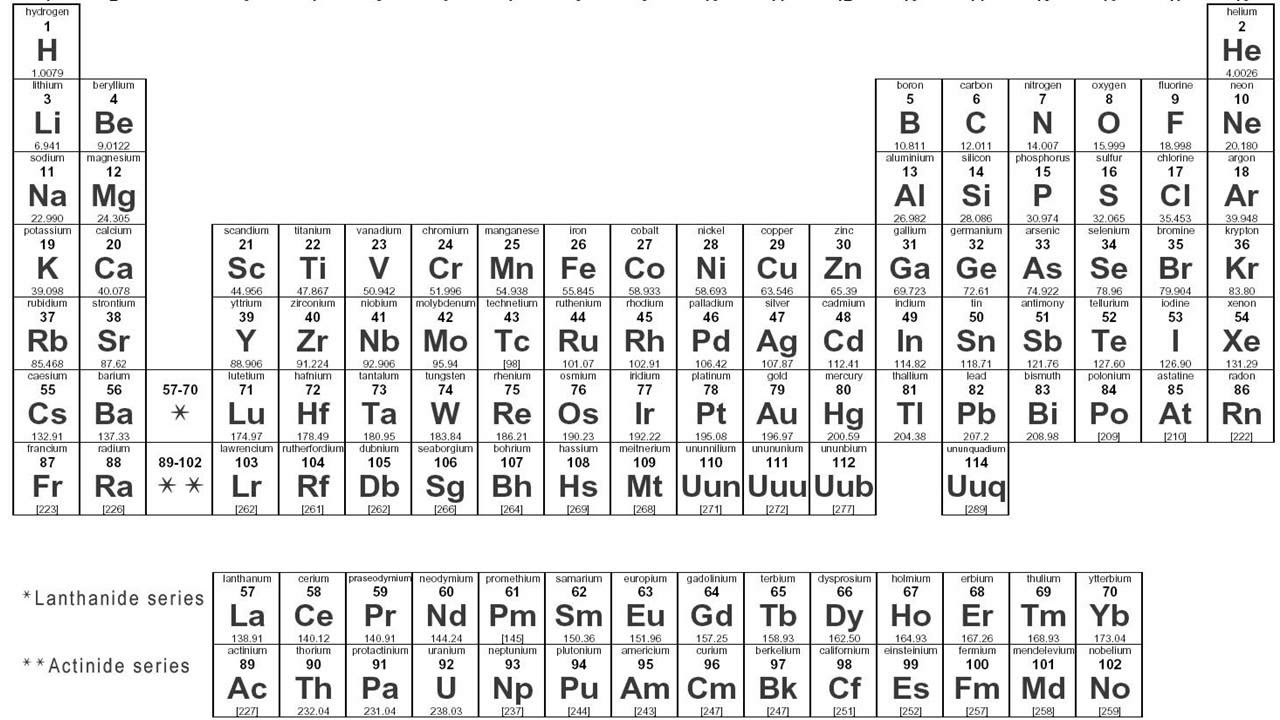
- 😀 Elements are represented in the periodic table by their atomic number (number of protons), atomic symbol, and mass number (total protons and neutrons).
- 😀 Isotopes are variants of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, leading to different mass numbers.
- 😀 Not all isotopes are stable; unstable isotopes decay into other elements through radioactive decay, emitting radiation (alpha, beta, gamma, or neutrons).
- 😀 Electrons in an atom occupy specific energy levels or shells, with each shell getting further from the nucleus and having higher energy.
- 😀 Electrons can gain energy from electromagnetic radiation and jump to a higher energy level, becoming 'excited' temporarily.
- 😀 After becoming excited, electrons will return to their original lower energy level and release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
- 😀 Ionization occurs when an electron absorbs enough energy to escape the atom, leaving behind a positively charged ion (more protons than electrons).
- 😀 Ionizing radiation is any radiation that has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, creating ions.
Q & A
What is the basic structure of an atom?
-An atom consists of a nucleus at the center, which contains protons and neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are electrons that orbit in shells.
What are the charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
-Protons have a positive charge (+1), neutrons have no charge (neutral), and electrons have a negative charge (-1).
What does the atomic number represent?
-The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom, which determines the element's identity.
How can isotopes of an element differ?
-Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different mass numbers.
What is the significance of the mass number in the periodic table?
-The mass number tells us the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. It helps in identifying different isotopes of an element.
What is the relationship between protons and electrons in a neutral atom?
-In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, ensuring the atom has no overall charge.
What are isotopes, and can you give an example?
-Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. An example is lithium-6, lithium-7, and lithium-8.
Why are some isotopes unstable?
-Some isotopes are unstable because they have an excess of energy or mass, causing them to decay into other elements over time by emitting radiation.
What happens when an electron absorbs energy and moves to a higher energy level?
-When an electron absorbs enough energy, it jumps to a higher energy level, and we say that it has become excited. This energy comes from electromagnetic radiation.
What occurs when an excited electron falls back to a lower energy level?
-When the excited electron falls back to a lower energy level, it re-emits the absorbed energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
What is ionization, and how does it occur?
-Ionization occurs when an outermost electron absorbs enough energy to completely leave the atom, leaving the atom with more protons than electrons, resulting in a positive ion.
What does the term 'ionizing radiation' mean?
-Ionizing radiation refers to radiation that has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, thereby ionizing them and creating charged particles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Atomística - Brasil Escola

Structure of Atom Class 11 Revision | CBSE 11th Chemistry Full Chapter-2 in 15 Mins | Rapid Revision

Matter (Atoms, Elements, and Compounds) - Explained
Fundamentals of chemistry

11AS01 - History of the atom - WACE Chemistry Year 11

Periodic Trends - Atomic Radius, Electronegativity, Ionization Energy - Chemistry Series
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)