Photosynthesis Overview
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an overview of the process of photosynthesis, explaining how sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide produce oxygen and glucose. It covers how sunlight powers photosynthesis by breaking down water molecules, creating ATP, and producing oxygen. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in structures called thylakoids. The video also explores the light-dependent and light-independent reactions, explaining how glucose is formed. Additionally, it discusses the connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in both plants and animals, using practical scenarios to illustrate the concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sunlight provides energy in the form of visible light, which drives photosynthesis.
- 😀 Visible light is a mixture of colors (ROYGBIV), and when passed through a prism, it forms a rainbow.
- 😀 Plants appear green because they reflect green light, while other colors are absorbed for photosynthesis.
- 😀 Photosynthesis involves two main stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle).
- 😀 Blue and red wavelengths are most effective in driving photosynthesis, while green light has minimal impact.
- 😀 Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into glucose and oxygen, using sunlight as an energy source.
- 😀 Autotrophs such as plants, algae, phytoplankton, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis.
- 😀 During light-dependent reactions, sunlight breaks down water molecules to release oxygen and generate energy molecules (ATP).
- 😀 In light-independent reactions, carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using the energy (ATP) produced in the first stage.
- 😀 Stomata are small pores in plant leaves that facilitate gas exchange, allowing plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
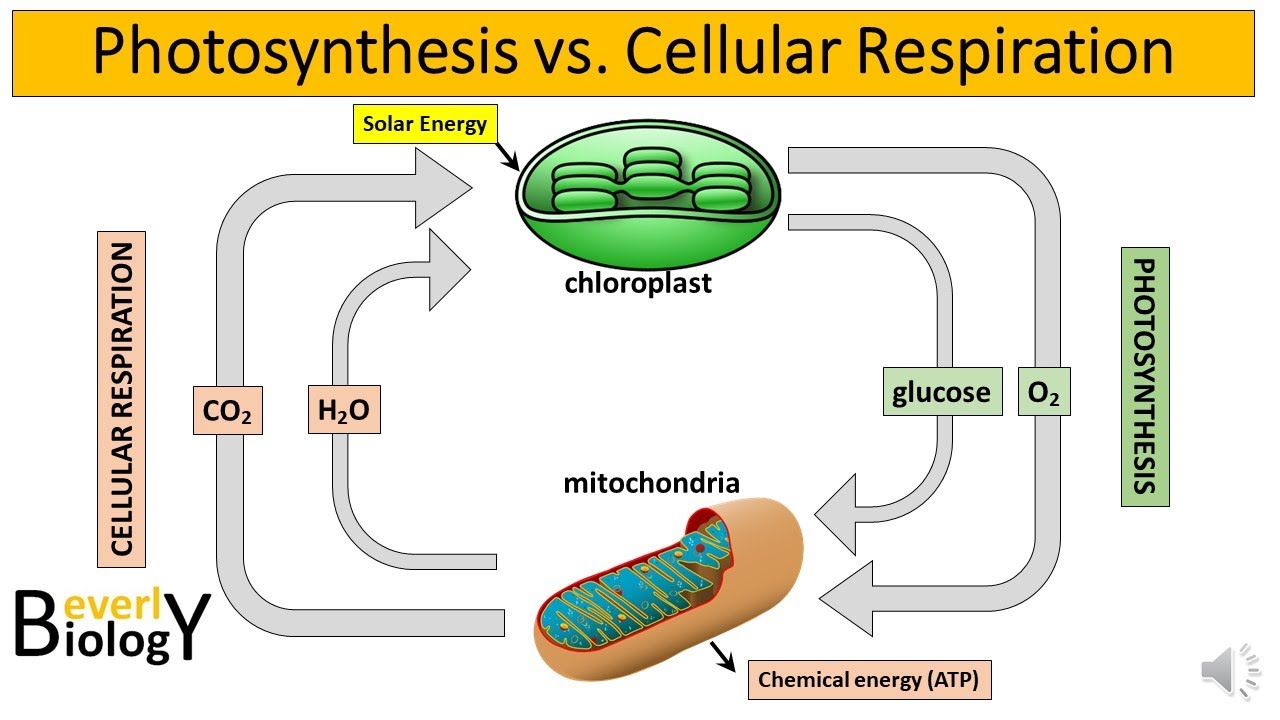
- 😀 Photosynthesis is connected to cellular respiration: plants use glucose for energy in mitochondria, while animals consume glucose to power their cells.
Q & A
What are the primary reactants in the photosynthesis process?
-The primary reactants in photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). These react with sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen.
How does sunlight contribute to photosynthesis?
-Sunlight provides the energy required to power photosynthesis. This energy is absorbed by chlorophyll in the plant cells and used to split water molecules, producing oxygen and energy-rich molecules like ATP.
Why do plants appear green?
-Plants appear green because chlorophyll, the pigment in their cells, reflects green wavelengths of light while absorbing other wavelengths, particularly red and blue light, to power photosynthesis.
What role do stomata play in photosynthesis?
-Stomata are pores on the underside of plant leaves that allow for the exchange of gases. They take in carbon dioxide (CO2) for photosynthesis and release oxygen (O2) as a waste product.
What is the significance of the thylakoid membrane in photosynthesis?
-The thylakoid membrane, found in the chloroplasts, is where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place. It absorbs sunlight and splits water molecules to generate ATP and oxygen.
What happens during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
-During the light-dependent reactions, sunlight breaks water molecules into oxygen, protons (hydrogen ions), and electrons. The energy from sunlight also helps form ATP, which will be used in the next stage of photosynthesis.
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
-The products of the light-dependent reactions are ATP, hydrogen ions (protons), and oxygen gas. These products will be used in the light-independent reactions to form glucose.
What is produced during the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
-During the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle), glucose (C6H12O6) is produced from carbon dioxide, ATP, and hydrogen ions.
What is the connection between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
-Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen, which are essential for cellular respiration. In cellular respiration, organisms, including plants, break down glucose to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
What would happen if a plant was kept in a sealed container with no access to sunlight?
-If a plant is kept in a sealed container with no sunlight, it cannot perform photosynthesis. Without sunlight, it cannot produce glucose, and the plant would not be able to take in carbon dioxide or release oxygen, resulting in a yellowish-green color due to the presence of carbon dioxide in the water.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)