Vektor Fisika Kelas 10 - Besaran Vektor - Kurikulum 2013 Revisi (Quipper Video)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Cecep Saepul Mukti introduces the concept of vector quantities, emphasizing their value and direction. The session covers fundamental topics like displacement, velocity, and force, explaining how to calculate their magnitude using Pythagoras' theorem. Cecep then explores vector addition, explaining the Polygon and Parallelogram methods, with a focus on the Polygon method for solving problems. Through practical examples, he demonstrates how vectors can be added and how to determine the resultant vector's magnitude and direction. The content is designed to make vector analysis accessible and applicable to everyday scenarios and test questions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Vector quantities have both magnitude and direction, unlike scalar quantities which only have magnitude.
- 😀 Examples of vector quantities include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and momentum.
- 😀 In daily life, vector quantities can be demonstrated through examples like pushing an object with a force of 10N, where the direction is crucial.
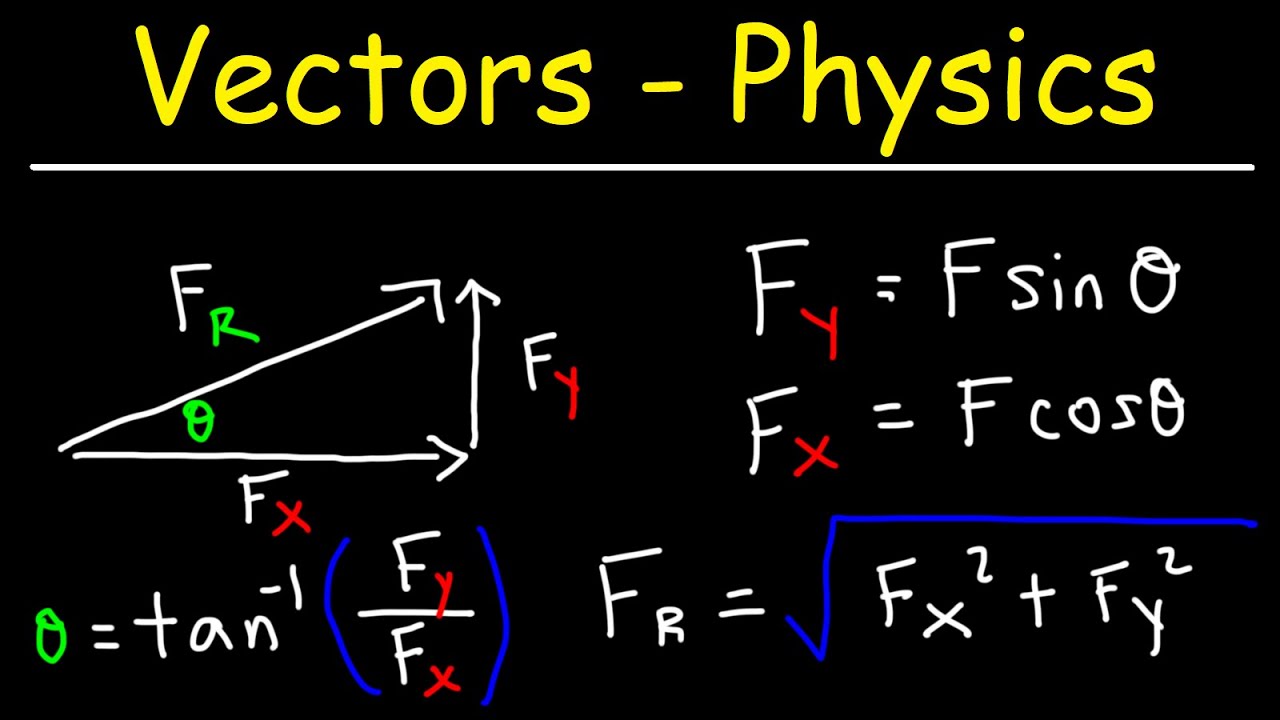
- 😀 To find the magnitude of a vector, the Pythagorean theorem can be applied when the vector is represented in a coordinate system.
- 😀 The direction of a vector can be calculated using trigonometric functions such as tangent, based on the ratio of the y and x components.
- 😀 Vectors are typically represented by arrows, with the length representing the magnitude and the direction indicated by the arrowhead.
- 😀 Vector addition involves combining multiple vectors into a single resultant vector, which has a different magnitude than the individual vectors.
- 😀 The polygon method is one way to add vectors, where vectors are placed end-to-end, and the resultant vector is drawn from the start of the first vector to the end of the last vector.
- 😀 To find the magnitude of the resultant vector, the Pythagorean theorem can again be applied if the vectors are perpendicular.
- 😀 The polygon method is a simple way of adding vectors visually, which is especially useful for solving questions in exams like SBMPTN.
- 😀 An example of vector addition involves determining the displacement from a series of movements, using the magnitude of the resultant vector and applying the Pythagorean theorem for calculation.
Q & A
What are vector quantities?
-Vector quantities are physical quantities that have both magnitude (value) and direction. Examples include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and momentum.
What is the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity?
-A scalar quantity only has magnitude, such as time or temperature, whereas a vector quantity has both magnitude and direction, such as displacement or velocity.
How is a vector represented graphically?
-A vector is represented by an arrow. The length of the arrow indicates the magnitude, while the direction of the arrow indicates the vector's direction.
How can the magnitude of a vector be calculated?
-The magnitude of a vector can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem if the vector components are known. For example, if the components are 6 units and 5 units, the magnitude is the square root of (6^2 + 5^2), which equals approximately 7.81 units.
What is the polygon method of vector addition?
-The polygon method involves arranging the vectors tip-to-tail in a sequence, creating a polygon. The resultant vector is drawn from the start point of the first vector to the end point of the last vector.
What is the parallelogram method of vector addition?
-The parallelogram method involves drawing two vectors from the same point, then completing a parallelogram. The diagonal of the parallelogram represents the resultant vector.
What does the term 'resultant vector' refer to?
-The resultant vector is the single vector that results from the addition of two or more vectors. It represents the combined effect of all the vectors involved.
How do you calculate the direction of a resultant vector?
-The direction of a resultant vector can be determined using trigonometric functions, such as the tangent of the angle, which is the ratio of the vertical component to the horizontal component of the vector.
What is an example problem for vector addition?
-An example problem involves finding the displacement after someone walks in different directions. For instance, if a person walks 3 units east and then 4 units north, the resultant displacement is 5 units, calculated using the Pythagorean theorem.
How is the value of a vector addition problem calculated when given grid squares?
-To calculate the vector magnitude in such a problem, count the number of grid squares along the x and y axes, then use the Pythagorean theorem. For example, if 3 squares are along the x-axis and 4 squares are along the y-axis, the resultant magnitude would be 5 units, with each square representing a certain length, like 4 meters.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GRANDEZAS FÍSICAS (ESCALARES E VETORIAIS) | Resumo de Física Enem. |Prof Marcus Rossetto
Vectors - Basic Introduction - Physics

GCSE Physics Revision "Scalar and Vector Quantities"

Besaran vektor dan besaran skalar (Fisika SMA/MA Sagufindo kls X smt 1 : Vektor)

03 01 Fisika Dasar 1- Pengenalan Vektor

Sistema Internacional de Unidades (SI) - Brasil Escola
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)