KAD TALKS 86: Fikri Aulia Rachman TALKS ABOUT URBAN HEAT ISLAND.
Summary
TLDRThe video script explores the phenomenon of Urban Heat Islands (UHI), where urban areas experience higher temperatures due to factors like dense development, loss of vegetation, and materials such as asphalt and concrete. This leads to heat waves, extreme weather, and health risks. It highlights the consequences of UHI, such as the tragic heatwave deaths in India and Europe. The script also discusses mitigation strategies, like green infrastructure, reflective surfaces, and improved urban planning, with a focus on Singapore's innovative 'Cooling Singapore' project aimed at combating UHI and improving urban resilience against climate change.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Earth's temperature rise of 2°C can lead to extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and severe heat waves, resulting in fatalities and ecosystem damage.
- 🔥 Heat waves, particularly in countries like India, have led to thousands of deaths, highlighting the deadly impact of rising temperatures.
- 🌆 Urban Heat Island (UHI) occurs when cities are hotter than surrounding rural areas due to factors like population density and the loss of vegetation.
- 🌳 UHI causes include replacing natural surfaces with heat-absorbing materials like asphalt and concrete, which retain more heat than natural environments.
- 💡 Historical research by Luke Howard in the 1800s identified key factors contributing to UHI, including heat sources, urban surface geometry, and water vapor availability.
- 📸 Satellite images show the stark temperature contrast between areas with vegetation (cooler) and paved surfaces (hotter), exemplified by New York City in 2002.
- 🏙️ Jakarta's UHI spread from 2008 to 2018, with temperature increases reaching 34°C, demonstrating the widespread impact of urban heat.
- 🌡️ UHI is exacerbated by dense urban structures, narrow roads forming urban canyons, and materials with low albedo, such as asphalt and concrete.
- 💧 Mitigation strategies include green infrastructure (e.g., green roofs, urban trees), reflective surfaces, water integration, and sustainable drainage systems (SUDs).
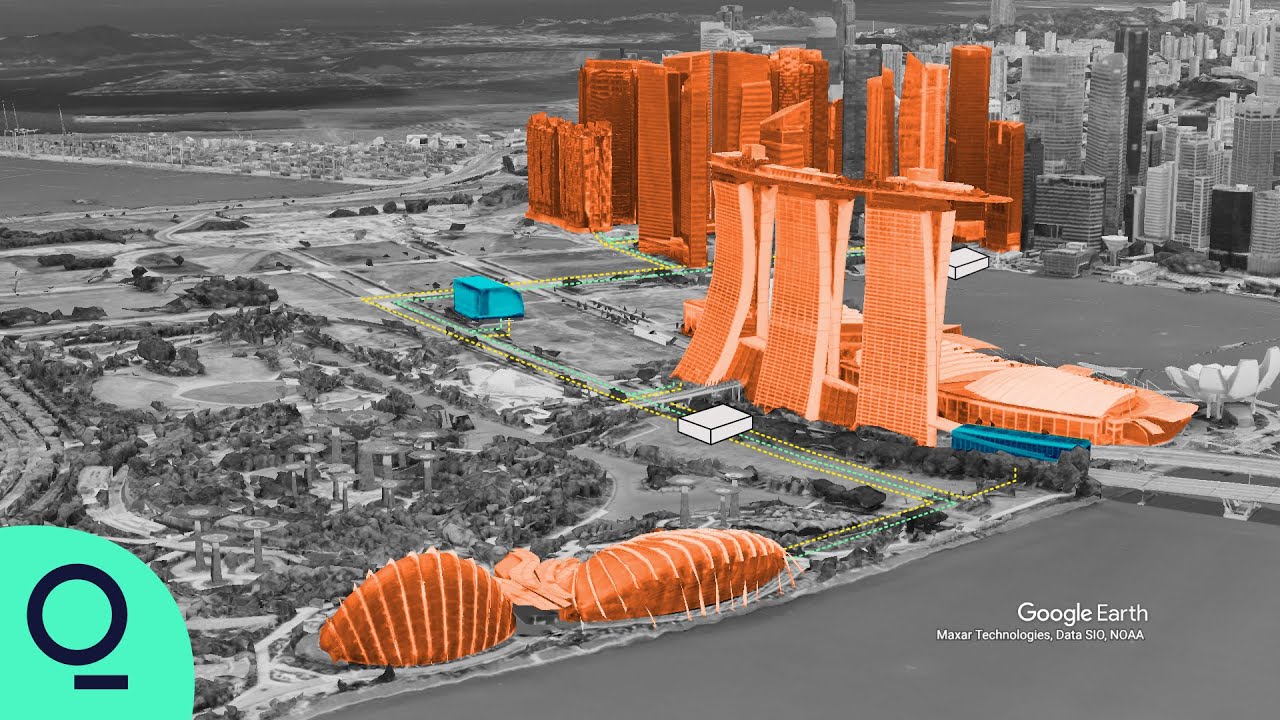
- 🌿 Singapore's Cooling Singapore project uses digital technologies and urban planning to combat UHI, focusing on cooling strategies, green solutions, and renewable energy.
Q & A
What happens if the Earth's temperature rises by 2°C?
-A 2°C rise in Earth's temperature can lead to extreme weather, climate change, rising sea levels, and significant damage to ecosystems. It also increases the frequency and intensity of heatwaves, which can be deadly in certain regions.
Why are heatwaves considered one of the deadliest natural disasters?
-Heatwaves are deadlier than many other natural disasters because they cause widespread health issues, including dehydration, heatstroke, and death. For example, in India, heatwaves in 2015 led to 2,338 deaths, while the 2003 heatwave in Europe caused approximately 70,000 deaths.
What is the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect?
-The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect refers to the phenomenon where urban areas are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. This is due to human activities and changes to the environment, such as the replacement of vegetation with hard, heat-absorbing surfaces like concrete and asphalt.
What are the causes of the Urban Heat Island phenomenon?
-The primary causes of UHI include the loss of vegetation, the replacement of natural surfaces with hard, dark-colored materials, dense urban geometry (creating urban canyons), and low-albedo materials like asphalt that absorb and retain heat.
How does urban geometry contribute to UHI?
-Dense urban structures with narrow streets can create 'urban canyons' that trap heat and prevent air circulation. This leads to the retention of solar radiation in cities, further increasing temperatures in urban areas.
What was Luke Howard's contribution to UHI research?
-Luke Howard, a British chemist and amateur meteorologist, was the first to study UHI in the 1800s. He identified several causes for temperature differences, including heat sources, urban geometry, and the availability of water vapor. His work laid the foundation for understanding UHI.
How does the loss of vegetation impact UHI?
-The loss of vegetation in urban areas reduces the natural cooling effect provided by plants and trees. Vegetation absorbs less solar radiation and helps in the evaporation of water, which cools the environment. Replacing greenery with hard surfaces like concrete increases the absorption of heat.
What is the impact of the UHI phenomenon in Jakarta?
-In Jakarta, UHI spread from the city center to surrounding areas between 2008 and 2018, with temperatures increasing by up to 34°C. This highlights the growing impact of UHI in urbanized areas of developing countries.
What are some mitigation strategies to combat UHI?
-Mitigation strategies for UHI include increasing green infrastructure (e.g., green roofs, urban trees), using reflective surfaces to reduce heat absorption, integrating water features for cooling, and promoting energy-efficient technologies. Singapore is a leading example of implementing these strategies.
How has Singapore addressed the UHI problem?
-Singapore has implemented a comprehensive strategy to combat UHI, including the use of green roofs, urban greenery, reflective surfaces, water bodies, and sustainable drainage systems. The city also uses digital technologies like urban climate twins to simulate and plan effective cooling strategies.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
How Singapore Uses Science to Stay Cool

PROBLEMAS AMBIENTAIS NAS ÁREAS URBANAS | Resumo de Geografia para o Enem

NASA | Urban Heat Islands

URBAN HEAT ISLAND - How cities change the weather.

Throwing Shade on Climate Change | Jeremy Hoffman | TEDxYouth@RVA

Can Trees Really Improve our Neighborhoods? | Earth Focus | PBS SoCal
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)